Introduction
Pregnancy leads to a myriad of changes in the musculoskeletal system, driven by the body's need to support fetal growth and prepare for childbirth. These physiological adaptations can result in various symptoms and conditions, affecting comfort and mobility in pregnant individuals.
Key Changes and Management Strategies
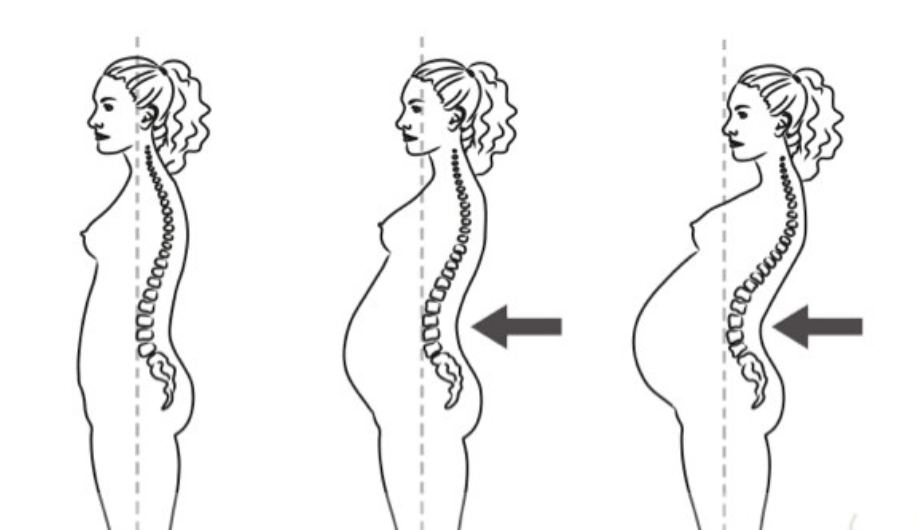
Increased Body Weight and Lumbar Lordosis
- Adaptation: The increase in body weight and a forward shift in the center of gravity during pregnancy lead to increased lumbar lordosis.
- Impact: This change can exacerbate back pain and discomfort due to the additional stress on the lower back.
- Management: Regular exercise, such as prenatal yoga and swimming, can help strengthen back muscles and alleviate pain. Supportive footwear and maternity belts may also provide relief.
Diastasis Recti and Meralgia Paresthetica
- Adaptation: Increased intraabdominal pressure can lead to diastasis recti, the separation of the rectus abdominis muscles, and meralgia paresthetica, characterized by numbness or pain in the outer thigh.
- Management: Postpartum, gentle core-strengthening exercises can be beneficial for diastasis recti. Managing meralgia paresthetica involves avoiding tight clothing and adopting comfortable sleeping positions.
Relaxation of Pelvic Girdle Ligaments
- Adaptation: Hormones such as progesterone and relaxin lead to the relaxation of the pelvic girdle ligaments and symphysis pubis, preparing the pelvis for childbirth.
- Impact: This relaxation can cause pelvic girdle pain and coccygeal pain, affecting mobility and comfort.
- Management: Pelvic support belts, physiotherapy, and specific exercises can help stabilize the pelvis and reduce discomfort. Pain management strategies, including heat or cold packs and safe pain medication under medical guidance, offer additional relief.
Fluid Retention and Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Adaptation: Fluid retention in tissues during pregnancy can lead to carpal tunnel syndrome, characterized by numbness, tingling, or pain in the hand and arm.
- Management: Wrist splints worn at night can help alleviate symptoms. Minimizing repetitive hand movements and maintaining a neutral wrist position during activities are also beneficial.
Additional Considerations
Posture and Alignment
- Maintaining proper posture and alignment is crucial during pregnancy to manage and prevent musculoskeletal discomfort. Education on posture during daily activities and work can further help in mitigating pain.
Exercise and Physical Activity
- Tailored exercise programs focusing on strength, flexibility, and cardiovascular health are important for supporting musculoskeletal health during pregnancy. Consulting with healthcare providers or physical therapists can ensure that activities are safe and effective.
Nutritional Support
- Adequate nutrition, including calcium and vitamin D intake, supports musculoskeletal health, aiding in the management of conditions like osteoporosis, which may be a concern postpartum.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing musculoskeletal system adaptations during pregnancy is vital for improving pregnant individuals' overall comfort and mobility. Through a combination of exercise, supportive devices, and lifestyle modifications, many of the discomforts associated with these changes can be effectively managed, ensuring a healthier pregnancy and recovery period.
احصل على التجربة الكاملة
اشترك للوصول لفيديوهات الشرح التفصيلي والبطاقات التعليمية التفاعلية وأسئلة الممارسة مع تتبع التقدم.