Summary
The orientation of the fetus within the uterus is critical for the management of labor and delivery. It encompasses the fetal lie, presentation, position, attitude, station, and engagement, all of which influence the delivery approach and potential outcomes.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
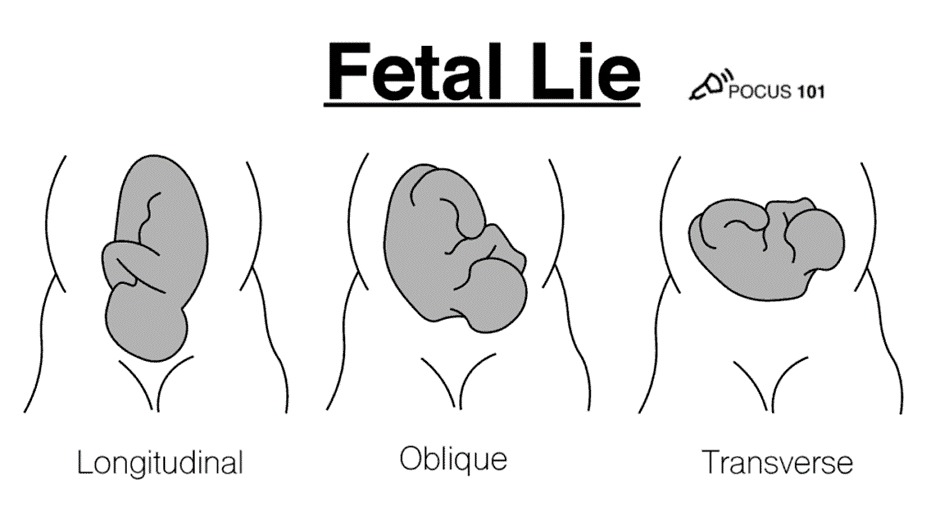
Fetal Lie
- Definition: The relationship between the fetal long axis and the maternal uterus's long axis.
- Types:
- Longitudinal Lie: The fetus is aligned with the maternal axis, facilitating vaginal delivery (most common).
- Transverse Lie: The fetus lies at a 90° angle, often requiring intervention for delivery.
- Oblique Lie: Positioned at a 45° angle, this lie may lead to complications during labor.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
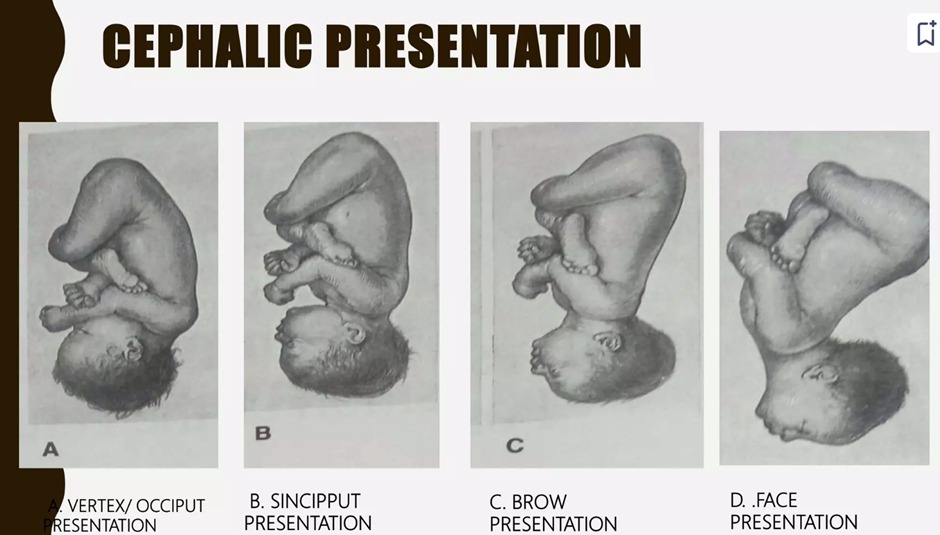
Fetal Presentation
Definition: The fetal part overlying the maternal pelvic inlet.
- Cephalic Presentation: The head descends first, the most favorable for vaginal delivery ( 97% at term ) .
