Definition
Shoulder dystocia is an unpredictable and emergent situation during vaginal birth, characterized by the requirement for additional obstetric maneuvers to deliver the fetal shoulders after the head has already been delivered.
Epidemiology
∼ 0.2–3% of vaginal deliveries with vertex presentation
Pathophysiology
Occurs when the anterior shoulder becomes lodged behind the maternal pubic symphysis, or less commonly, when the posterior shoulder impinges on the sacral promontory.
Risk factors
- History of shoulder dystocia
- Fetal macrosomia
- Maternal diabetes mellitus or gestational diabetes
- Maternal obesity
- Prolonged second stage of labor
Always be prepared for shoulder dystocia, as it can occur even in the absence of risk factors
Diagnosis
- The diagnosis is confirmed when standard gentle traction fails to deliver the shoulders.
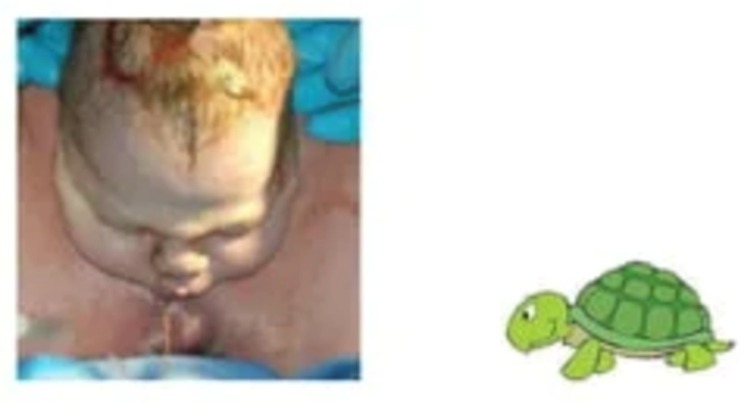
- Often indicated by the "turtle sign," where the fetal head retracts against the perineum after delivery.
Management
- Establish the Presence of Shoulder Dystocia: This is a clinical diagnosis made when the shoulders fail to deliver following the head, often indicated by the "turtle sign" where the baby's head retracts against the perineum.
- Perform Initial Shoulder Dystocia Maneuvers:
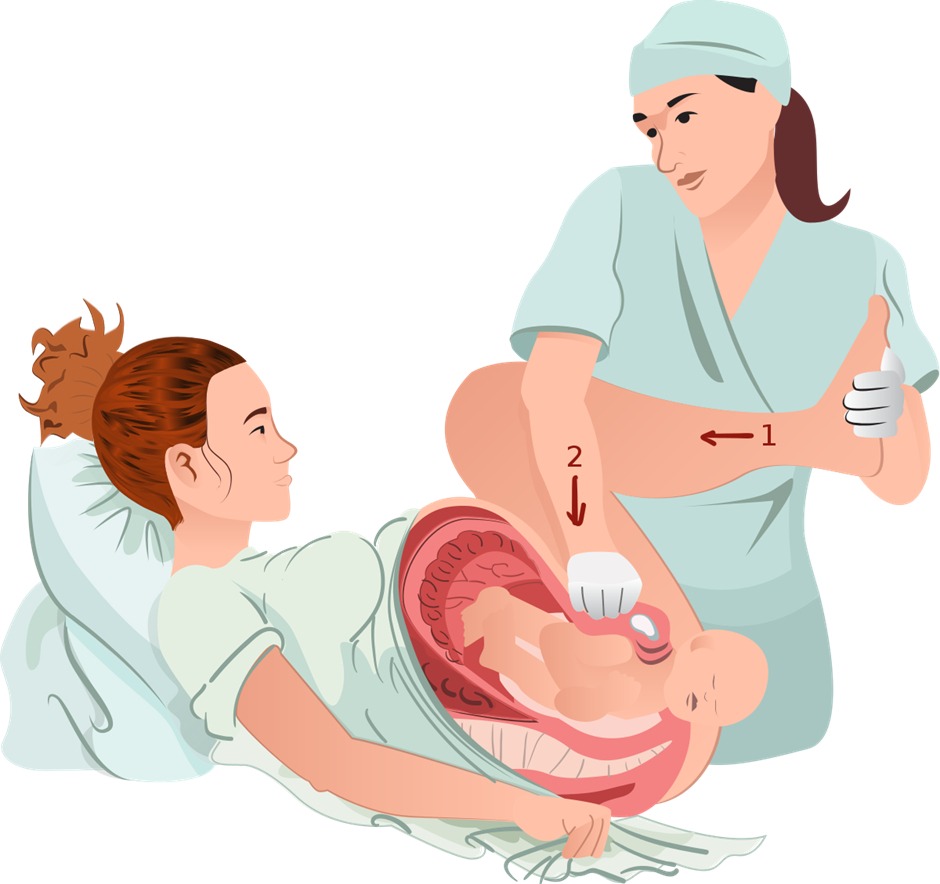
- McRoberts Maneuver: Position the patient supine with the hips abducted, externally rotated, and hyperflexed. This maneuver realigns the pelvic anatomy to facilitate delivery.
