Summary
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Monitoring Fetal Growth
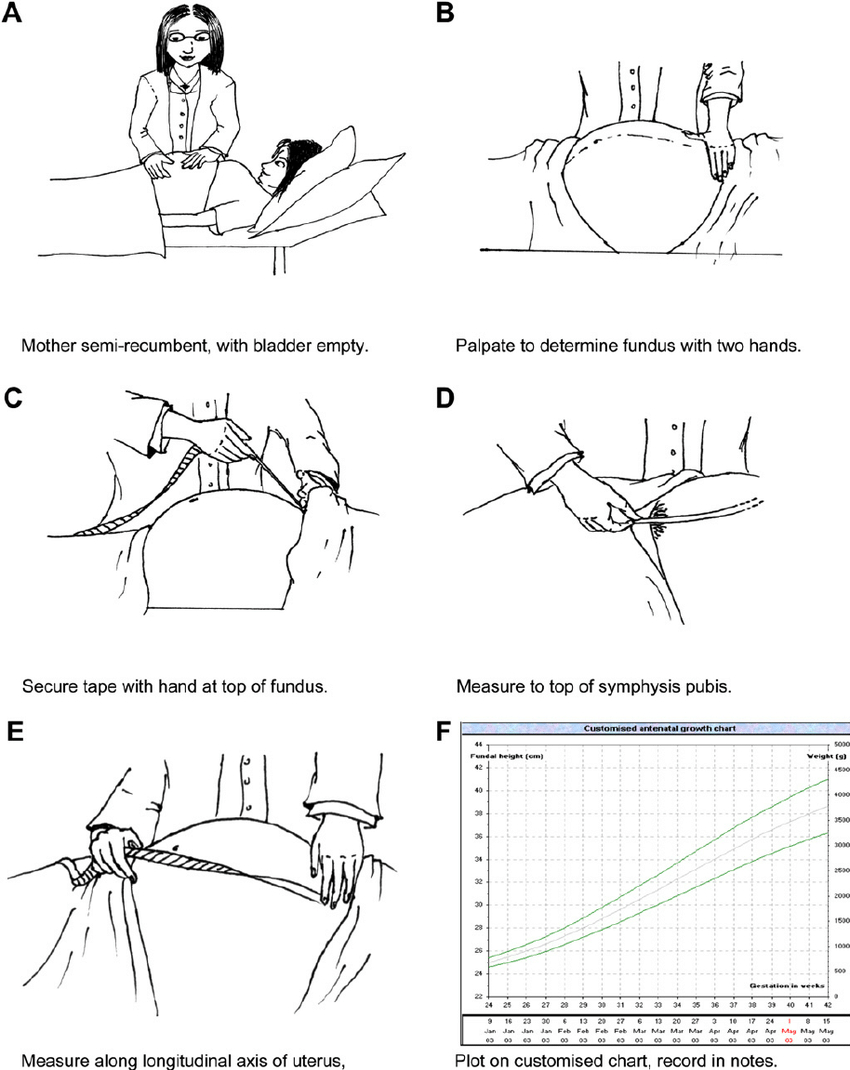
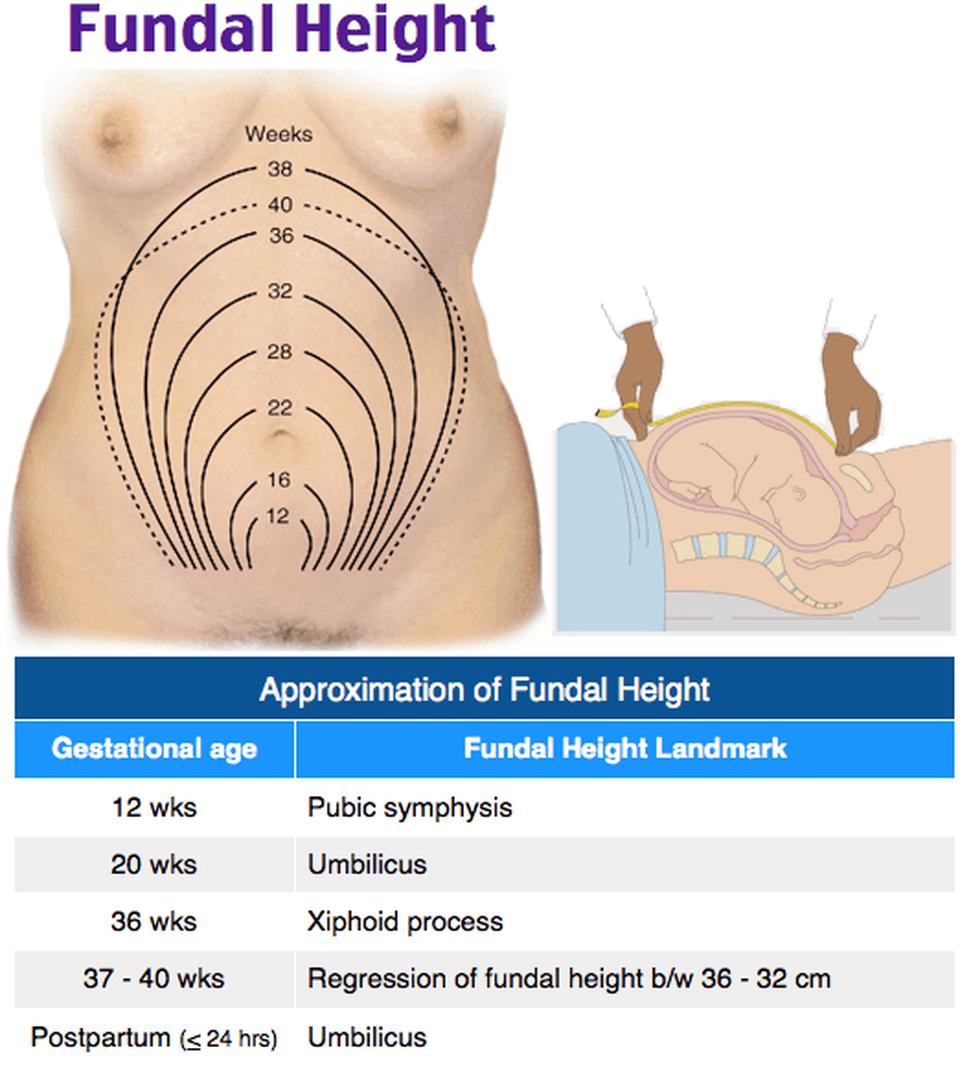
- Routine assessments include measuring the symphysis-fundal height to track fetal growth.
- At 12 weeks of gestation, the uterus enlarges to be palpable abdominally just above the symphysis pubis.
- At 16 weeks' gestation, the fundal height is midway between the symphysis pubis and the umbilicus.
- By 20 weeks' gestation, the fundus is at the level of the umbilicus. Post 20 weeks, the measurement in centimeters from the symphysis pubis to the fundus should approximate the gestational age in weeks.
- Accuracy may be impacted by factors like leiomyomata, maternal obesity, multifetal gestation, or anatomical variations (e.g., a retroverted uterus), affecting the palpation of the uterus or actual uterine size.
- Ultrasounds are performed as indicated to monitor fetal development, amniotic fluid volume, and placental position.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Risk Assessment for Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes
- Continuous evaluation for any risk factors that may lead to adverse pregnancy outcomes, managing pregnancies deemed high-risk with appropriate interventions.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Hypertensive Pregnancy Disorders Screening
- Ongoing vigilance for signs of hypertensive disorders, such as preeclampsia, which are more prevalent in the third trimester.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Prevention of Neonatal Infection
- Implement third-trimester STI screening protocols as necessary.
- Administer Tdap vaccine between 27–36 weeks to protect against pertussis.
- Offer the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine between 32–36 weeks, where recommended.
- Perform Group B streptococcus (GBS) screening between 36–37+6 weeks to guide the use of intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Rh Antibody Screening
- For Rh-negative nonsensitized individuals, perform antibody screening at 28 weeks and administer Anti-D immunoglobulin as indicated to prevent Rh sensitization.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Anemia and Gestational Diabetes Screening
- If not previously done, screening for anemia and gestational diabetes is performed to manage any maternal health issues that could impact the pregnancy or delivery.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Preparation for Delivery
- Counseling on peripartum care and the labor process, including the development of a birth plan.