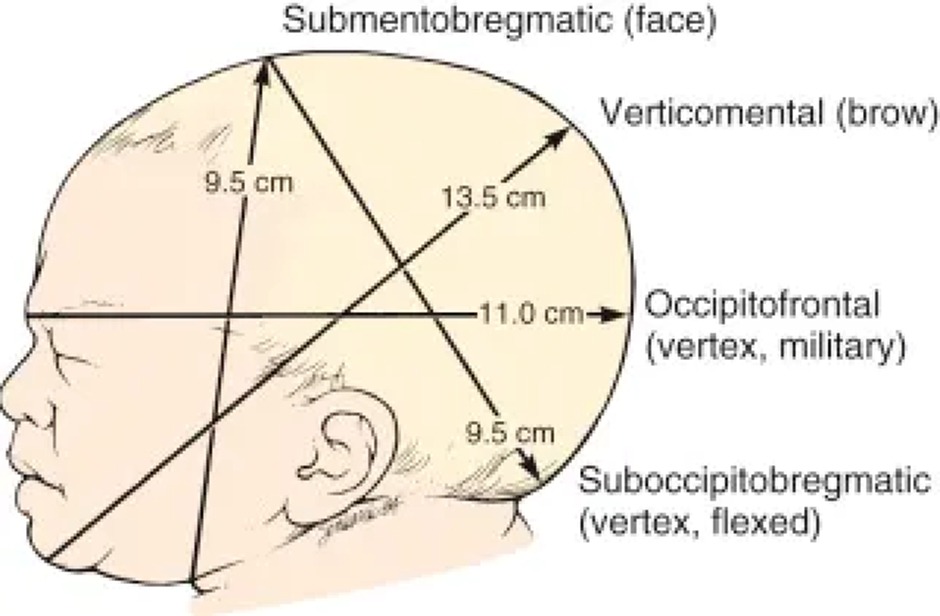
- Vertex ( Occiput ) Presentation ( suboccipitobregmatic diameter 9.5 cm or occipitofrontal diameter ( 11.5 cm ) )
- Description: The head is maximally flexed, making it the most common and favorable position for vaginal delivery.
- Implication: This presentation facilitates the smooth passage of the baby through the birth canal.
- Brow Presentation ( verticomental diameter 13.5 cm )
- Description: The fetal head is partially extended, leading to a brow-first presentation.
- Implication: This position can complicate vaginal delivery due to the increased diameter of the head needing to pass through the birth canal.
- Face Presentation ( submentobregmatic diameter 9.5 cm )
- Description: In this maximally extended position, the face presents first.
- Mentum Anterior: The chin is facing the birth canal, allowing for the possibility of a spontaneous vaginal delivery.
- Mentum Posterior: The chin is facing away from the birth canal, often requiring delivery intervention due to difficulty in delivery.
- Forehead ( Sinciput ) Presentation ( occipitofrontal diameter 11.5 cm )
- Description: The fetal head is in a partially flexed position, known as the military attitude.