- Suprapubic Pressure (Rubin I Maneuver): Apply pressure above the pubic bone to help dislodge the anterior shoulder.
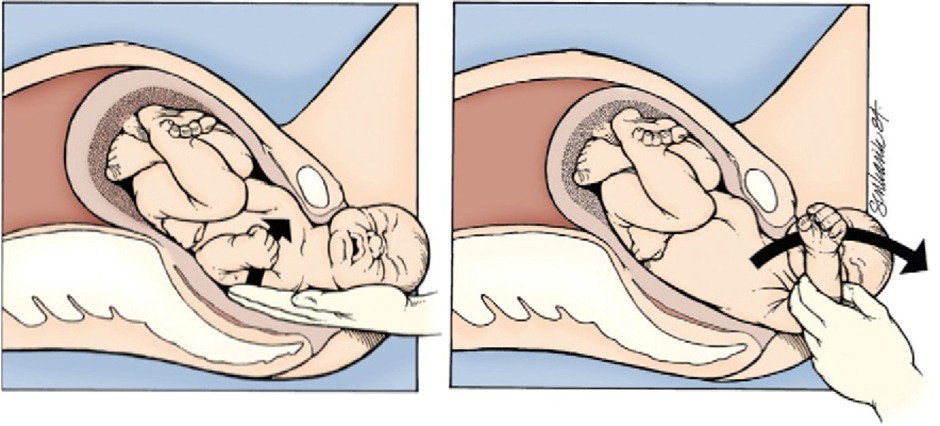
- Manual Delivery of the Posterior Fetal Arm: If the initial maneuvers are unsuccessful, attempt to deliver the posterior arm by reaching into the vagina, locating the arm, and gently pulling it out.
- Secondary Maneuvers:
