سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Background
- Neck masses can either be inflammatory/infectious, congenital or neoplastic
- Lymphadenopathy is the most common neck mass
- Neck masses in adults are cancer until proven otherwise (fine needle aspiration must be performed)
| Neck masses | ||
| Inflammatory/infectious |
|
|
| Congenital | Midline |
|
| Lateral |
|
|
| Neoplastic | Malignant |
|
| Benign |
|
|
Version 2
Definition: Neck masses are abnormal swellings in the neck that can be inflammatory/infectious, congenital, or neoplastic in origin.
Epidemiology:
- Most common neck mass overall: Lymphadenopathy (reactive)
- Most common congenital neck mass: Thyroglossal duct cyst
- Age-specific patterns:
- Children: 90% benign (mostly inflammatory/congenital)
- Adults >40 years: 80% malignant until proven otherwise ★
- Rule of 80s: In adults, 80% of non-thyroid neck masses are neoplastic, 80% of neoplastic masses are malignant, 80% of malignancies are metastatic, and 80% of metastases are from primary sites above the clavicle
⚠️ High-Yield Clinical Pearl: Any neck mass in an adult (especially >40 years) requires fine needle aspiration (FNA) to rule out malignancy ★
| Classification of Neck Masses | ||
| Inflammatory/Infectious |
|
|
| Congenital | Midline |
|
| Lateral |
|
|
| Neoplastic | Malignant |
|
| Benign |
|
|
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
DIAGNOSTIC APPROACH -- Was not included in version 1
| High-Yield Diagnostic Algorithm | |
| Best Initial Test |
|
| Most Accurate Test |
|
| Additional Studies |
|
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Pediatric neck masses
| Pediatric neck masses | ||
|---|---|---|
| Diagnosis | Location | Distinguishing features |
| Thyroglossal duct cyst | Midline |
|
| Dermoid cyst | Midline |
|
| Branchial cleft cyst | Lateral |
|
| Reactive adenopathy | Lateral |
|
| Lymphadenitis | Lateral |
|
| Cystic hygroma | Posterior |
|
Version 2
| Pediatric Neck Masses - High-Yield Features | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnosis | Location | Classic Features ★ | Diagnostic Test |
| Thyroglossal duct cyst | Midline |
|
Ultrasound (shows cystic mass) |
| Dermoid cyst | Midline |
|