- Implication: Similar to the mentum anterior face presentation, spontaneous vaginal delivery is possible but requires careful management due to the unusual presentation.
- Vertex ( Occiput ) Presentation ( suboccipitobregmatic diameter 9.5 cm or occipitofrontal diameter ( 11.5 cm ) )
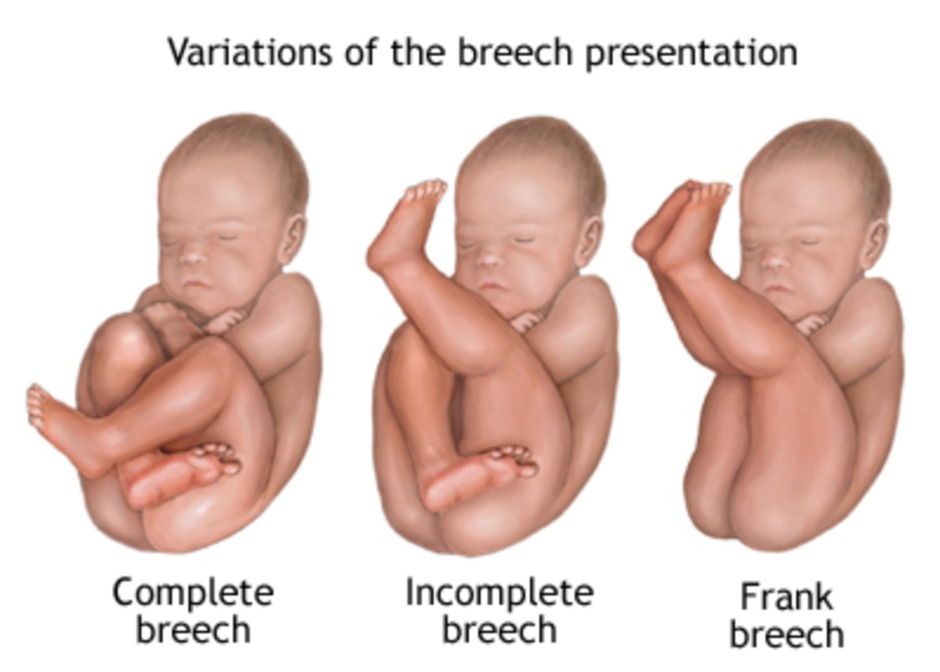
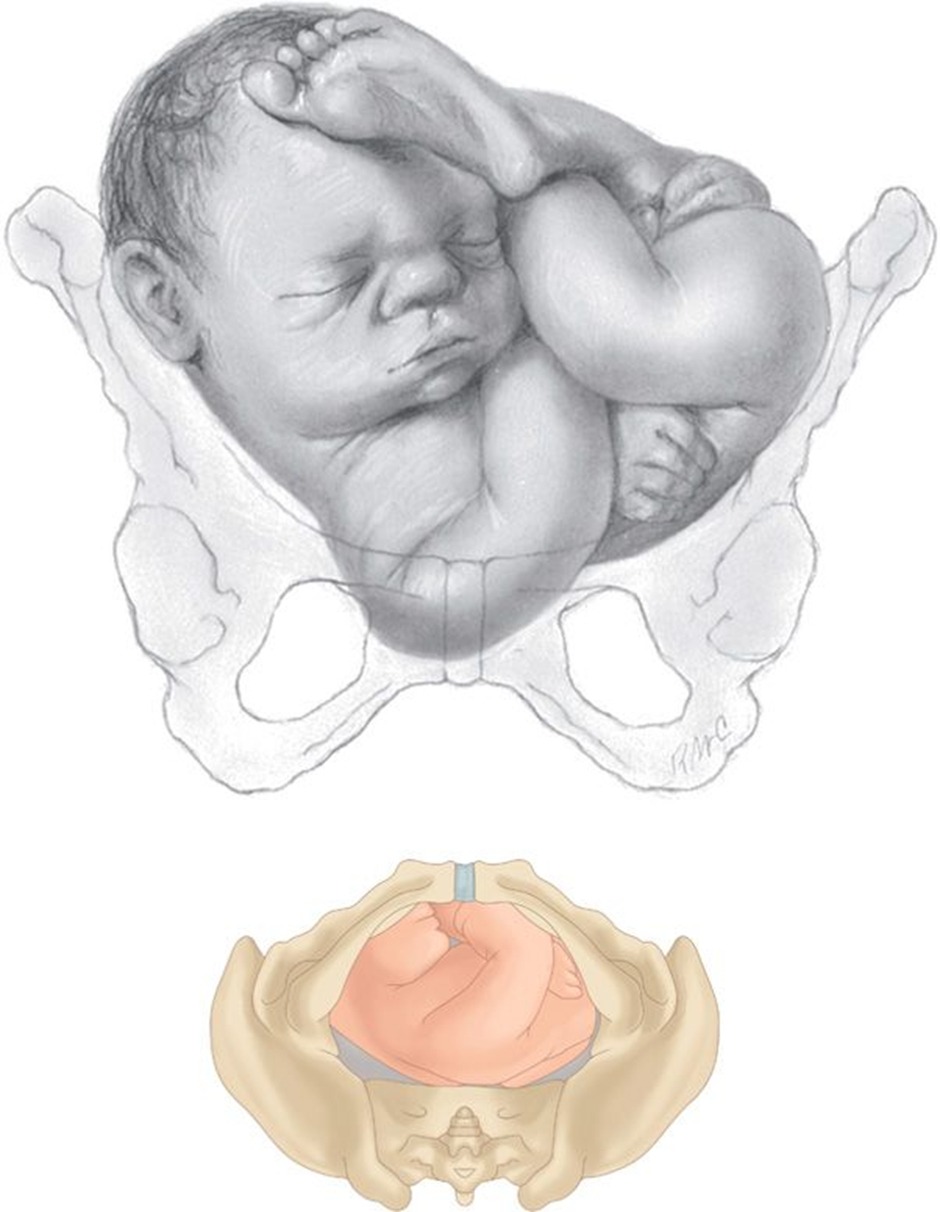
- Breech Presentation: Presentation of the buttocks or feet first ( 3% at term ).
- Frank Breech
- Characteristics: Hips flexed, knees extended, with feet near the head.
- Prevalence: 50 - 70 percent of breech fetuses at term.
- Clinical Note: Often considered for cesarean delivery due to positioning.
- Complete Breech
- Characteristics: Both hips and knees flexed, resembling a squatting position.
- Prevalence: 5 - 10 percent of breech presentations at term.
- Clinical Note: May have a more favorable outlook for vaginal delivery, with conditions.
- Incomplete Breech
- Characteristics: One or both hips not fully flexed; may present as footling breech.
- Prevalence: 10 - 40 percent of breech fetuses at term.
- Clinical Note: Cesarean delivery is often recommended due to increased risks associated with vaginal delivery.