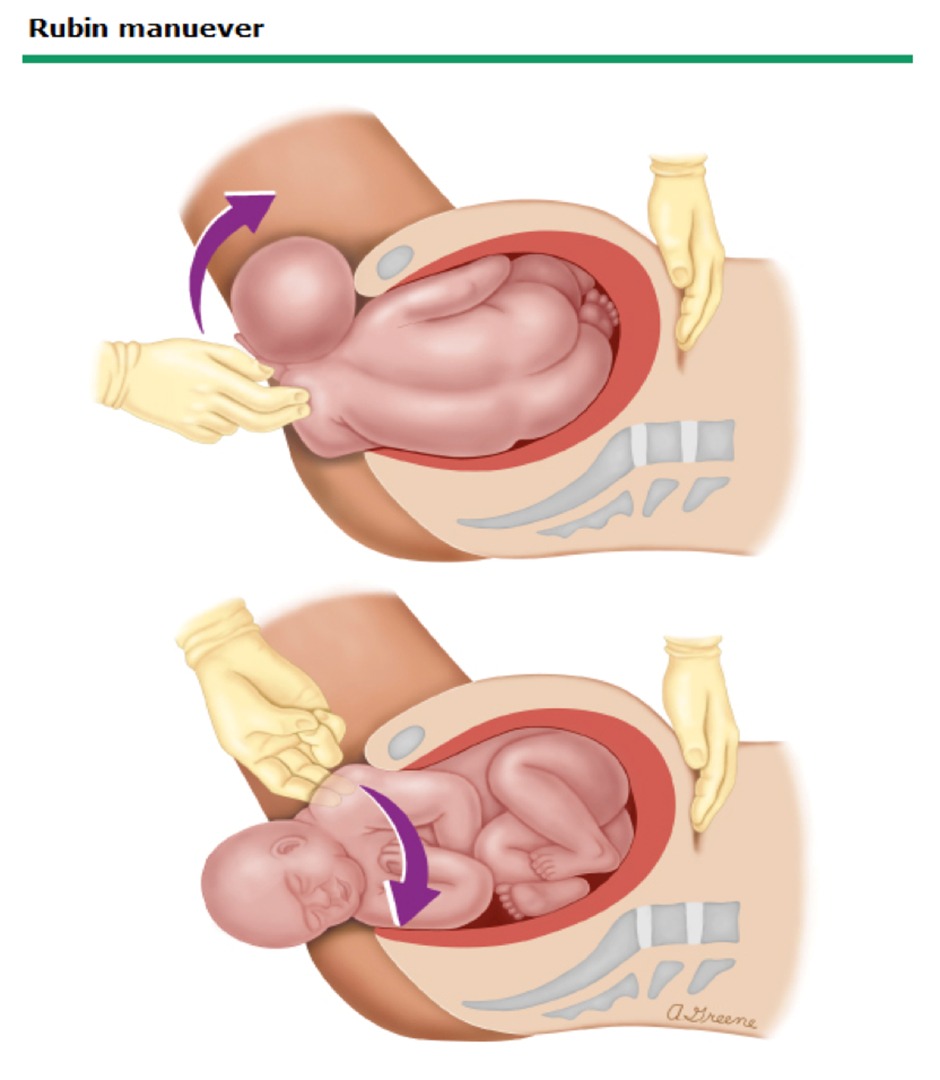
- Rubin II Maneuver: Rotate the fetal shoulder girdle by applying pressure to the back of the anterior shoulder to encourage its rotation and descent.
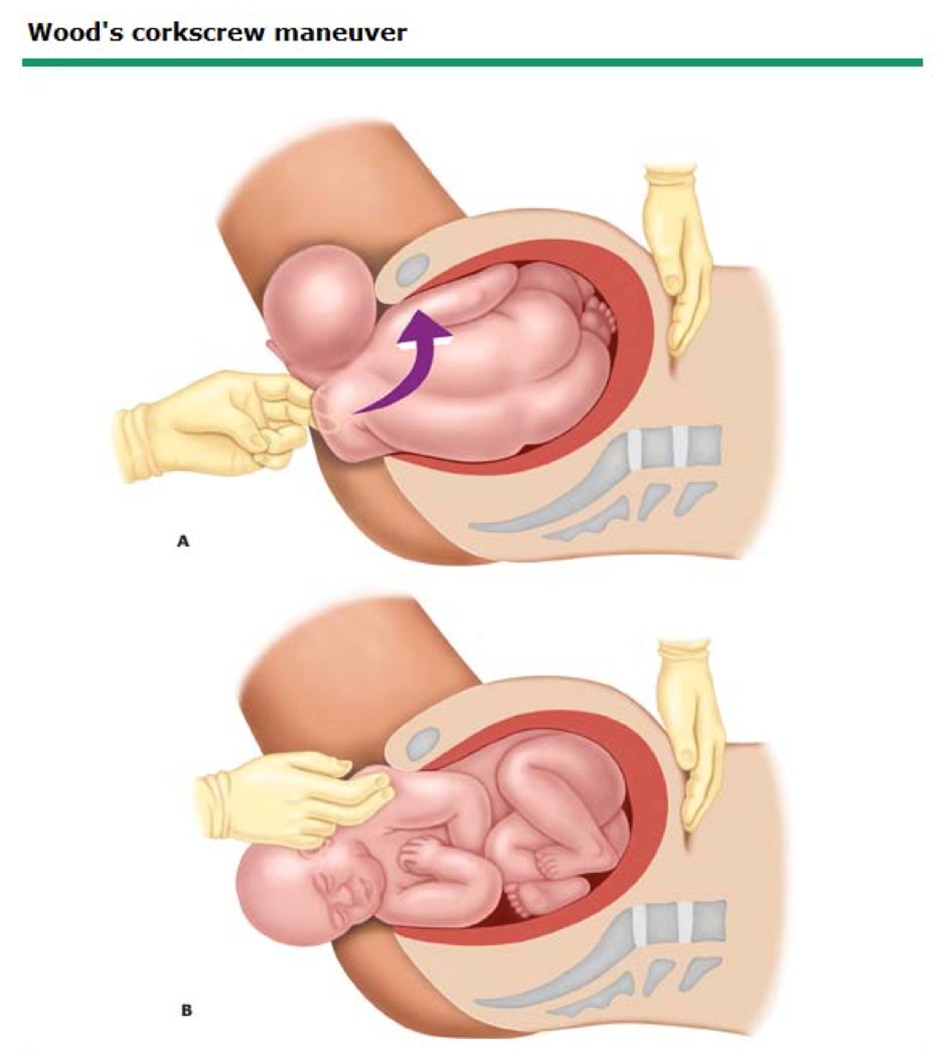
- Woods Corkscrew Maneuver: Similar to the Rubin II, but pressure is applied to the front of the posterior shoulder to rotate the fetal shoulders.
