Introduction
- External cephalic version (ECV) is a pivotal obstetric procedure aimed at rotating a noncephalic fetus to a cephalic presentation through maternal abdominal manipulation.
- Performed electively near term in nonlaboring patients, ECV seeks to enhance the likelihood of a vaginal cephalic birth.
Factors Affect the success
Impeding Factors
- Anterior or lateral placenta
- Decreased amniotic fluid
- Descent of the breech into the pelvis
- Maternal obesity
Enhancing Factors
- Posterior placenta
- Complete breech position
- Nonlongitudinal fetal lie
Complications
- Stillbirth
- Placental Abruption
- Emergency Cesarean Birth
- Abnormal Fetal Heart Rate Changes
- Fetomaternal Transfusion
- Vaginal Bleeding
- Rupture of Membranes
- Cord Prolapse
When considering External Cephalic Version (ECV), it's important to balance its risks against those associated with persistent breech presentation and planned cesarean birth:
- Risks Associated with Persistent Breech Presentation:
- Cord Prolapse
- Probable Cesarean Birth
- Complications of Breech Birth
- Risks Associated with Planned Cesarean Birth:
- Maternal Risks:
- Surgical site infection
- Surgical injury
- Hemorrhage
- Fetal/Neonatal Risks:
- Laceration during hysterotomy
- Transient tachypnea of the newborn
- Admission to high care unit
- Immune sequelae likely related to microbiome disturbance from lack of exposure to vaginal flora
- Maternal Risks:
Candidacy for ECV
ECV is offered to most patients with a noncephalic fetal lie, barring contraindications.
Absolute Contraindications
Absolute contraindications to ECV are conditions where any attempt at labor and vaginal birth, regardless of fetal presentation, would pose too high a risk. These include:
- Placenta Previa: Where the placenta covers the cervical opening, posing a risk of severe bleeding during labor.
- Previous Classical Cesarean Birth: Due to the higher risk of uterine rupture with a vertical uterine incision.
Relative Contraindications
- Fetal Growth Restriction: Limited movement space and increased stress risks on the fetus.
- Hyperextended Fetal Head: Makes version more difficult and increases risk.
- Multiple Gestation: Especially in cases where the first twin is not cephalic. While ECV can be attempted, its success and safety vary, and breech extraction may also be considered.
- Nonreassuring Fetal Monitoring Test Results: Indicating fetal distress, making manipulation risky.
- Placental Abruption: Where there is a separation of the placenta from the uterus, posing a risk to the fetus.
- Previous Vertical Lower Uterine Segment Cesarean Birth: Increases the risk of uterine rupture.
- Ruptured Membranes: Where the amniotic sac has broken, increasing infection risk and possibly making ECV less successful.
- Severe Oligohydramnios: Low amniotic fluid making fetal movement more difficult and risky.
- Significant Fetal or Uterine Anomaly: Such as hydrocephaly or septate uterus, where ECV may not be advisable due to the increased risk or reduced chance of success.
Timing and Alternatives
ECV is typically recommended after 36 0/7 weeks of gestation, often performed at 37 weeks.
Alternatives include :
- Expectant Management
- Planned Cesarean Birth
- Trial of Labor
- Delaying Cesarean Birth
- Postural Maneuvers
- Pelvic Elevation and Knee-Chest Position
- Supine Head-Down Position
- Lateral Positioning
- Moxibustion and Acupuncture
- Moxibustion: This traditional Chinese medicine technique involves burning a herb near the skin to encourage fetal movement and version.
- Acupuncture
Procedure Details
Pre-Procedure Preparation for External Cephalic Version (ECV)
- Ultrasound Examination: This confirms the fetal and placental positions, identifying potential challenges like oligohydramnios or anomalies that could impact the procedure's success.
- Fetal Well-being Assessment: A reactive fetal heart rate pattern or satisfactory biophysical profile score is necessary to confirm the fetus can safely undergo the stress of an ECV.