- Frank Breech
- Compound Presentation: More than one anatomical part presents simultaneously.
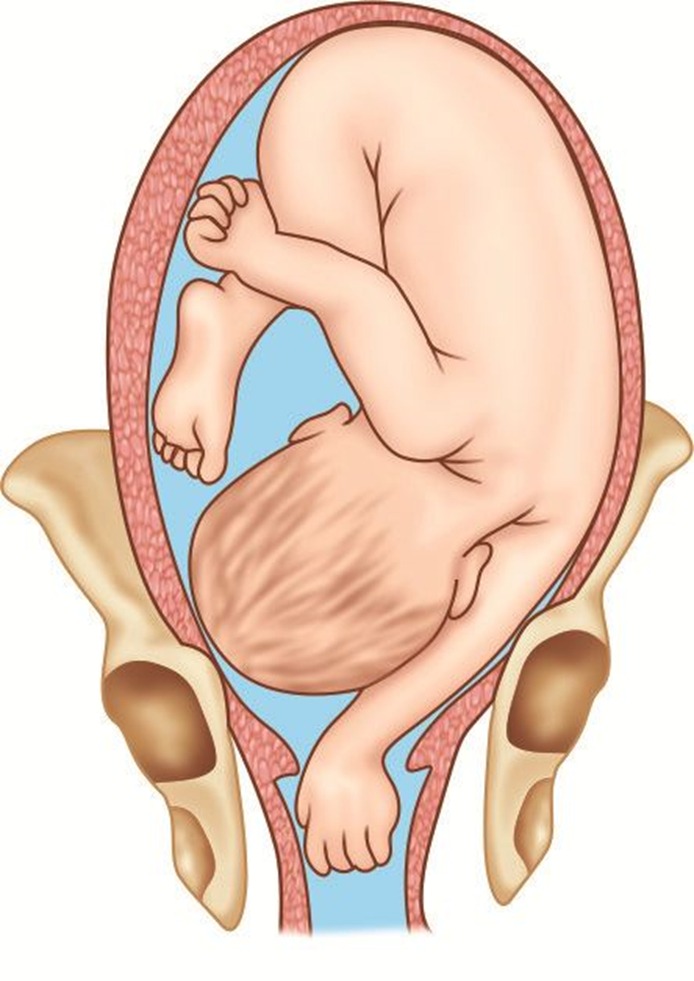
- Shoulder Presentation: Associated with transverse or oblique lie, complicating delivery.
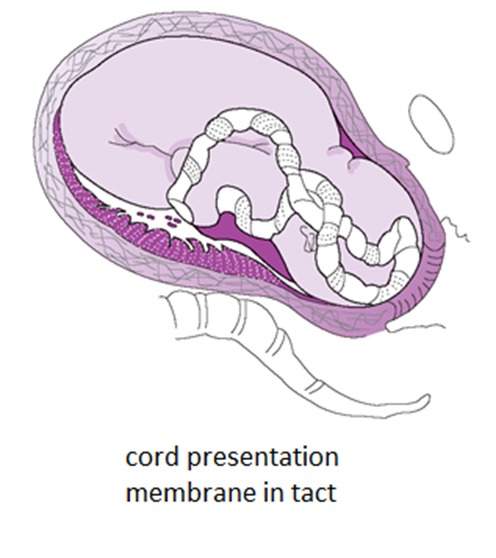
- Cord Presentation: the umbilical cord lies between the fetal presenting part and the cervix, potentially with or without the membranes having ruptured.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Fetal Position
- Definition: The presenting part's orientation relative to the maternal pelvis.
- The denominator: is a bony landmark on the presenting part used to denote the position, In vertex it is the occiput , In face it is the mentum (chin) and In breech it is the sacrum.
- The occiput's position:
- Occiput Anterior (OA) Position:
- The baby's occiput (back of the head) is facing towards the maternal symphysis pubis, with the fetus looking downward.
- Left Occiput Anterior (LOA) (most common)
- Right Occiput Anterior (ROA)
- The baby's occiput (back of the head) is facing towards the maternal symphysis pubis, with the fetus looking downward.
- Occiput Posterior (OP) Position: (most common fetal malposition)
The baby's occiput is pointing towards the maternal sacral promontory, meaning the baby is facing upwards. This position can make labor more challenging due to the larger head diameter presenting to the birth canal — occipitofrontal diameter ( 11.5 cm ).- Left Occiput Posterior (LOP)
- Right Occiput Posterior (ROP)
- Direct Anterior (OA): directly facing the maternal symphysis pubis without a left or right deviation.