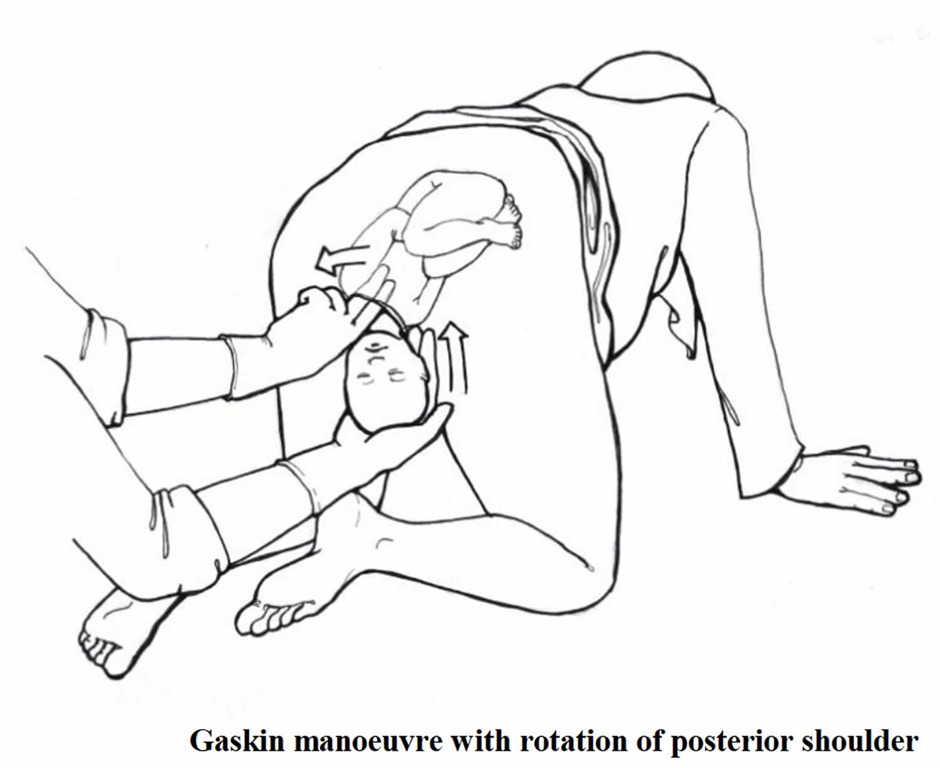
- Gaskin Maneuver: The patient moves to a hands-and-knees position to increase the pelvic diameter and assist with delivery.
- Rubin II Maneuver: Rotate the fetal shoulder girdle by applying pressure to the back of the anterior shoulder to encourage its rotation and descent.
- Maneuvers of Last Resort:
- Intentional Clavicular Fracture: Deliberately fracture the clavicle to reduce the shoulder width and facilitate delivery.