- Assess indications for antepartum fetal surveillance and conduct monitoring as indicated, such as non-stress tests or biophysical profiles.
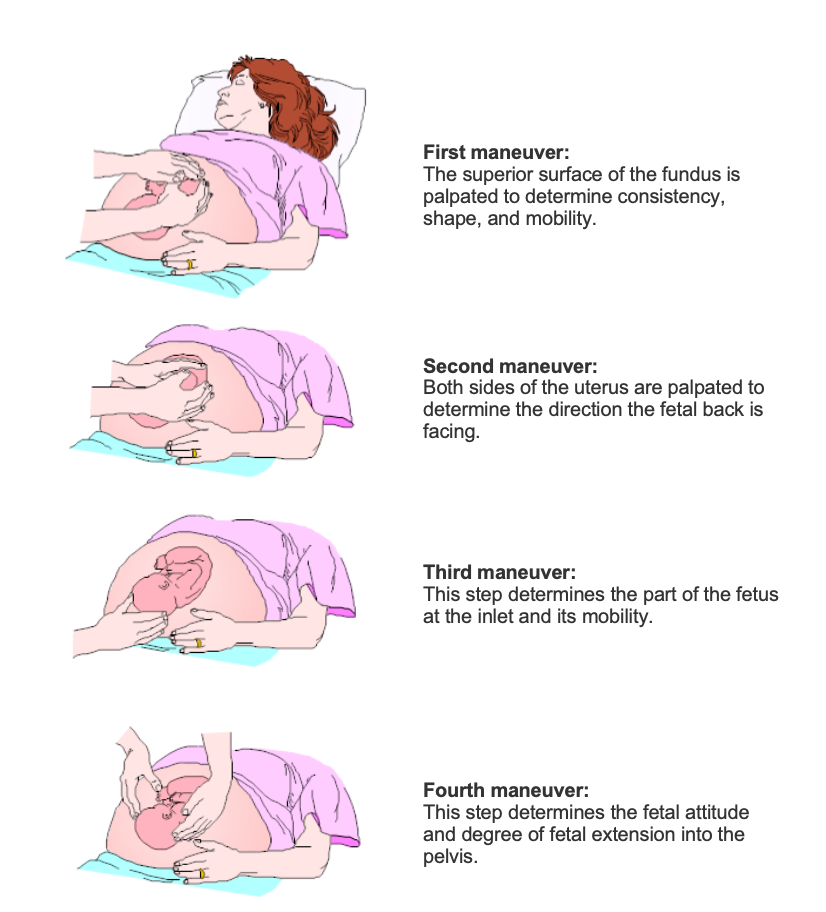
- From 36 weeks, employ Leopold maneuvers to assess fetal presentation and prepare for possible delivery scenarios.
- Utilize ultrasound as necessary to confirm fetal lie and placental position, especially if there's any uncertainty or abnormal presentation is suspected.
Leopold Maneuvers:
- A series of four palpation techniques used to assess fetal position, presentation, and engagement.
- Helps in determining the fetal lie (longitudinal, oblique, transverse), fetal presentation (cephalic or breech), and engagement of the presenting part.
- If abnormal presentations such as breech are suspected or fetal position cannot be accurately determined, ultrasound evaluation is recommended to confirm findings and plan for delivery accordingly.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Frequency of Visits
- The cadence of prenatal visits typically increases during the third trimester, with appointments every two weeks from 28 to 36 weeks and then weekly until delivery. This schedule allows for timely identification and management of any issues as the pregnancy progresses towards term.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
احصل على التجربة الكاملة
اشترك للوصول لفيديوهات الشرح التفصيلي والبطاقات التعليمية التفاعلية وأسئلة الممارسة مع تتبع التقدم.
فيديوهات الشرح
بطاقات تفاعلية
أسئلة ممارسة
اشترك الآن