- Direct Posterior (OP): directly facing the maternal sacrum occipitofrontal diameter ( 11.5 cm )
- Left Occiput Transverse (LOT):The baby's occiput is oriented towards the mother's left hip
- Right Occiput Transverse (ROT): the baby's occiput is oriented towards the mother's right hip
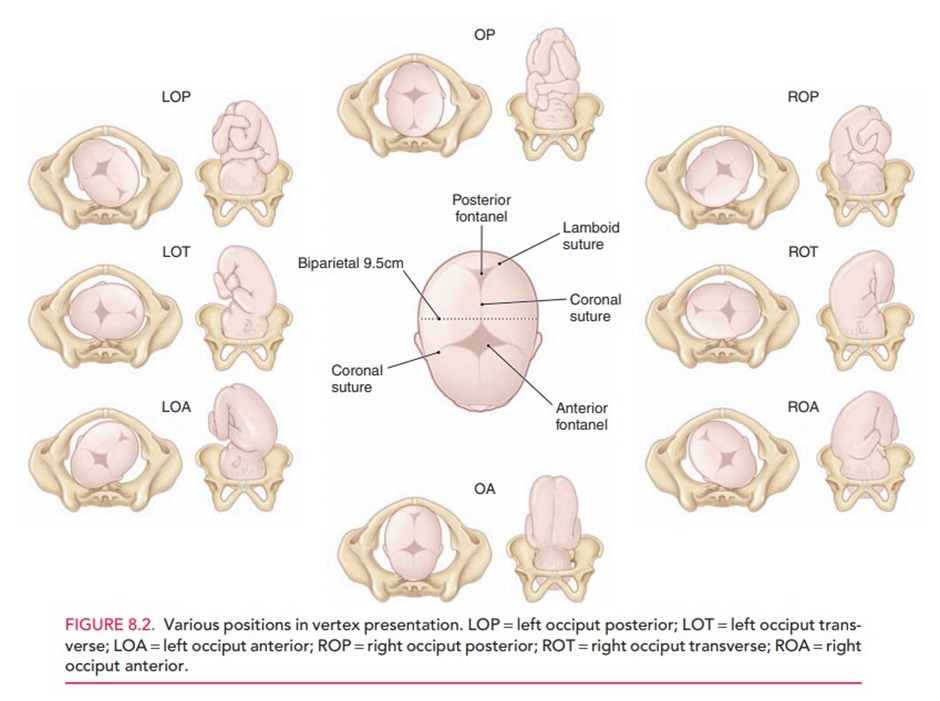
- Occiput Anterior (OA) Position:
- The Sacrum’s position:
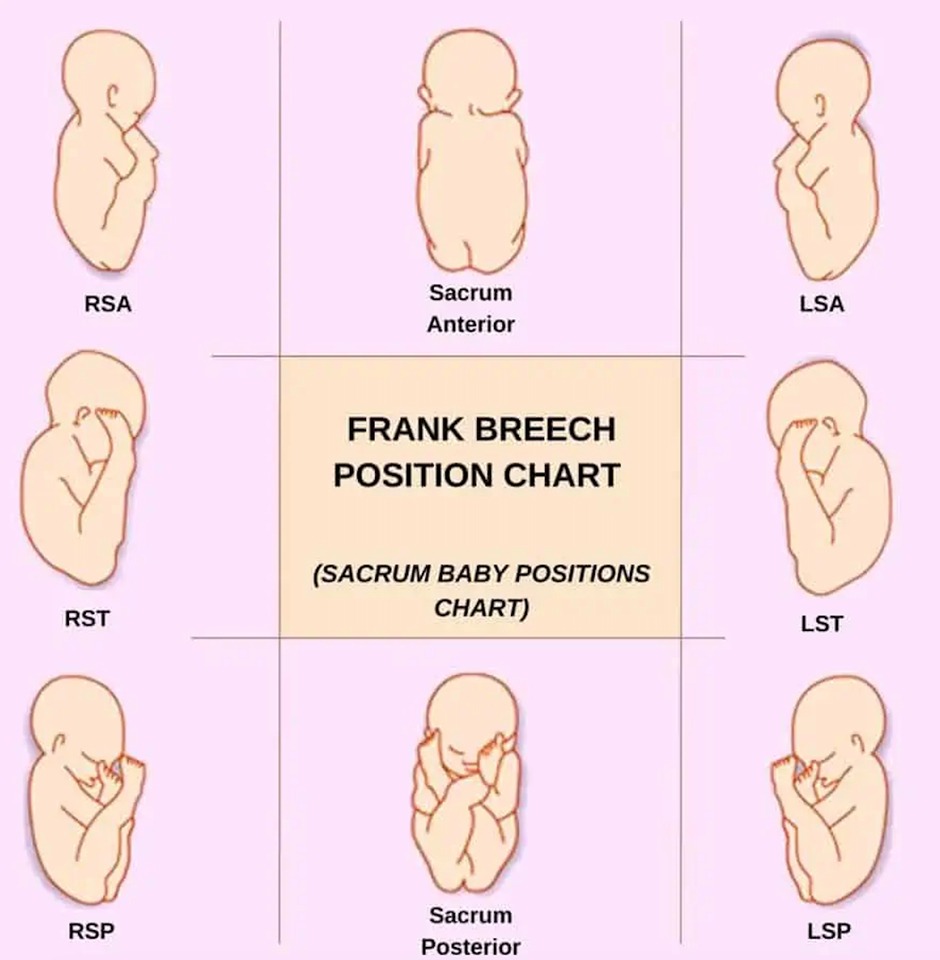
- The mentum’s position:
- Mentum posterior — In the mentum posterior face presentation, the fetal neck is already maximally extended and cannot extend further to allow the occiput to pass under the symphysis. Therefore, the mentum posterior face presentation will not deliver vaginally unless spontaneous rotation to mentum anterior occurs
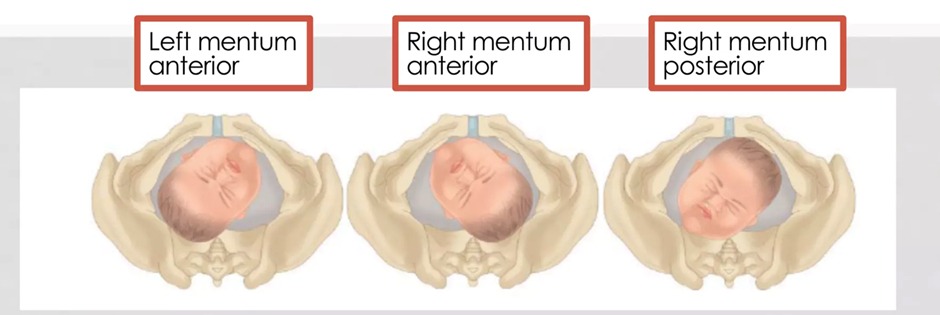
- Mentum posterior — In the mentum posterior face presentation, the fetal neck is already maximally extended and cannot extend further to allow