- Counseling: Patients receive detailed information about the procedure, including its purpose, alternatives, success rates, and potential risks.
- Oral Intake: Generally, there are no strict requirements against oral intake before ECV due to the low complication rate. However, guidelines vary, with some recommending a period of fasting in preparation for potential emergency cesarean delivery.
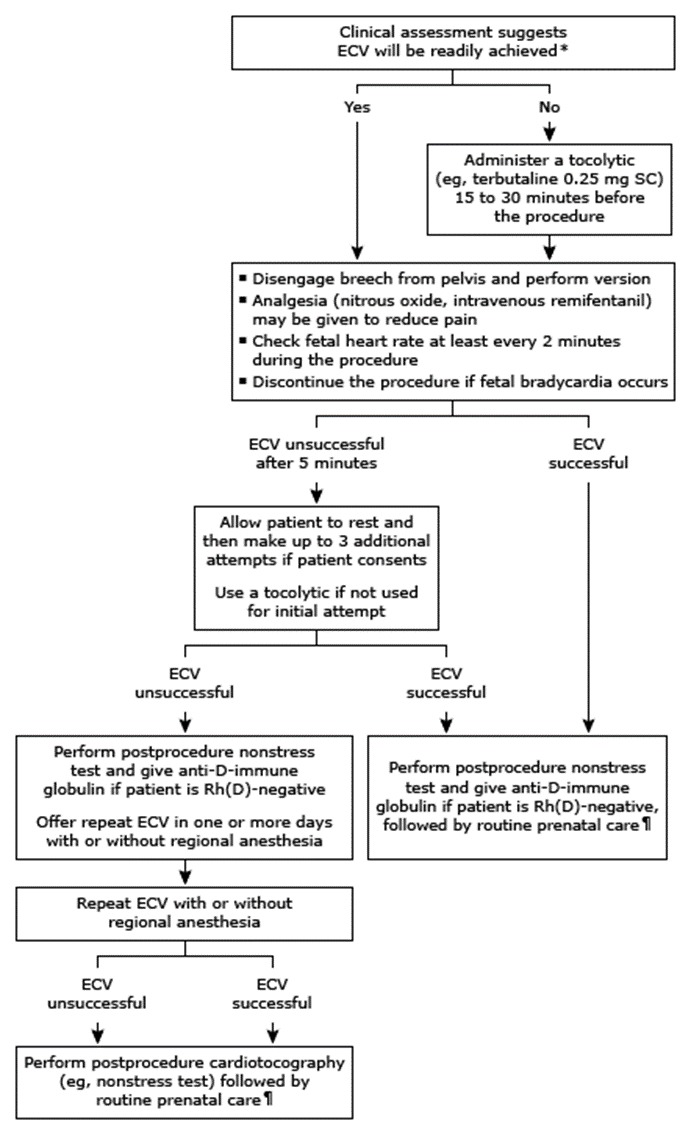
Procedure Technique for ECV
- Positioning the patient on a firm table, with the fetus's back towards the operator.
- Applying tocolysis to relax the uterus, improving the chances of a successful version.
- Using ultrasound gel or powder to facilitate smooth movements over the abdominal surface.
- Carefully manipulating the fetus, typically starting with the breech disengagement from the pelvis, followed by attempts to rotate the fetus into a cephalic position.
- Monitoring the fetal heart rate throughout the procedure to ensure fetal safety.
