summary
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Introduction
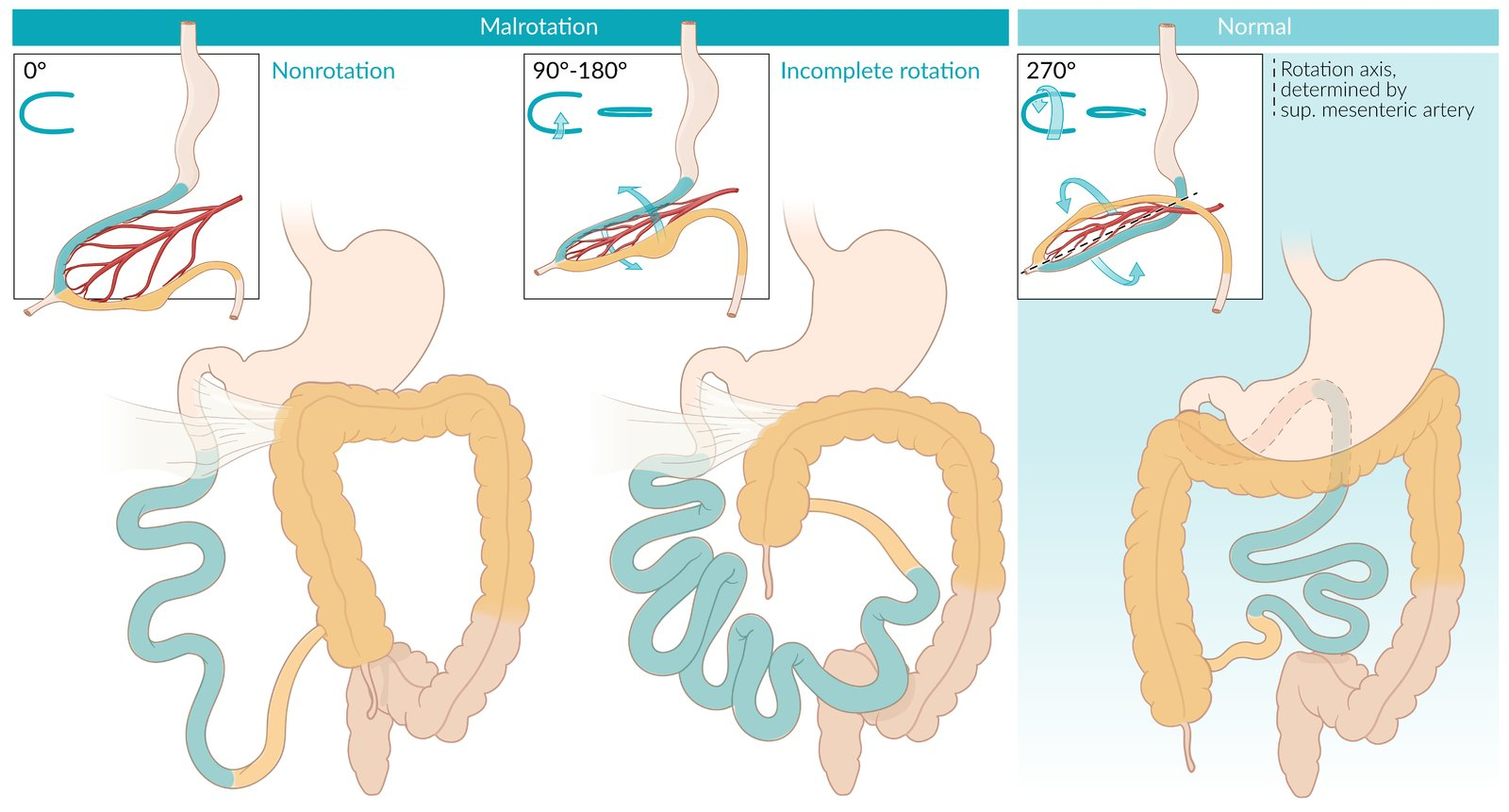
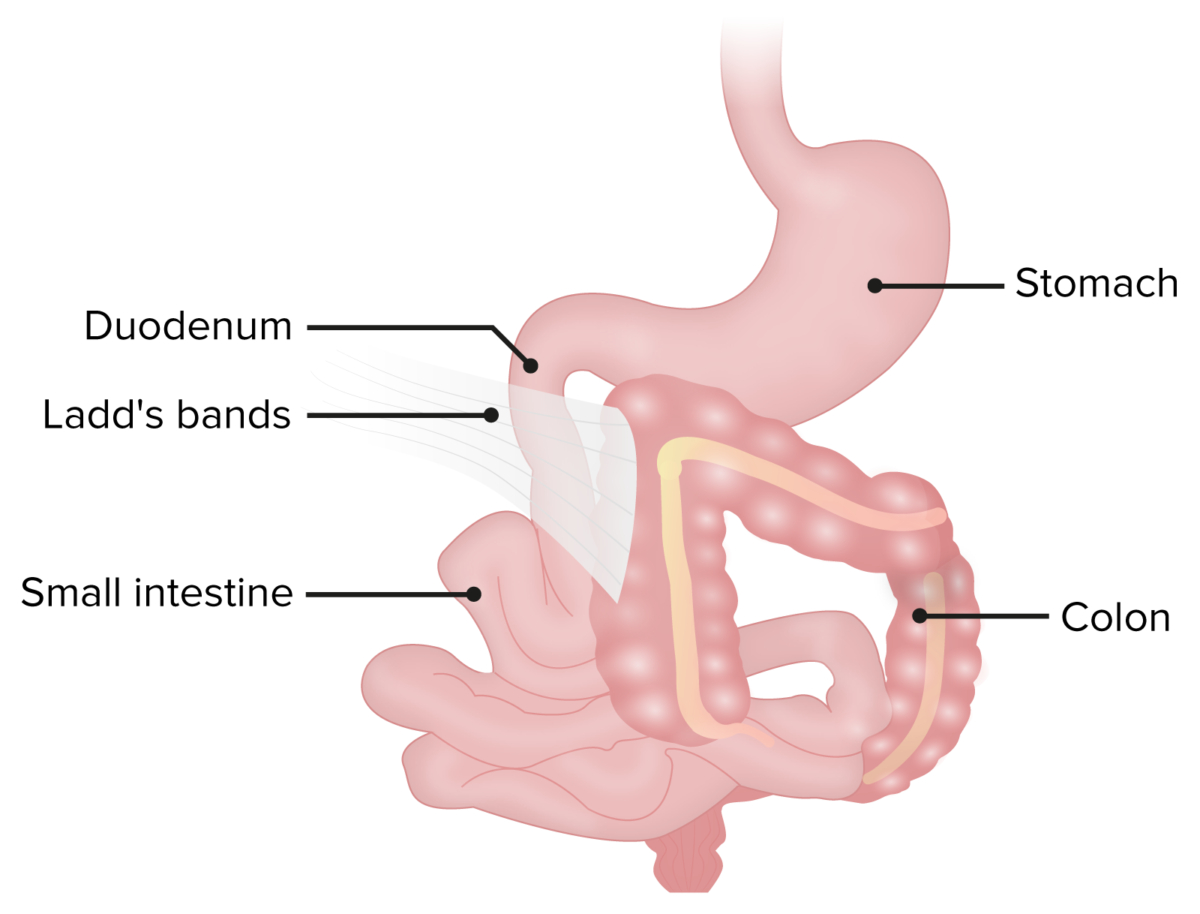
- Malrotation is an anomaly that occurs in fetal life that is characterized by improper positioning of bowel and formation of fibrous bands (Ladd bands).
- Malrotation increases the risk of midgut volvulus.
- Midgut volvulus is an anatomic abnormality of intestinal rotation and twisting of bowel around its mesentery and blood supply.
- This condition can lead to duodenal volvulus and/or duodenal obstruction.
- Midgut volvulus is due to pathological adhesions that fixate the bowel around itself (twisting around superior mesenteric arteries and compromising the blood flow to the intestines).
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Sigmoid Volvulus
| Sigmoid Volvulus | |
|---|---|
| Risk factors |
|
| Presentation |
|
| Imaging |
|
| Management |
|
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Cecal Volvulus
| Cecal Volvulus | |
|---|---|
| Definition |
|
| Risk factors |
|
| Clinical presentation |
|
| Diagnosis |
|
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Epidemiology
- Incidence of malrotation is 1 in 500 live births with male predominance.
- Midgut volvulus can occur at any location in the intestinal tract and is more common in newborns (80% of cases).
- Midgut volvulus is more common in infants and children while sigmoid volvulus is more common in older adults.
- Associated conditions include; gastroschisis, omphalocele, situs inversus, cardiovascular defects, hirschsprung’s disease.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Etiology
- During the 10th week of gestation, the bowel undergoes counterclockwise rotation around the superior mesenteric artery. Subsequently, the intestines are fixed to the abdominal wall.
- Malrotation occurs when there is failure in this process (when normal bowel rotation is interrupted).
- Due to the small bowel not being fixated, peritoneal bands (Ladd bands) are formed.
- Ladd bands can compress the duodenum leading to intestinal obstruction.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Presentation
- Bilious vomiting (neonates within the first week of life) and sudden onset of colicky abdominal pain.
