Summary
Labor and childbirth are complex processes that involve a series of coordinated events leading to the delivery of the baby. However, complications can arise due to abnormalities in fetal orientation, including fetal malpresentation and fetal malposition. These conditions are associated with increased perinatal risks and may necessitate assisted delivery methods or cesarean delivery to prevent maternal and fetal complications.
Fetal Malpresentation
Fetal malpresentation refers to any presentation or lie of the fetus that is not cephalic (head-first).
Examples of Fetal Malpresentation
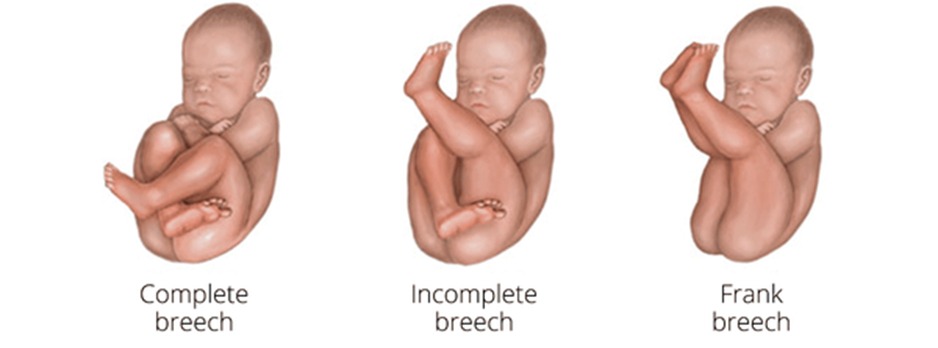
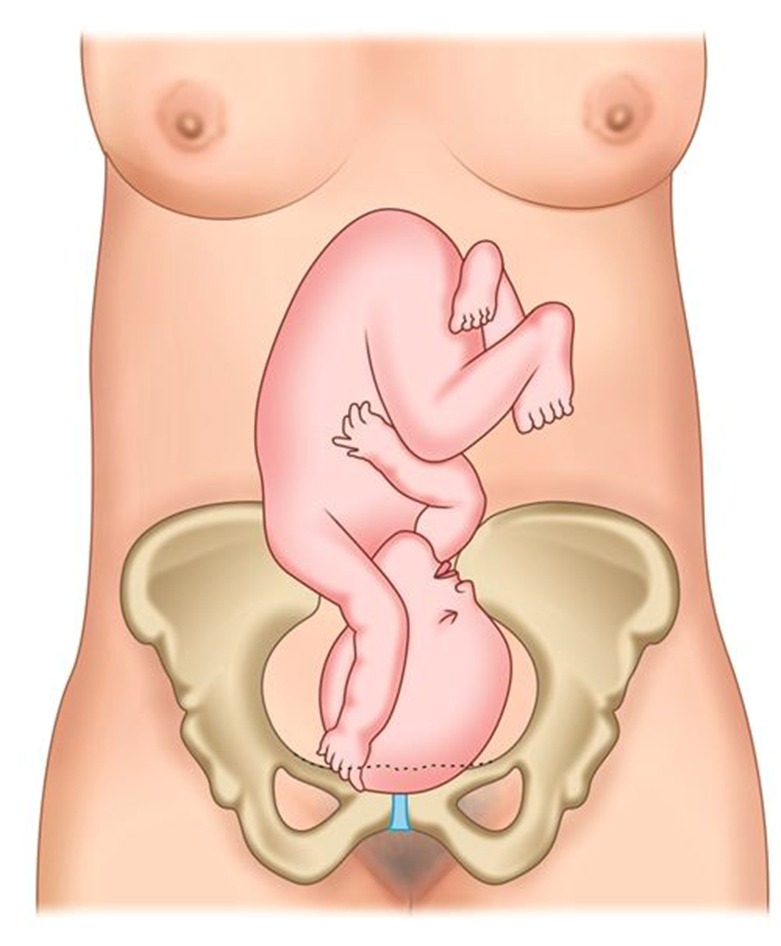
- Breech Presentations: The fetus is positioned to deliver buttocks or feet first rather than the head. There are several types of breech presentations:
- Frank Breech: The fetus's buttocks are aimed toward the birth canal with legs straight up in front of the body, and feet near the head.
- Complete Breech: Both knees and hips are flexed, and the buttocks or feet may enter the birth canal first.
- Single Footling Breech: One leg is extended down into the birth canal.
- Double Footling Breech: Both feet are positioned to be delivered first.