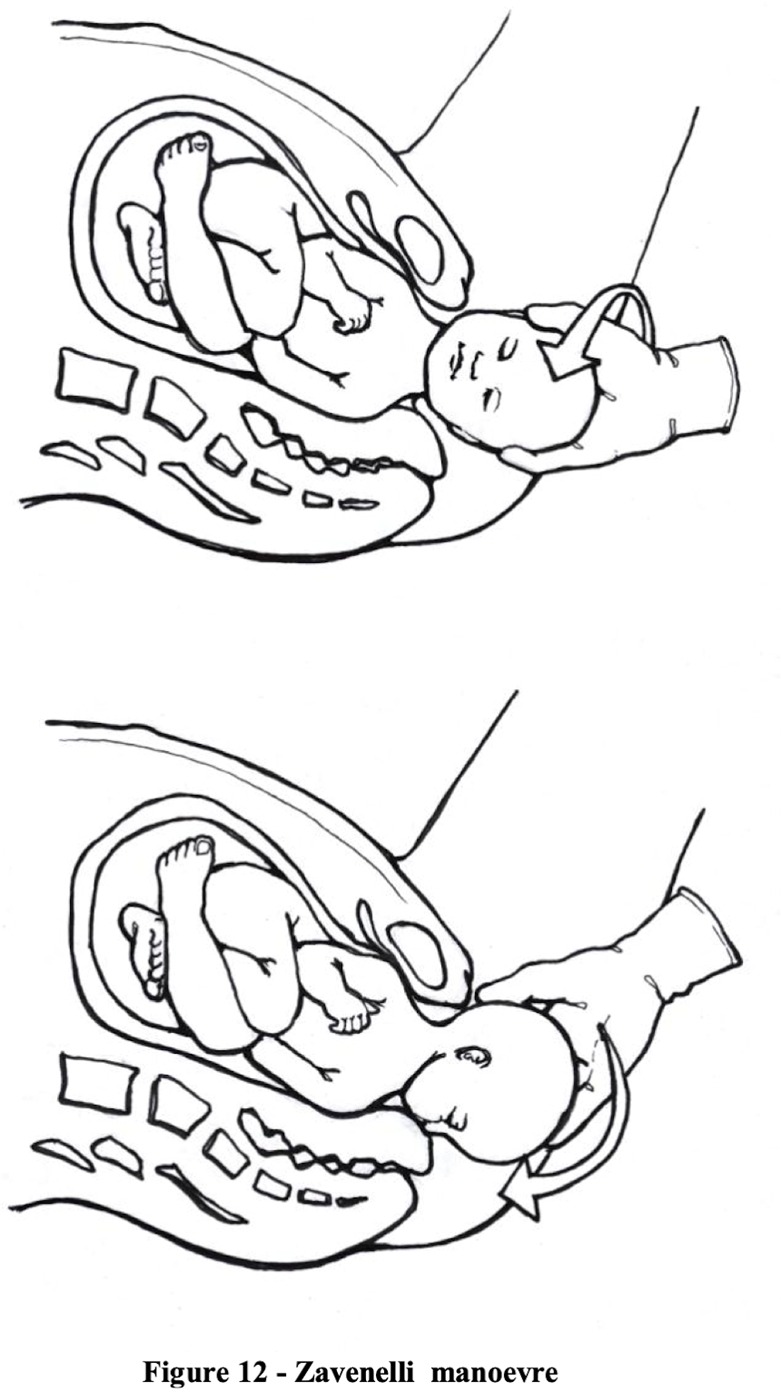
- Zavanelli Maneuver: Reinsert the fetal head into the pelvis and proceed with an emergency cesarean section.