- Older patients tend to present with nonbilious emesis, change in bowel habits and abdominal pain.
- Anorexia, distention, and blood-tinged stool are common.
- Initially, the physical examination can be normal. However, delay in diagnosis can present as peritonitis.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
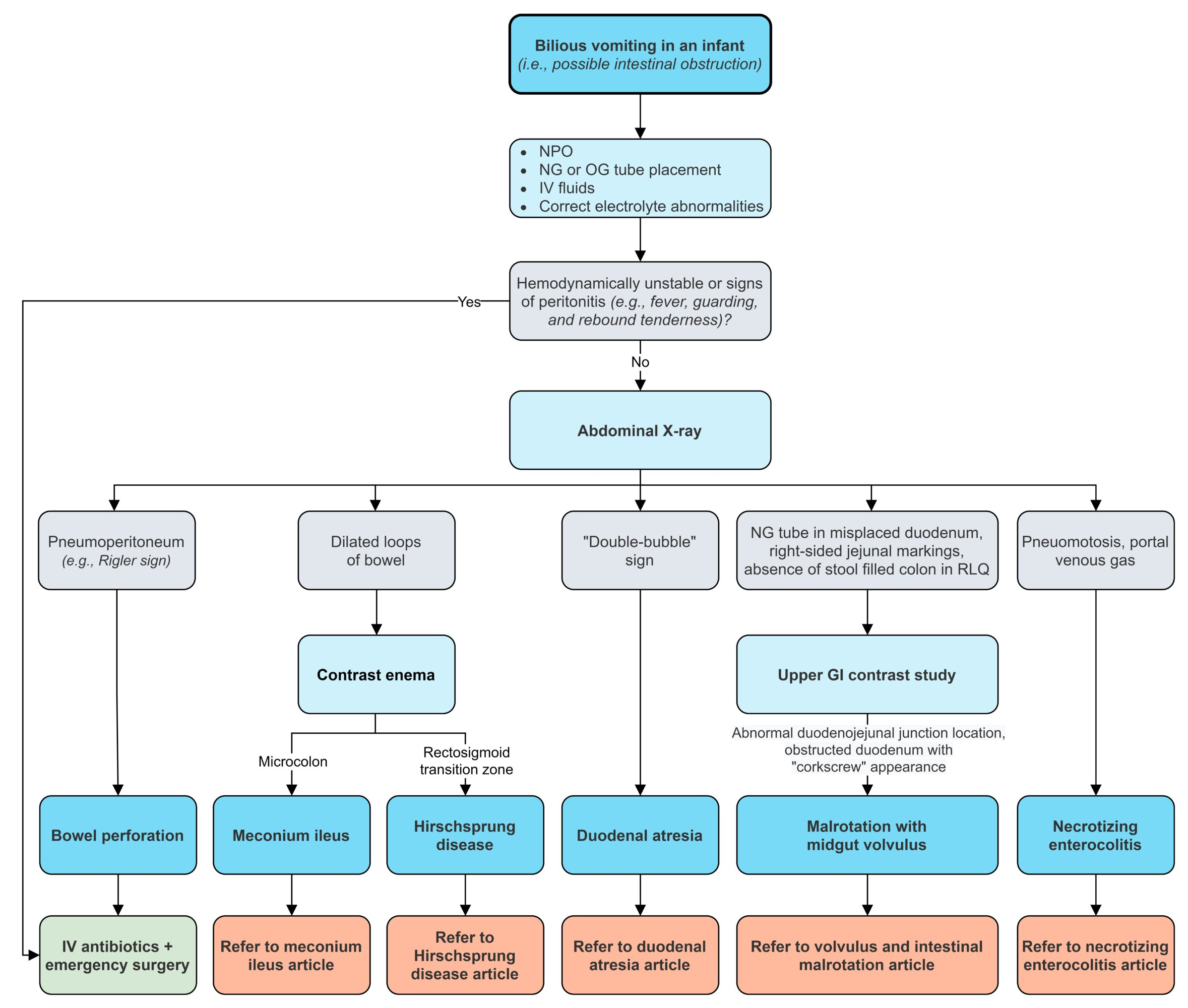
Diagnosis
- Abdominal radiography may demonstrate multiple air-fluid levels and/or dilated loops of bowel with loss of haustra.
- Upper GI series with barium enema may demonstrate bird beak sign at site of rotation.
- Failure of duodenum to cross midline suggests malrotation
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Differential diagnosis
- Intussusception.