CT (shows fat density) |
| Branchial cleft cyst | Lateral |
|
Ultrasound or CT |
| Cystic hygroma | Posterior triangle |
|
Ultrasound (shows multiloculated cysts) |
| Reactive lymphadenopathy | Lateral (usually) |
|
Clinical observation |
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
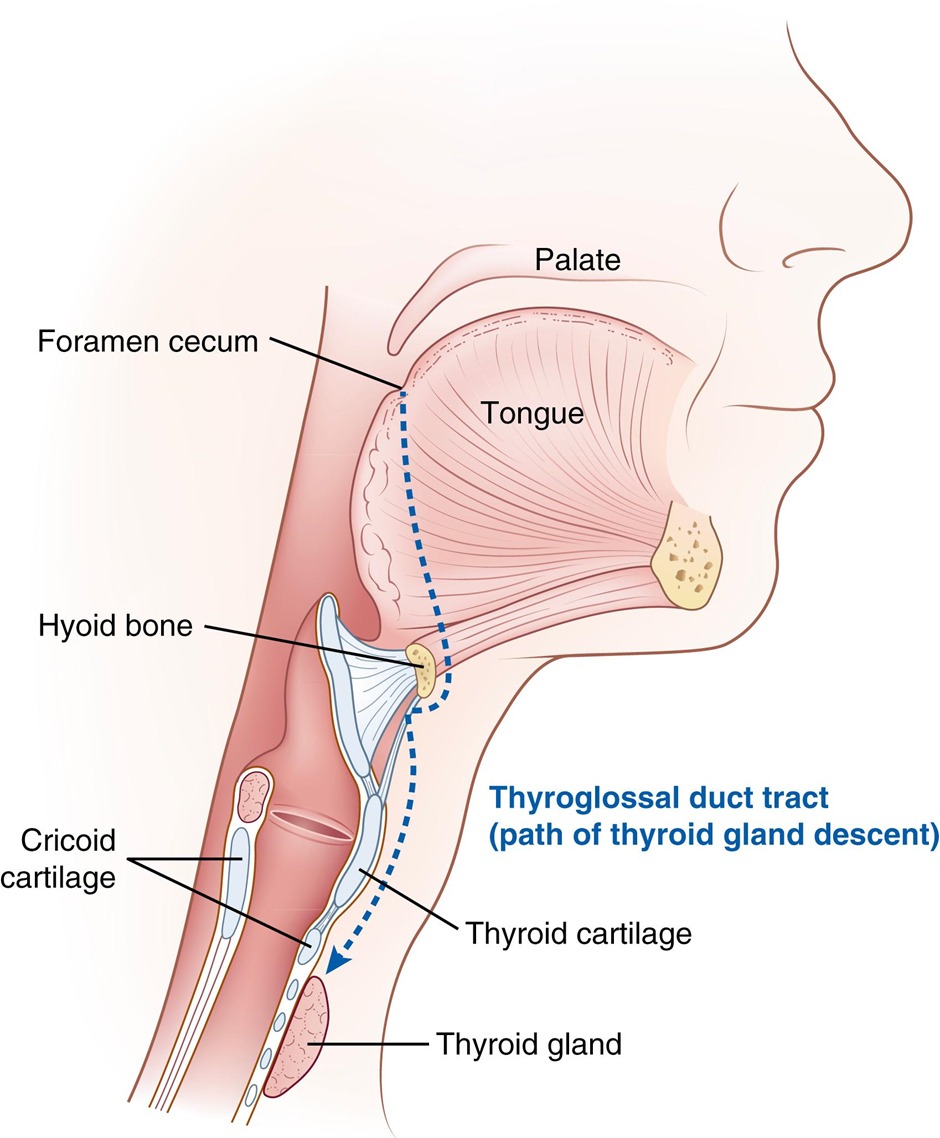
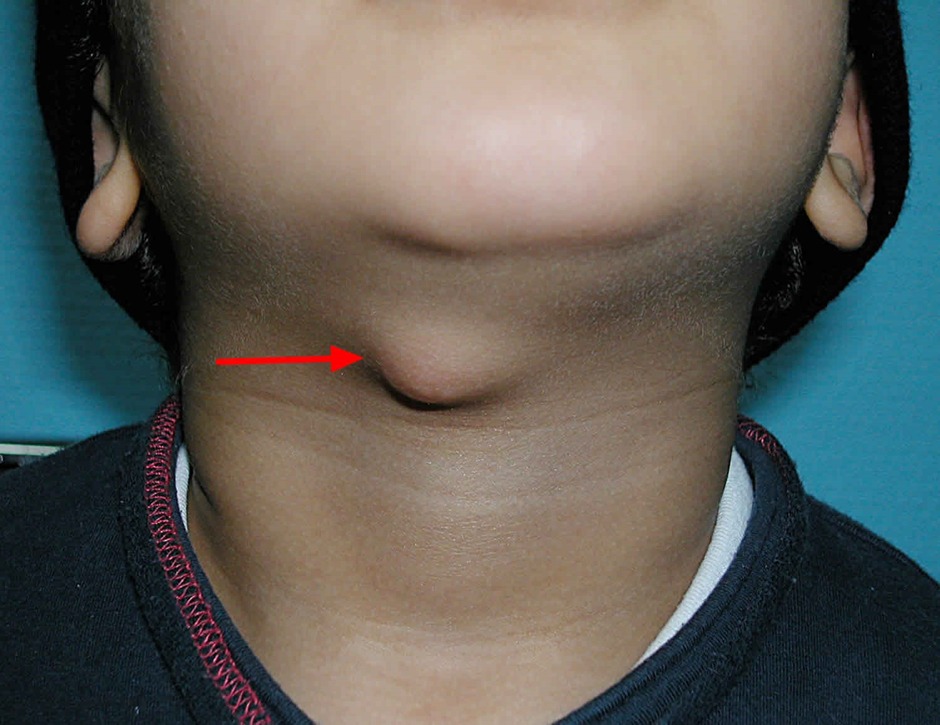
Thyroglossal duct cyst
| Thyroglossal duct cyst | |
| Embryology |
|
| Clinical presentation |
|
| Diagnosis |
|
| Management |
|
version 2
| Thyroglossal Duct Cyst | |
| Embryology |
|
| Epidemiology |
|
| Clinical Features |
|
| Diagnosis |
|
| Management |
|
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Branchial cleft cyst
| Branchial cleft cyst | |
| Embryology |
|
| Clinical presentation |
|
| Diagnosis |
|
| Management |
|
Version 2
| Branchial Cleft Cyst | |
| Embryology |
|
| Clinical Features |
|
| Type-Specific Features |
|
| Diagnosis |
|
| Management |
|
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Lymphadenopathy
| Lymphadenopathy | ||
|---|---|---|
| Reassuring | Worrisome | |
| Palpation |
|
|
| Location |
|
|
| Systemic symptoms |
|
|
| Further investigations |
|
|
Version 2
| Lymphadenopathy Assessment | ||
|---|---|---|
| Reassuring Features | Worrisome Features ★ | |
| Size | <1 cm (normal) <2 cm (reactive) |
>2 cm ★ |
| Consistency | Soft, mobile | Hard, fixed, matted ★ |
| Location | Localized Cervical chain |
Supraclavicular ★ Generalized |
| Duration | <2 weeks | >4 weeks ★ |
| Associated Symptoms | URI symptoms Tender nodes |
B symptoms ★ Weight loss Night sweats |
| Action Required |
|
|
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Cervical Lymphadenitis
| Cervical lymphadenitis in children | ||
|---|---|---|
| Category | Pathogen | Key clinical findings |
| Unilateral |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Content |
|
|
Version 2
| Cervical Lymphadenitis in Children - High-Yield Pathogens | ||
|---|---|---|
| Category | Pathogen | Key Clinical Features ★ |
| Unilateral | S. aureus/S. pyogenes (Most common) ★ |
|
| Anaerobes |
|
|
| Bartonella henselae (Cat scratch disease) |
|
|
| Mycobacterium avium (Atypical mycobacteria) |
|
|
| Francisella tularensis (Tularemia) |
|