- Compound Presentation: When an extremity is prolapsed alongside the presenting part (usually the head).
- Shoulder Presentation: The fetus is in a transverse lie, with the shoulder presenting towards the birth canal.
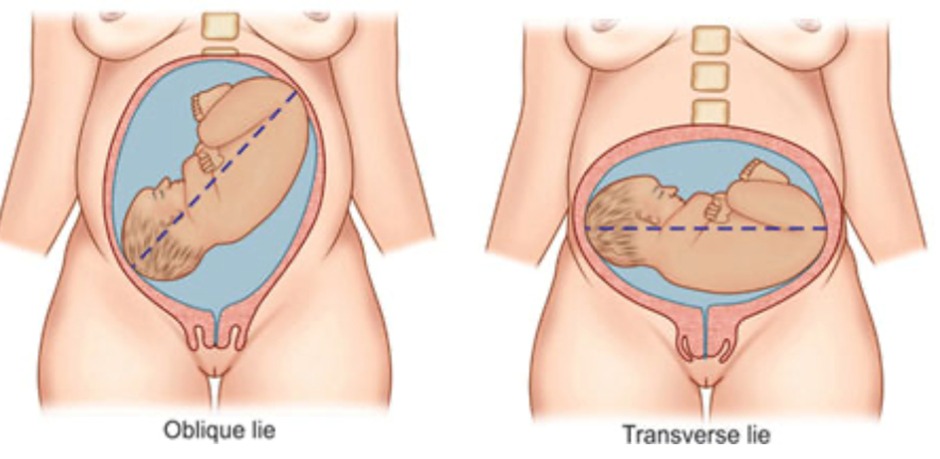
- Transverse Lie: The fetus is positioned horizontally in the uterus, making vaginal delivery impossible without intervention.
- Oblique Lie: The fetal long axis is angled against the maternal long axis, potentially leading to labor complications.
Fetal Malposition
Fetal malposition occurs when the fetus is in a cephalic presentation but with an orientation that is not anteriorly aligned with the maternal pelvis.
Examples of Fetal Malposition
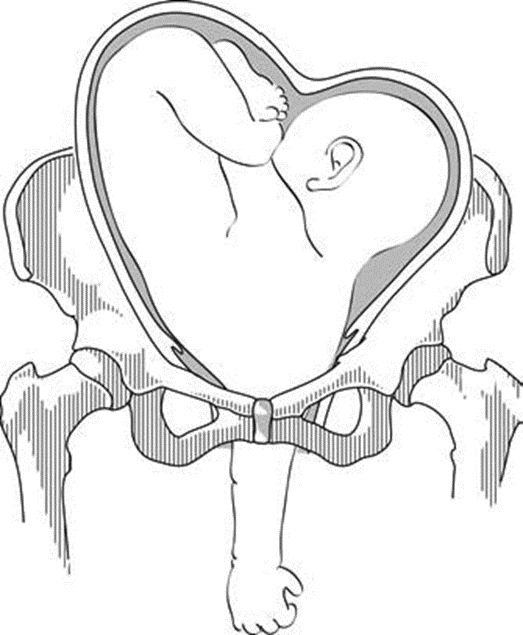
- Occiput Posterior Position (OP): The fetus's head is down, but the back of the head (occiput) is aligned towards the mother's back. This position can result in a longer and more painful labor, often referred to as "back labor."
- Occiput Transverse Position: The occiput is positioned transversely across the pelvis, neither fully anterior nor posterior. This position may delay labor progression and increase the need for interventions.
Management and Intervention
The management of fetal malpresentation and malposition often depends on the specific type and timing during labor. Options include:
- External Cephalic Version (ECV) for breech presentations: An attempt to rotate the fetus to a cephalic presentation through abdominal manipulation.
- Assisted Delivery Techniques: Such as the use of forceps or vacuum extraction, especially in cases of occiput posterior or transverse positions.
- Cesarean Delivery: Often considered when safe vaginal delivery is compromised due to the abnormal orientation of the fetus.
Conclusion
Abnormalities in fetal orientation, including malpresentation and malposition, present significant challenges during labor and delivery. Understanding these conditions and their implications allows healthcare providers to plan and implement appropriate interventions to ensure the safety and well-being of both mother and baby.
احصل على التجربة الكاملة
اشترك للوصول لفيديوهات الشرح التفصيلي والبطاقات التعليمية التفاعلية وأسئلة الممارسة مع تتبع التقدم.