the occiput to pass under the symphysis. Therefore, the mentum posterior face presentation will not deliver vaginally unless spontaneous rotation to mentum anterior occurs
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Fetal Attitude
- Definition: The degree of flexion or extension of the fetal head during delivery.
- Flexion (Full Flexion): fully flexed towards the chest, and the chin touches the chest.
- Moderate Flexion: not fully flexed nor extended .
- Extension (Deflexed): extended backward, such that the face or forehead presents to the birth canal instead of the top of the head
- Hyperextension: tilted back as far as possible, often leading to face presentation with the chin (mentum) being the leading part.
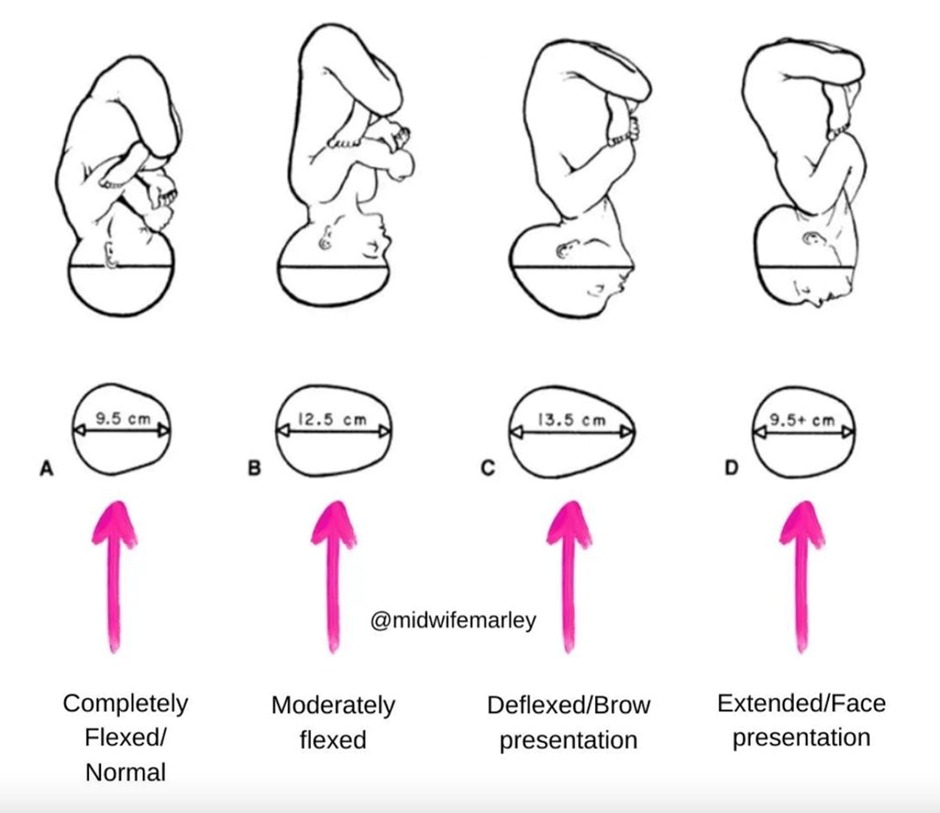
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Station
- Station: Refers to the presenting part's position relative to the ischial spines, critical for assessing labor progress.