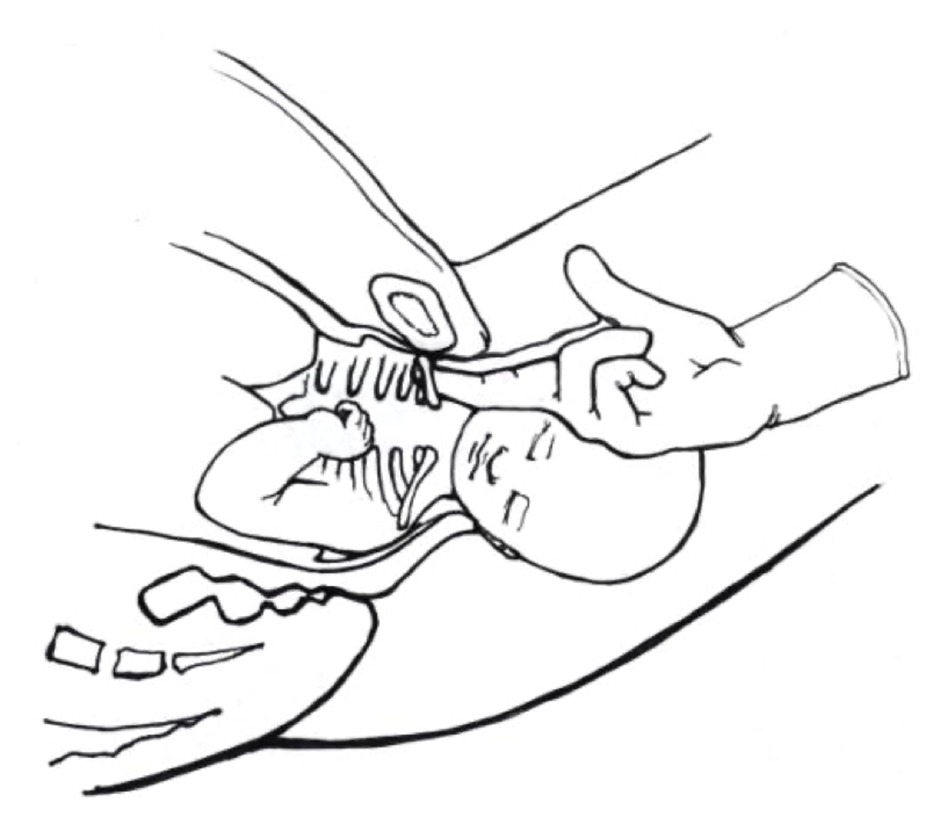
- Symphysiotomy: A rarely used procedure that involves cutting the symphysis pubis to widen the pelvis. This is typically considered only if other maneuvers fail and cesarean delivery is not an option.
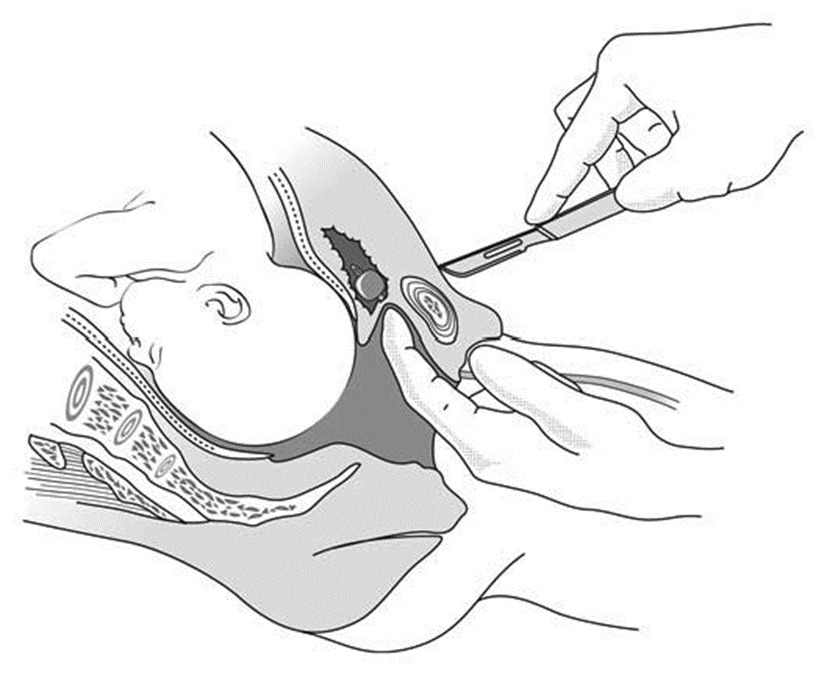
- Intentional Clavicular Fracture: Deliberately fracture the clavicle to reduce the shoulder width and facilitate delivery.
- General Considerations:
- Avoid excessive force to prevent brachial plexus injuries.
- An episiotomy may be necessary for internal maneuvers.
- Continuously communicate with the team and document all actions taken during the management process.