|
| Bilateral | Viral (Most common bilateral) ★ |
|
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck
| Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck summary | |
| Pathogenesis |
|
| Clinical presentation |
|
| Diagnosis |
|
| Treatment |
|
Version 2
| Squamous Cell Carcinoma - High-Yield Facts | |
| Risk Factors |
|
| Clinical Presentation |
|
| Most Common Sites |
|
| Diagnosis |
|
| Treatment |
|
| Prognosis |
|
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
HIGH-YIELD EXAM FACTS BOX
★ MUST-KNOW FACTS FOR EXAMS ★
- Adult with neck mass = cancer until proven otherwise (especially if >40 years)
- Thyroglossal duct cyst: Moves with swallowing AND tongue protrusion
- Branchial cleft cyst: Lateral, anterior to SCM
- Supraclavicular lymphadenopathy: Always pathologic
- Right = lung, esophagus, mediastinum
- Left (Virchow's node) = GI malignancy below diaphragm
- Sistrunk procedure: Must remove central hyoid bone
- Most common neck infections:
- Acute bacterial: S. aureus/S. pyogenes
- Chronic: Mycobacteria or cat scratch disease
- HPV-associated SCC: Better prognosis than smoking-related
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
CLINICAL PEARLS
⚠️ HIGH-YIELD CLINICAL PEARLS
- Cystic hygroma: Only neck mass that transilluminates
- Dermoid cyst: Midline but does NOT move with swallowing (unlike thyroglossal)
- Cat scratch disease: Look for papule at inoculation site
- Atypical mycobacteria: Violaceous skin, no systemic symptoms
- Rule of 7s: Lymph node concerning if >1 cm for >1 month in patient >40 years
- Never do open biopsy of neck mass before imaging - risk of tumor seeding
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
MEMORY AIDS
MEMORY AIDS
THYROGLOSSAL duct cyst moves with:
- Tongue protrusion
- Swallowing
Branchial Cleft Cyst Location - "BEAST":
- Branchial
- Exterior (lateral)
- Anterior to
- SCM
- Triangle
Worrisome Lymph Nodes - "HELPS":
- Hard
- Enlarged (>2cm)
- Lasting (>4 weeks)
- Persistent
- Supraclavicular
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
احصل على التجربة الكاملة
اشترك للوصول لفيديوهات الشرح التفصيلي والبطاقات التعليمية التفاعلية وأسئلة الممارسة مع تتبع التقدم.
فيديوهات الشرح
بطاقات تفاعلية
أسئلة ممارسة
اشترك الآن