|
Station |
Description |
|
0 |
|
|
-1, -2, -3 , -4, -5 |
|
|
+1, +2, +3, +4 , +5 |
|
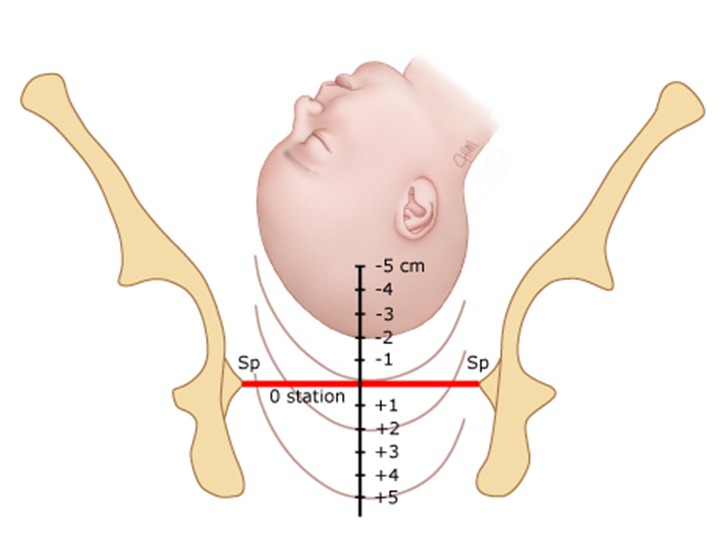
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
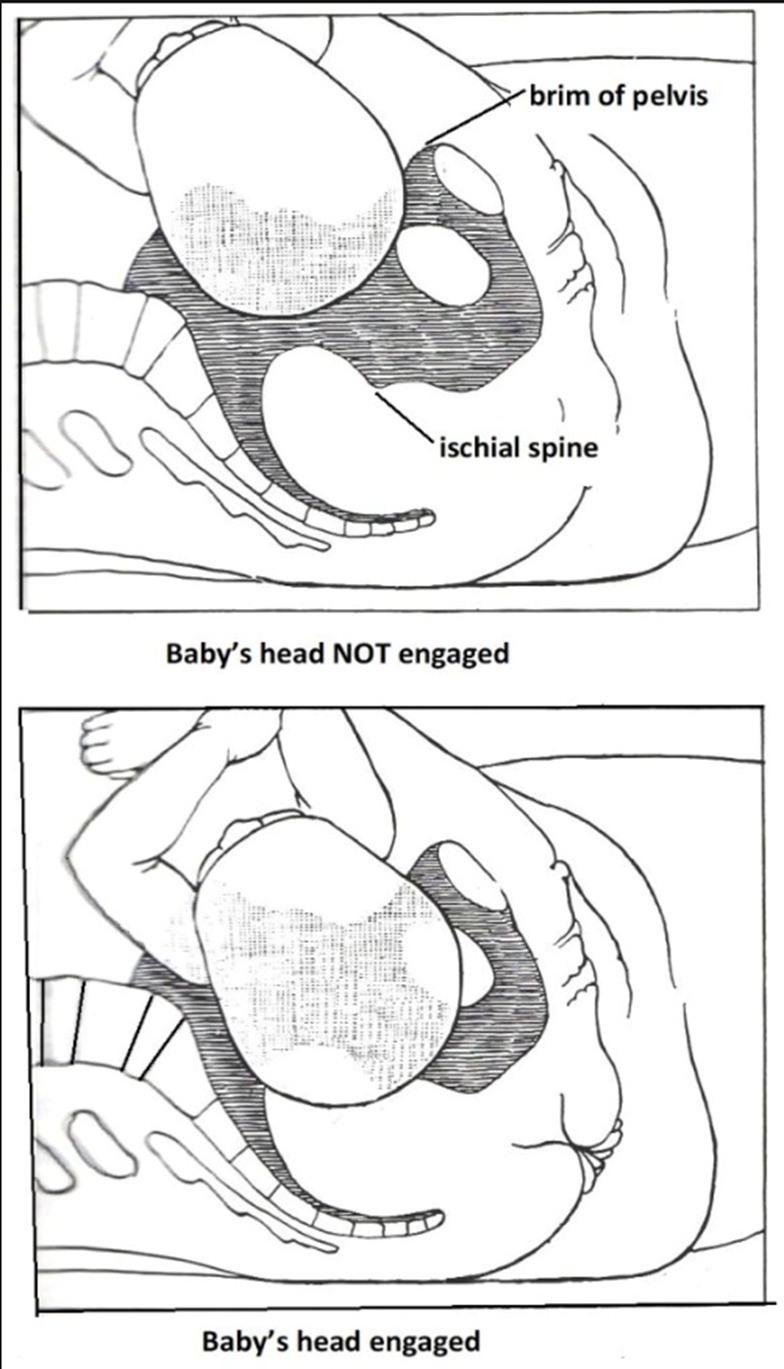
Engagement
- The moment during pregnancy when the widest part of the fetal head (the biparietal diameter) passes through the pelvic inlet and enters the maternal pelvis.
