شرح المدرسين
Summary
The second trimester of pregnancy, from 14 to 27+6 weeks, marks a critical phase of growth and development for both the mother and the fetus. During this period, routine prenatal visits aim to monitor the pregnancy's progress, manage symptoms, and detect any potential complications early.
Routine Clinical Assessment
Routine clinical assessments are pivotal during the second trimester. These assessments include:
- Symptom Assessment: Healthcare providers look for signs of potential pregnancy complications, such as vaginal bleeding, contractions, symptoms of preeclampsia, or leakage of amniotic fluid.
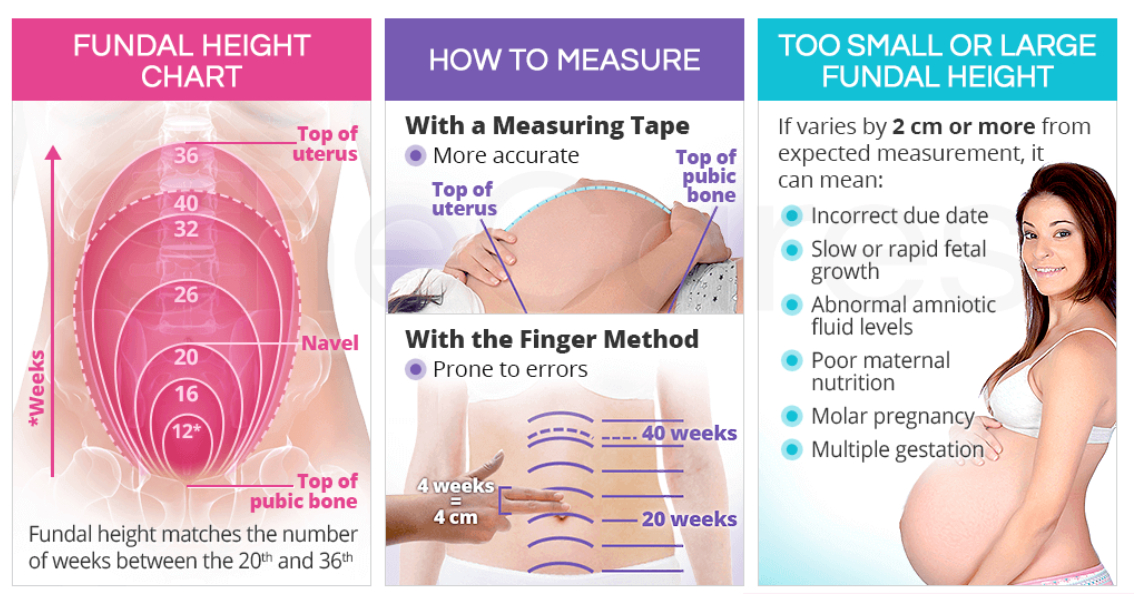
- Physical Examination: Key components include measuring weight, blood pressure (to screen for hypertensive disorders), and fundal height (to monitor fetal growth). Additionally, auscultation of the fetal heart rate confirms the fetus's wellbeing.
Obstetric Ultrasound
A comprehensive fetal anatomy scan, conducted between 18 to 22 weeks of gestation, is a cornerstone of second-trimester care. This ultrasound plays a crucial role in:
- Assessing fetal growth
- Determining placental location and amniotic fluid volume
- Revisiting and confirming the estimated due date (EDD), particularly if established by a first-trimester ultrasound
Fetal Anatomy Scan
The fetal anatomy scan offers an in-depth examination of the fetus, placenta, and maternal anatomy, focusing on:
- General Principles: The primary objectives are to screen for fetal anomalies and confirm or adjust gestational age estimations.
- Modalities: The scan typically begins with a transabdominal ultrasound, with transvaginal or transperineal ultrasound used as needed for enhanced clarity.
- Components:
- Fetal Evaluation:
- Number of fetuses and their presentation
- Cardiac activity and rhythm
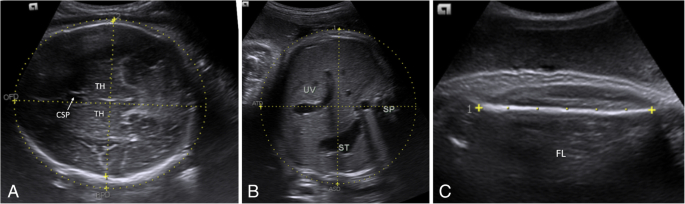
- Comprehensive anatomy survey to check for structural abnormalities and determine fetal sex
- Fetal biometric measurements, including biparietal diameter (BPD), femur length (FL), abdominal (AC), and head circumferences (HC)
- Placental and Amniotic Fluid Evaluation: Location, appearance, and cord insertion of the placenta, as well as the amniotic fluid volume
- Maternal Pelvic Anatomy: Includes assessment of the cervix and any relevant maternal structures
- Fetal Evaluation:
Additional Ultrasounds
Further ultrasounds may be necessary to guide invasive procedures, assess suspected abnormalities, or address potential obstetric emergencies such as vaginal bleeding or premature rupture of membranes.
Screening Tests
Key screenings during the second trimester include:
| Screening test | |||
| Test | Indication | Purpose | Management of abnormal results |
| CBC |
|
|
|
| Oral glucose tests |
|
|
|
Prenatal Counseling
This period also offers an opportunity for discussing preterm labor signs, addressing concerns about pregnancy, labor, and delivery, and preparing for the upcoming stages of pregnancy.
Risk Assessment
Healthcare providers assess risk factors for adverse pregnancy outcomes, adjusting management plans for high-risk pregnancies as needed.
Fetal Movement Monitoring
An essential aspect of the second trimester is the emphasis on fetal movement awareness. Pregnant individuals are encouraged to pay attention to and report the movements they feel. The sensation of the baby moving is a reassuring sign of the fetus's well-being and plays a significant role in strengthening the bond between the mother and the baby. In first-time pregnancies, these movements, often referred to as "quickening," are usually felt between 18 and 19 weeks of gestation. In subsequent pregnancies, mothers might notice these movements a bit earlier, typically between 16 and 18 weeks. This awareness is vital, as it not only provides comfort but also serves as an early indicator of fetal health.
احصل على التجربة الكاملة
اشترك للوصول لفيديوهات الشرح التفصيلي والبطاقات التعليمية التفاعلية وأسئلة الممارسة مع تتبع التقدم.
