سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Introduction
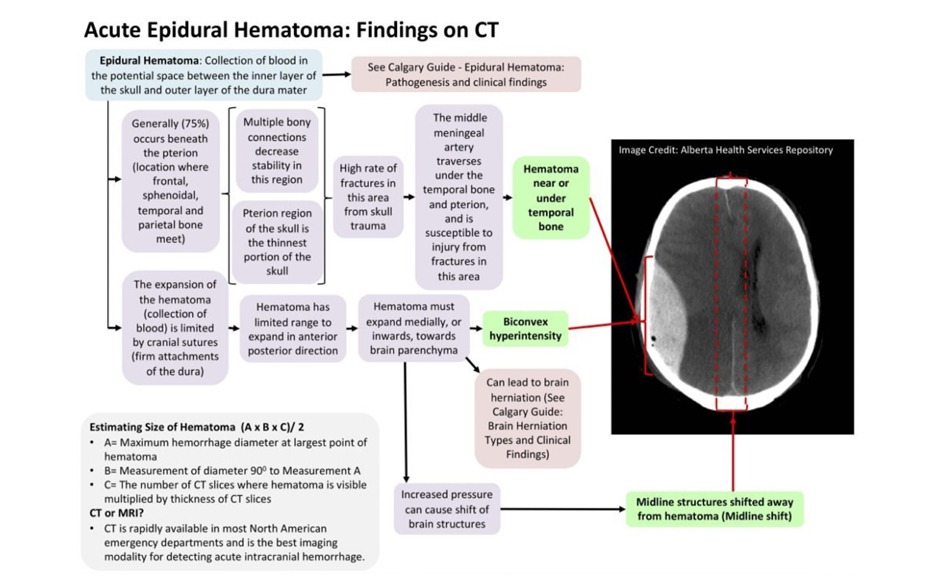
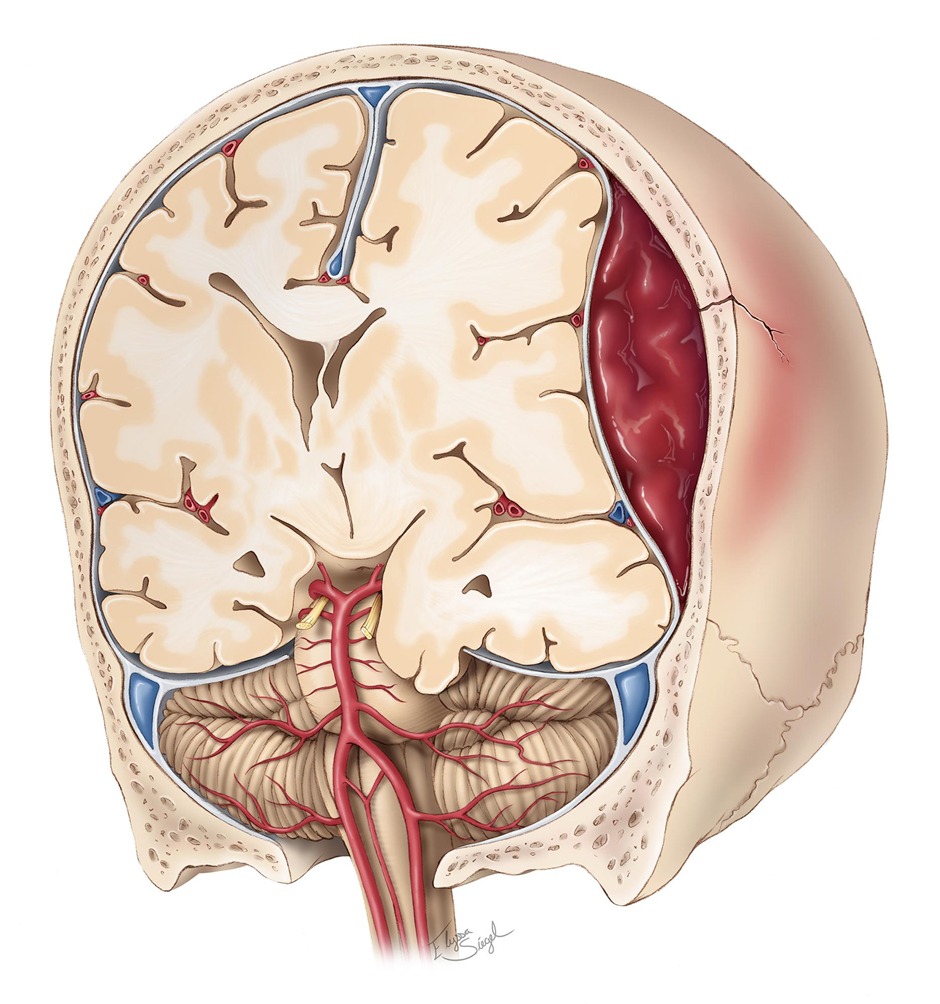
- In most cases the haemorrhage is the result of rupture of the middle meningeal artery, which is a branch of the maxillary artery (It is very important to remember: the source of bleeding is arterial)
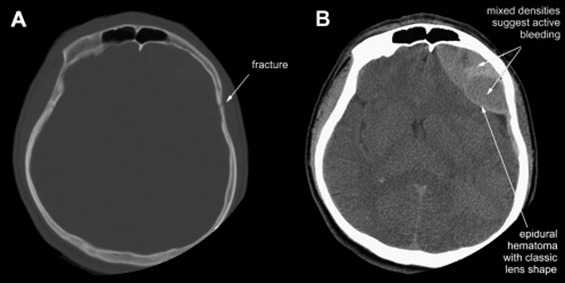
- A fracture overlies the hematoma in nearly 95% of adults
- Most common sites for epidural hematomas are the temporal region followed by the frontal area
- A typical clinical scenario includes transient loss of consciousness followed by recovery (lucid interval) and then subsequently followed by rapid deterioration due to hematoma expansion
- CT shows biconvex hyperdense collection of blood that DOES NOT cross the suture lines
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Epidemiology
- An epidural hematoma is a collection of blood within the space between dura mater and the skull. It is confined by the lateral sutures ( the coronal sutures)