- Intestinal atresia.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
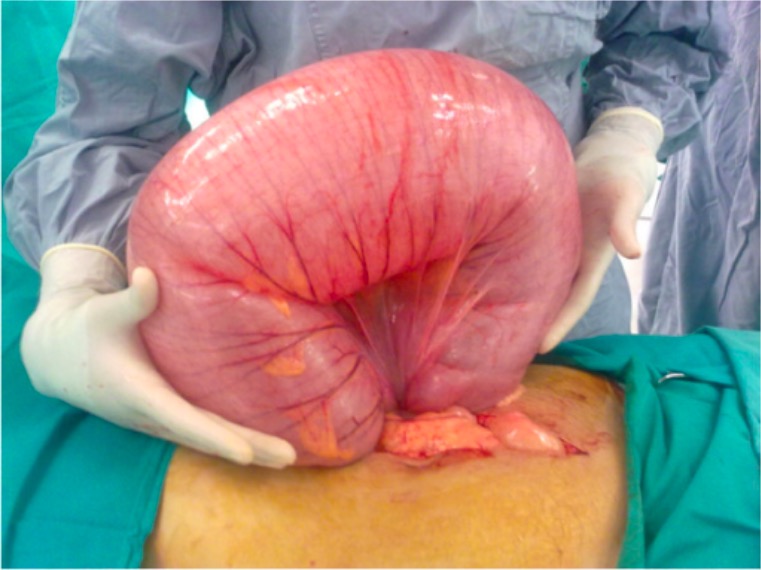
Treatment
- Fluid resuscitation, nasogastric suctioning and broad spectrum antibiotics should be administered.
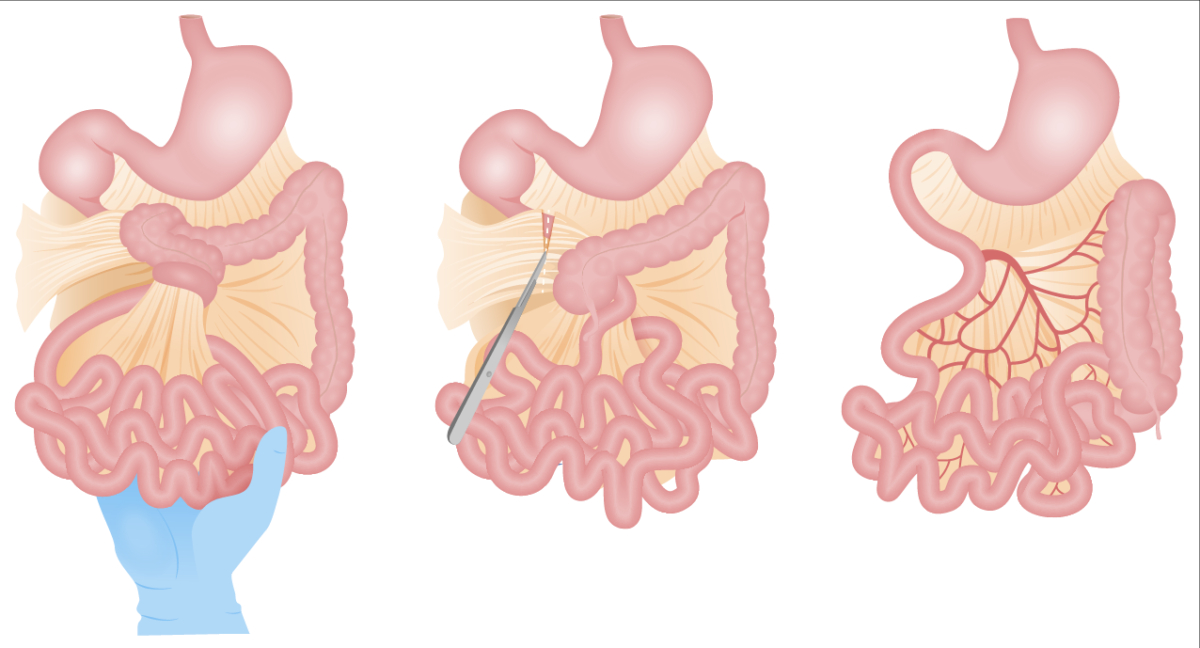
- Volvulus is a surgical emergency (immediate exploration, untwisting of the bowel, resection of any nonviable segments and fixation of the bowel to prevent recurrence).
- Malrotation without volvulus (elective Ladd procedure).
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Complications
- Bowel necrosis and perforation.
- Sepsis.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
احصل على التجربة الكاملة
اشترك للوصول لفيديوهات الشرح التفصيلي والبطاقات التعليمية التفاعلية وأسئلة الممارسة مع تتبع التقدم.
فيديوهات الشرح
بطاقات تفاعلية
أسئلة ممارسة
اشترك الآن