Introduction
- Minerals are essential nutrients for growth, development, immune function, enzyme activation, and overall health.
- Deficiencies or excesses in these minerals can lead to significant health problems, particularly in growing infants.
- In this lecture, we will discuss some of the most important minerals for infants.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Copper
- Significance
- Copper is essential for iron metabolism, the formation of red blood cells, the maintenance of healthy bones, and immune system function.
- It also plays a role in brain development and the synthesis of connective tissue.
- Daily requirements for an infant; 200-220 µg/day.
- Sources
- Breast milk, formula milk, Liver, seafood, nuts, seeds, whole grains, legumes, and dark leafy greens.
- Deficiency
- Copper deficiency in infants is rare but can lead to: Anemia, Neutropenia, bone abnormalities (osteoporosis or fractures), impaired immune function and delayed growth.
- Excess
- Copper toxicity is uncommon but can occur with excessive intake or in genetic disorders like Wilson’s disease.
- Symptoms include:Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, liver damage or failure, neurological problems (tremors, difficulty walking) and jaundice.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Fluorine (Fluoride)
- Significance
- Fluoride is important for the enhancement of tooth mineralization, reversal of tooth demineralization, and inhibition of acid-producing bacteria that cause caries
- Daily requirements for an infant after 6 months of age is 0.25 mg/day.
- Sources
- Fluoridated water, Toothpaste (not recommended under 2 years)
- Deficiency
- Fluoride deficiency can increase the risk of: dental caries (tooth decay), weaker tooth enamel.
- Excess
- Excess fluoride intake can lead to: Dental fluorosis : a cosmetically disfiguring condition resulting in the enamel having white flecks, opaque white appearance, or brown discoloration (>4-8 mg/day) during the teeth-developing years.
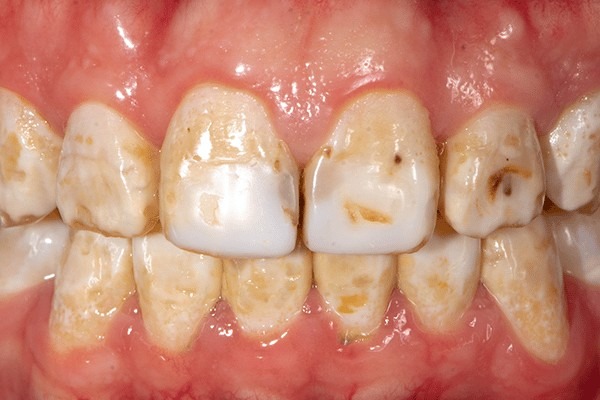
- Excess fluoride intake can lead to: Dental fluorosis : a cosmetically disfiguring condition resulting in the enamel having white flecks, opaque white appearance, or brown discoloration (>4-8 mg/day) during the teeth-developing years.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Selenium
- Significance
- Selenium is an antioxidant that protects cells against damage caused by free radicals.
- It is essential for thyroid function regulation, and immune response.
- Daily requirements for an infant; 15-20 µg/day.
- Sources
- Breast milk, infant formula, nuts, seafood (especially tuna, shrimp), eggs, whole grains.
- Deficiency: Selenium deficiency is uncommon but can lead to:
- Impaired immune system.
- Muscle weakness and pain.
- Keshan disease (a potentially fatal form of cardiomyopathy due to selenium deficiency)
- Excess
- Selenosis (High selenium level): Hair loss, brittle nails and skin lesions, gastrointestinal disturbances (nausea, vomiting), fatigue and irritability.
- In extreme cases, it can cause nerve damage.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Zinc
- Significance
- Zinc-containing enzymes are involved in nucleic acid and protein metabolism, so zinc deficiency affects rapidly growing cells.
- It also supports growth, taste, and smell, and plays a role in the development of the brain and body.
- Daily requirements for an infant; 2-3 mg/day.
- Sources
- Breast milk, formula milk, meat, poultry, seafood (especially oysters), dairy products, whole grains, legumes, and nuts.
- Deficiency
- Any condition that leads to zinc deficiency leads to the same clinical findings.
- Many disorders with malabsorption, such as cystic fibrosis and Crohn disease, will result in zinc deficiency.
- Zinc deficiency can lead to:
- Poor growth and development, weakened immune system, delayed wound healing, diarrhea and poor appetite, skin rashes (often around the mouth, face, and anus)
- Acrodermatitis Enteropathica
- Definition: a disorder of impaired zinc uptake by the enterocytes.
- Clinical Picture: poor growth, diarrhea, rash, hair loss, and hypogeusia (reduced taste).
- The rash is characterized by eczematous lesions that are vesiculobullous and occur particularly around the mouth and anus.
*DAD: triad of: dermatitis ( face,hands, and perianal area),alopecia, and diarrhea.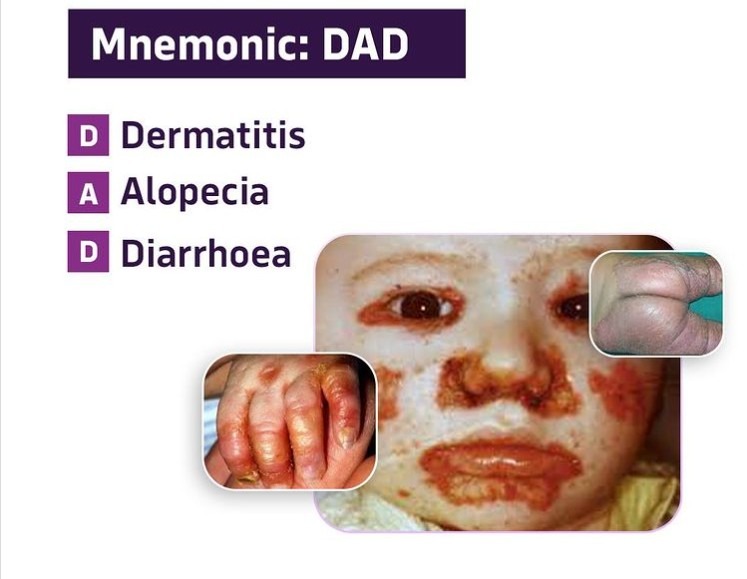
- Excess: Zinc toxicity can result in:
- Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, headaches and fatigue.
- Impaired immune function and copper absorption (leading to secondary copper deficiency)
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
احصل على التجربة الكاملة
اشترك للوصول لفيديوهات الشرح التفصيلي والبطاقات التعليمية التفاعلية وأسئلة الممارسة مع تتبع التقدم.
فيديوهات الشرح
بطاقات تفاعلية
أسئلة ممارسة
اشترك الآن