Complications
Fetal Complications
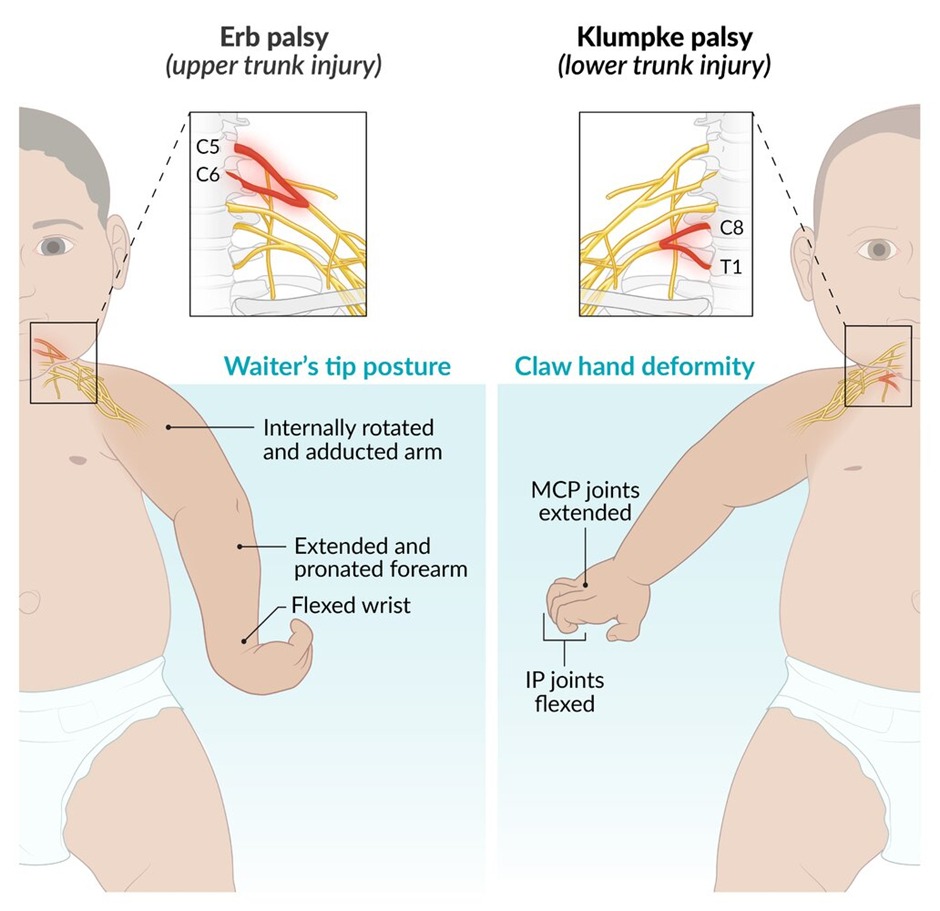
- Brachial Plexus Injury: Damage to the nerves of the brachial plexus can occur, with Erb's palsy being more common than Klumpke palsy. Erb's palsy affects the upper arm, while Klumpke palsy affects the lower arm and hand.
- Clavicle or Humerus Fracture: The clavicle (collarbone) or humerus (upper arm bone) may fracture as a result of maneuvers to resolve the dystocia. These injuries typically heal well in newborns but require proper diagnosis and management.
- Perinatal Asphyxia and Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy: Delays in resolving shoulder dystocia can lead to decreased oxygen supply, resulting in asphyxia. Prolonged asphyxia may cause hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, a condition that can result in permanent brain damage.
Maternal Complications
- Perineal Lacerations: Efforts to deliver the baby, including the use of maneuvers or instruments, can cause tears in the perineum that may extend to the muscles or even the rectum.
- Postpartum Hemorrhage: The physical stress of labor, especially with complicated deliveries like shoulder dystocia, can lead to excessive bleeding after delivery.
Conclusion
Shoulder dystocia, though infrequent, demands prompt and efficient management to mitigate the risks of severe maternal and neonatal complications. Preparedness, skill in executing resolution maneuvers, and a systematic approach are paramount for clinicians to navigate this obstetric emergency successfully. Continuous training and adherence to established protocols can enhance outcomes for both mothers and infants experiencing shoulder dystocia.
احصل على التجربة الكاملة
اشترك للوصول لفيديوهات الشرح التفصيلي والبطاقات التعليمية التفاعلية وأسئلة الممارسة مع تتبع التقدم.