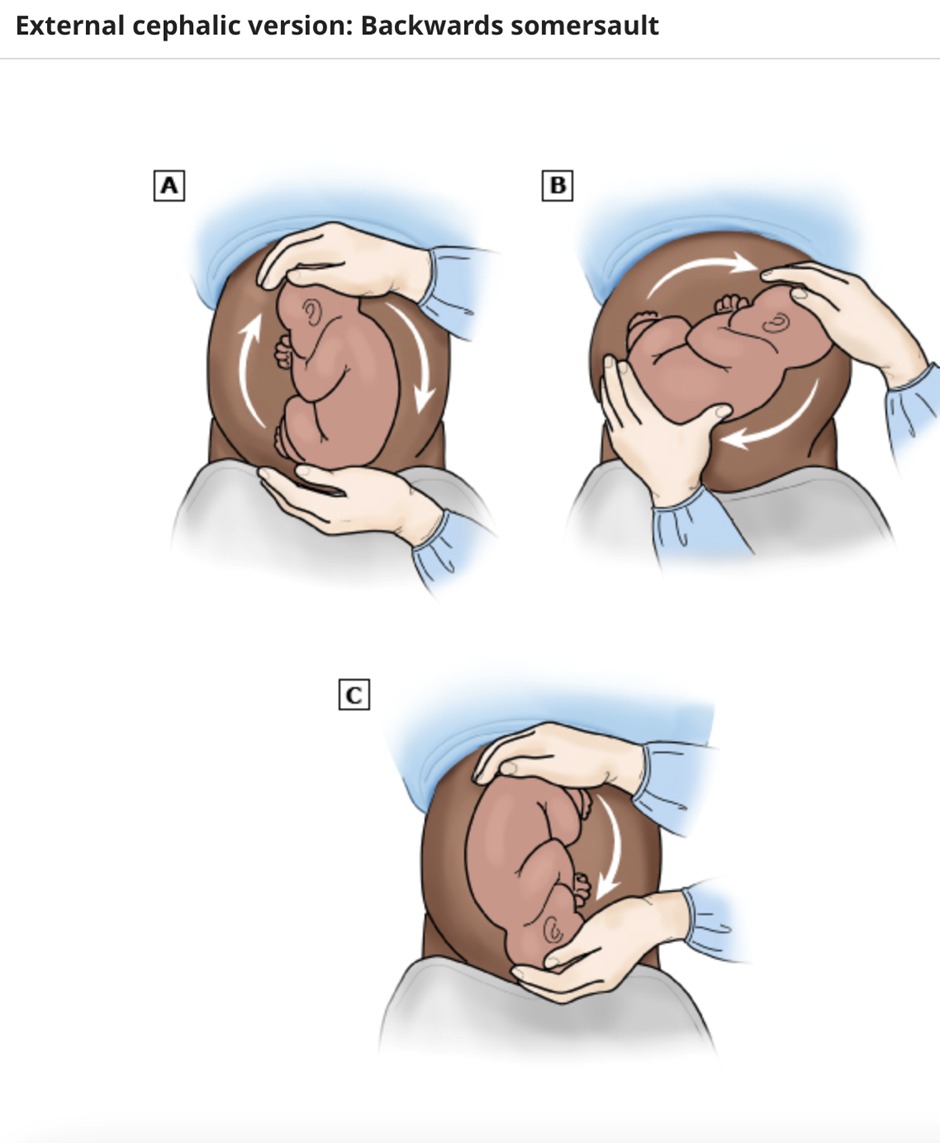
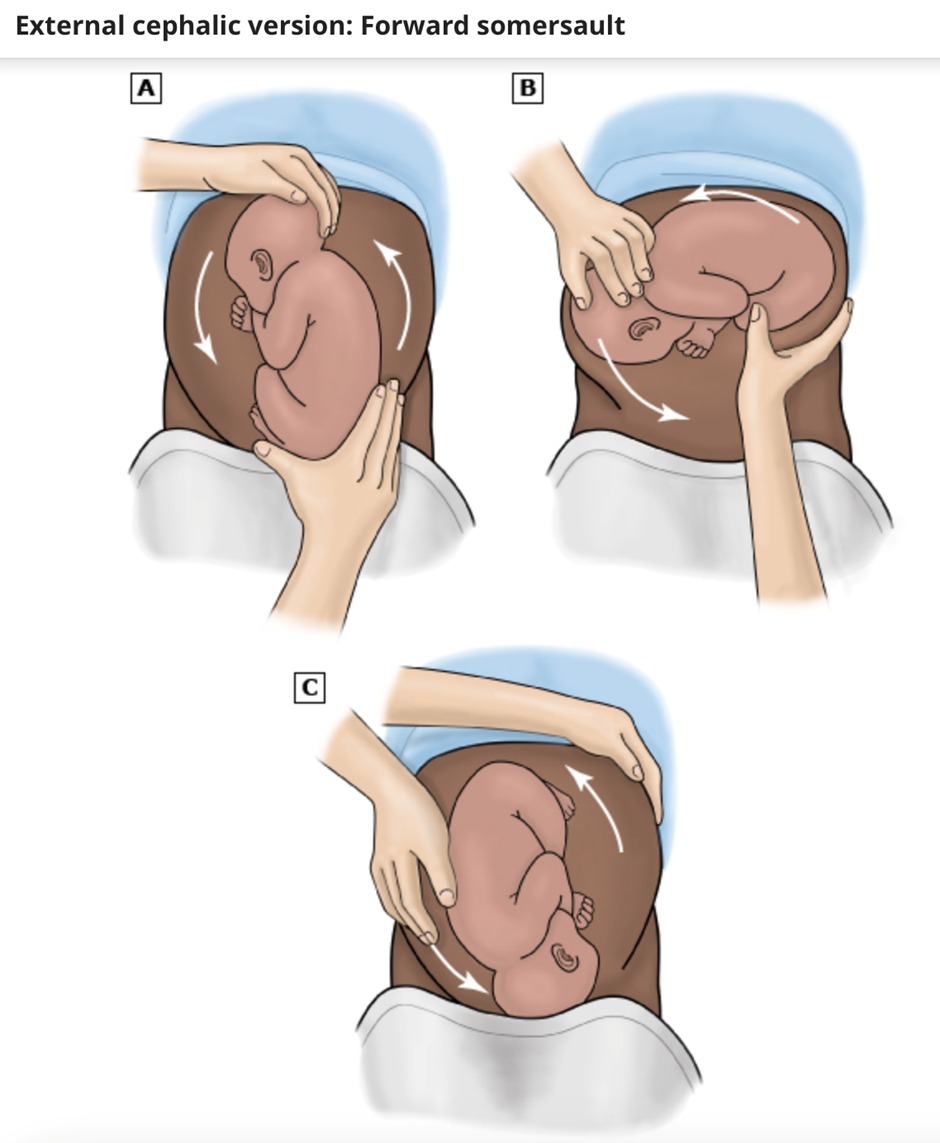
Ancillary measures like tocolysis (commonly with beta-adrenergic agonists like terbutaline), and in some cases, neuraxial anesthesia, may enhance the success rate of ECV by relaxing the uterus and reducing maternal discomfort.
Post-Procedure Management
- Fetal Monitoring: Continued monitoring of the fetal heart rate ensures the fetus remains well following the procedure.
- Anti-D Immune Globulin: Administered to Rh-negative patients to prevent alloimmunization.
- Outcome Management:
- Following a successful ECV, routine prenatal care resumes, avoiding immediate induction unless medically indicated.
- After an unsuccessful attempt, options may include reattempting ECV, expectant management, or planning for delivery with a persistent breech presentation.
Conclusion
ECV represents a critical intervention in modern obstetrics, offering a significant opportunity to reduce cesarean deliveries due to breech presentations. Understanding the factors influencing its success, alongside a careful assessment of risks and alternatives, enables informed decision-making and optimizes outcomes for both mothers and their babies.
احصل على التجربة الكاملة
اشترك للوصول لفيديوهات الشرح التفصيلي والبطاقات التعليمية التفاعلية وأسئلة الممارسة مع تتبع التقدم.