- It is a life-threatening condition that may require immediate intervention and can be associated with significant morbidity and mortality if left untreated
- Rapid diagnosis and evacuation are important for a good outcome
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Clinical Presentation
- An epidural hematoma may occur as a result of severe head injury. It will begin as only a transient loss of consciousness and in approximately one-quarter of the cases there has been no initial loss of consciousness
- Headache is the initial symptom in a patient who has not lost consciousness or who has regained consciousness. It is usually followed by vomiting
- Focal neurological signs include dilation of the pupil secondary to 3rd cranial nerve palsy
| Extradural hemorrhage | Subdural hemorrhage | Subarachnoid hemorrhage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Location |
|
|
|
| Pathophysiology |
|
|
|
| Clinical presentation |
|
|
|
| CT findings | Convex shaped |
|
|
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Diagnosis
- CT scan is the radiological investigation of choice
- CT scan will show hyperdense (white) biconvex hematoma that does not cross the sutures
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Treatment
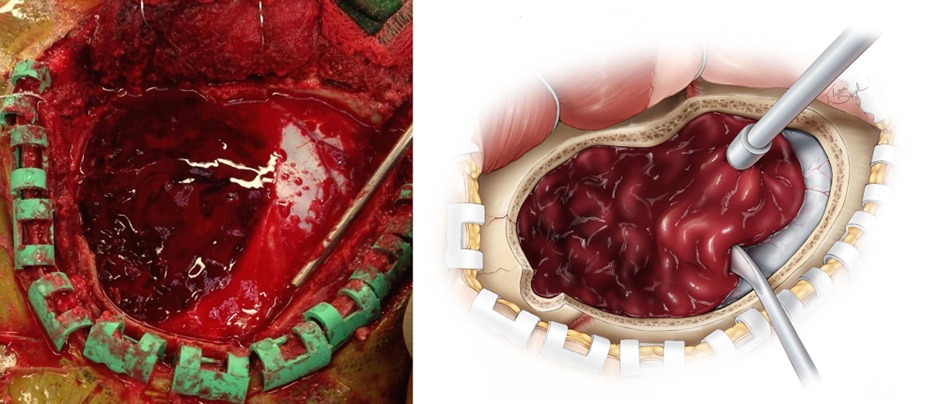
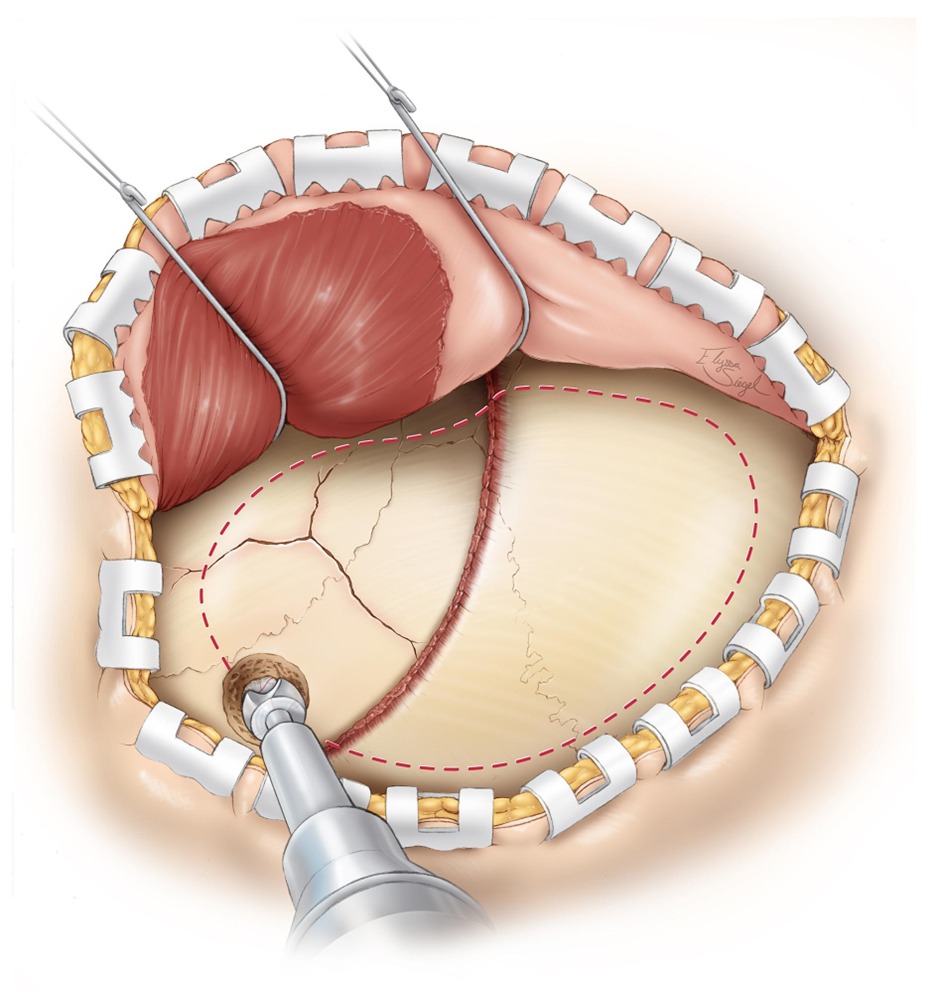
- Treatment of epidural hematoma is urgent craniotomy with evacuation of the blood
- It is a surgical emergency which will result in death if not removed promptly
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Prognosis
- If the initial head injury has resulted only in a transient loss of consciousness, the patient should make full recovery following the evacuation of the hematoma
- Early evacuation of the hematoma prevents permanent neurological disability
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
احصل على التجربة الكاملة
اشترك للوصول لفيديوهات الشرح التفصيلي والبطاقات التعليمية التفاعلية وأسئلة الممارسة مع تتبع التقدم.
فيديوهات الشرح
بطاقات تفاعلية
أسئلة ممارسة
اشترك الآن