Summary
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Introduction
- Infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis (IHPS) is a congenital hypertrophy of pyloric smooth muscle (leads to pyloric narrowing and gastric outlet obstruction).
- This condition classically presents in an infant age 3-6 weeks after birth as projectile nonbilious vomiting, visible peristalsis, olive-like mass in the abdomen (more common in first born males).
- Multiple conditions are associated with pyloric stenosis (Down syndrome, eosinophilic gastroenteritis, hypergastrinemia).
- Definitive treatment is surgery (pyloromyotomy).
| Infantile Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis | |
|---|---|
| Risk Factors |
|
| Clinical Presentation |
|
| Associations |
|
| Laboratory Findings |
|
| Diagnostic Studies |
|
| Treatment |
|
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Epidemiology
- Caucasians and first born male infants are more commonly affected (male-to-female ratio is 4:1).
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Etiology
- Etiology is unknown.
- Primary risk factors are male gender and a positive family history of pyloric stenosis.
- Other risk factors include; younger maternal age, preterm birth, maternal smoking during pregnancy, formula feeding and postnatal exposure to macrolide antibiotics.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Presentation
- Nonbilious (nonbloody) milky projectile (forceful) vomiting (occurs shortly after feeding) that starts the second or third week of life.
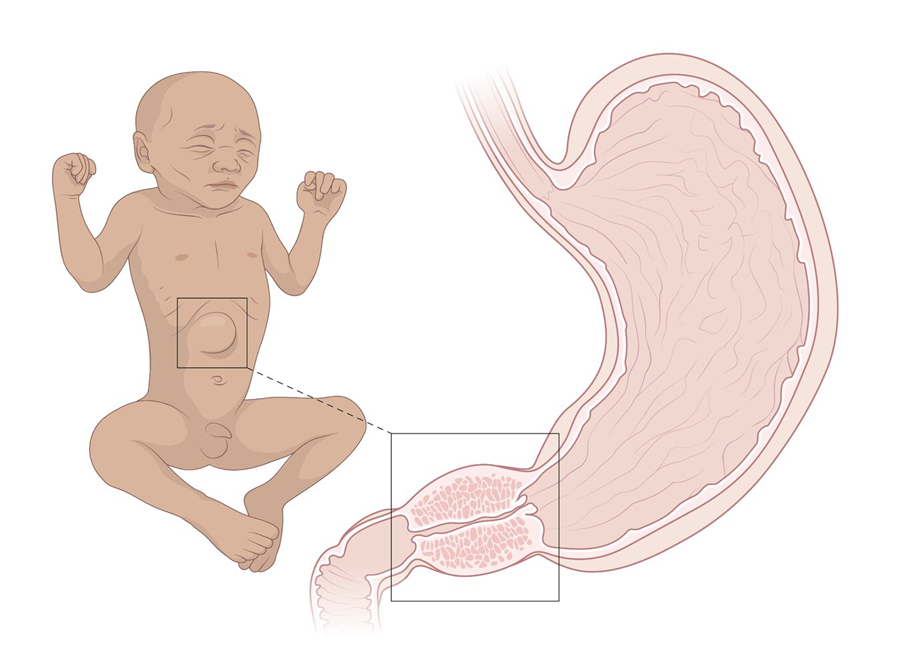
- Palpable olive-shaped mass in the epigastrium.
- Visible gastric peristalsis.
- In the early stage of disease, the infant remains hungry post-vomiting.
- In cases of delay in diagnosis, complications can include; dehydration, poor weight gain, malnutrition and metabolic alterations.
- Jaundice officers in 5% of infants (associated with low levels of the enzyme glucuronyl transferase).
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Physical Examination
- Palpable hypertrophic pyloric muscle just above and to the right of the umbilicus (referred to as the “olive”).
- Visible gastric peristalsis.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Imaging
- Thickening of pyloric muscle on abdominal ultrasound (imaging of choice).
- Muscle wall thickness 3 mm or greater and pyloric channel length 14 mm or greater are considered diagnostic.
- When abdominal ultrasound is not diagnostic, barium upper GI study can be used (may show double track sign or string sign).
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Labs
- Hypochloremic hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis.
- Hypochloremia is due to the loss of hydrochloric acid with the repeating vomiting of stomach acid.
- Hypokalemia is due the kidneys exchanging potassium for protons to attempt to compensate.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Differential Diagnosis
- Gastroenteritis
- Gastroesophageal reflux
- Over-feeding
- Sepsis
- Urinary tract infection
- Food allergy
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Treatment
- Stopping oral feeds.
- Insertion of nasogastric tube.
- Proper fluid resuscitation and correction of electrolyte derangements and base deficit (all derangements must be corrected prior to surgery).
- Ramstedt pyloromyotomy remains the standard procedure of choice.
- Infants can resume feeding after 6 hours.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Complications
- 1-2% of infants experience restenosis.
- Incomplete myotomy.
- Bleeding.
- Perforation.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
احصل على التجربة الكاملة
اشترك للوصول لفيديوهات الشرح التفصيلي والبطاقات التعليمية التفاعلية وأسئلة الممارسة مع تتبع التقدم.
فيديوهات الشرح
بطاقات تفاعلية
أسئلة ممارسة
اشترك الآن