- When 2/5 or less of the fetal head is palpable above the symphysis pubis, the head is considered engaged in the pelvis.
- First-Time Pregnancies: Engagement often occurs several weeks before labor begins.
- For Subsequent Pregnancies: Engagement may not happen until labor is more imminent.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
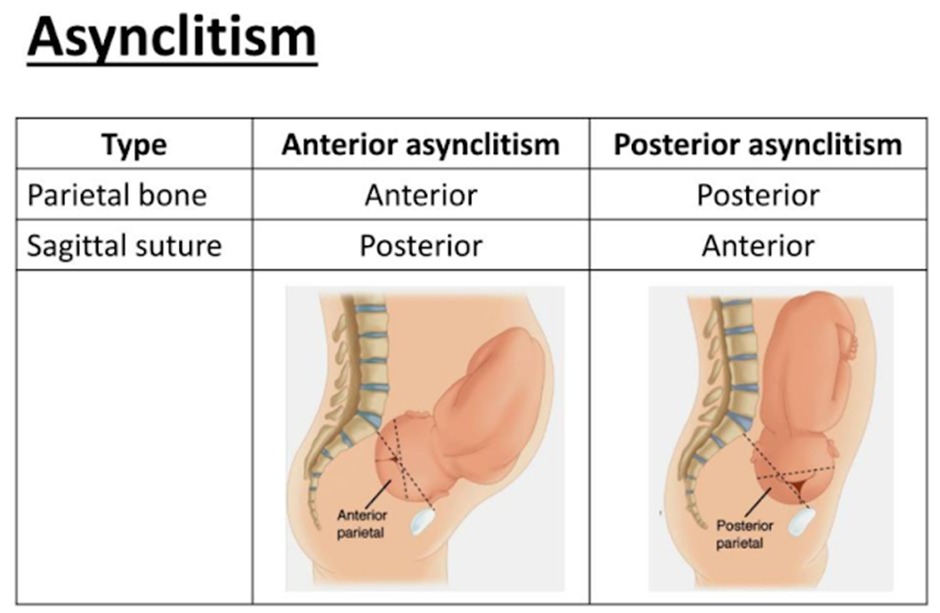
Synclitism and Asynclitism
- Definition: The relationship between the fetal head and the pelvic plane.
- Synclitism: alignment or parallelism between the pelvic plane of the mother and the plane of the fetal head, specifically when the fetal head is neither tilted forward nor backward as it descends into the birth canal.
- Asynclitism: deviation from the ideal alignment, leading to challenges during delivery. It is characterized by the tilt of the fetal head, with the sagittal suture off-center relative to the maternal pelvic inlet.
- Anterior Asynclitism (Naegele Obliquity)
- The sagittal suture is closer to the sacral promontory, with the fetal head tilted slightly forward.
- Posterior Asynclitism (Litzmann Obliquity)
- The sagittal suture is closer to the symphysis pubis, indicating that the fetal head is tilted backward.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Conclusion
Understanding the intricate details of fetal orientation within the uterus is paramount for the effective management of labor and delivery. Medical professionals, especially those in training, must be adept at recognizing and addressing various fetal lies, presentations, positions, attitudes, stations, and engagement patterns to optimize maternal and fetal outcomes.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
احصل على التجربة الكاملة
اشترك للوصول لفيديوهات الشرح التفصيلي والبطاقات التعليمية التفاعلية وأسئلة الممارسة مع تتبع التقدم.
فيديوهات الشرح
بطاقات تفاعلية
أسئلة ممارسة
اشترك الآن