Summary
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Introduction
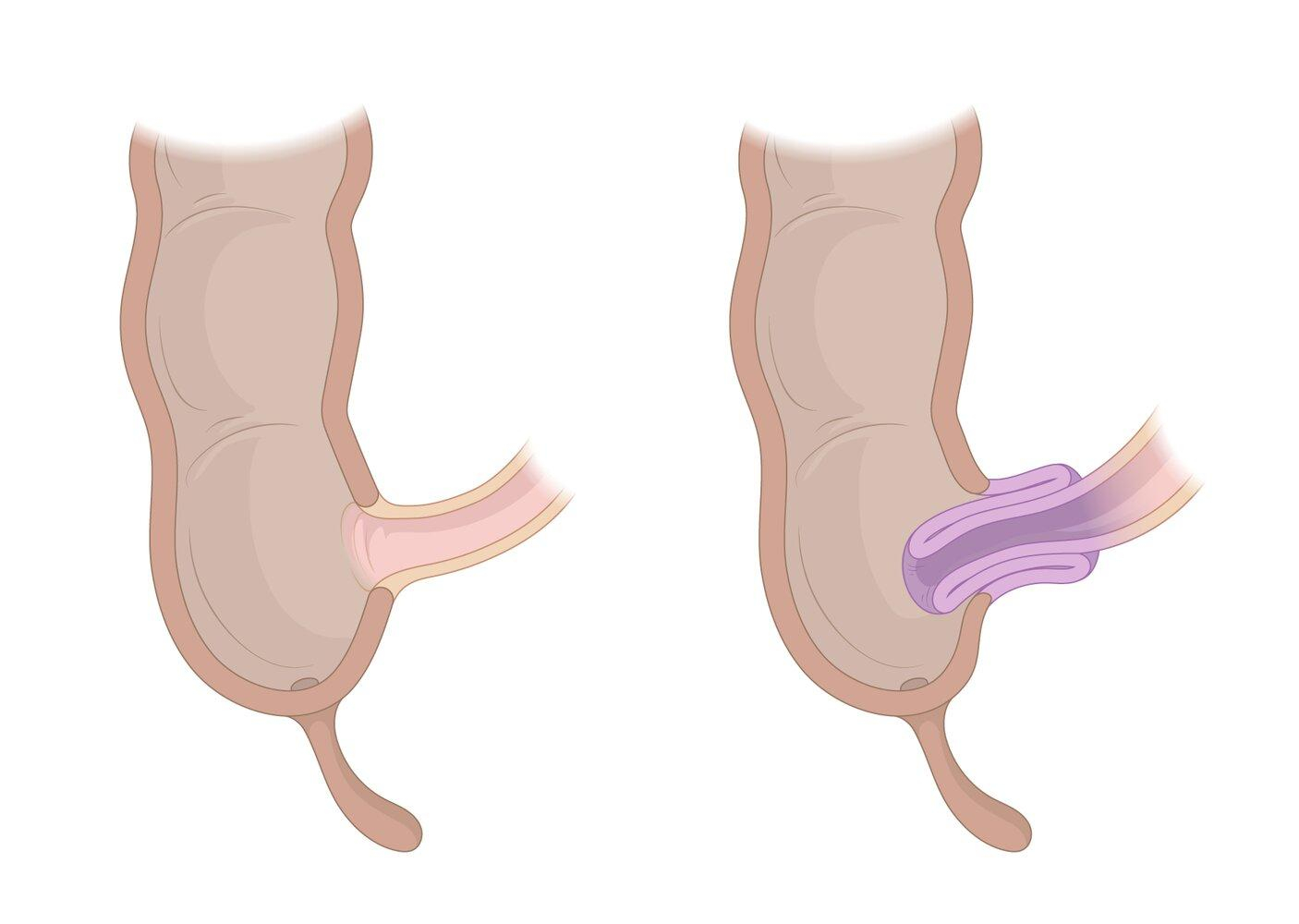
- Intussusception is invaginating or telescoping of a proximal bowel segment into a distal segment (most commonly occurs at the ileocecal junction).
- This condition is typically seen in infants (rare in adults).
- Etiology is usually idiopathic in children (can be associated with recent viral infections or rotavirus vaccine; peyer’s patches hypertrophy may act as a lead point).
- This condition causes small bowel obstruction, vascular compromise, intermittent abdominal pain, vomiting, and bloody “currant jelly” stools.
- Physical exams may show sausage shaped mass in the right abdomen (patients may draw their legs to chest to ease pain).
- Treatment involves enema and/or surgical removal of lead point.
| Intussusception | |
|---|---|
| Feature | Details |
| Risk factors |
|
| Clinical presentation |
|
| Diagnosis |
|
| Treatment |
|
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Epidemiology
- Intussusception is the most common cause of bowel obstruction after the neonatal period in infants younger than 2 years.
- Incidence is 1.5-4 in 1000 live births (peak incidence occurs at 5-9 months of age).
- There is a slight male predominance.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Etiology
- Etiology is generally unknown, but a lead point may act to draw the proximal intestine inward.
- Ileocolic intussusception is the most common site (This condition can occur at multiple sites within the intestine).
- Intussusception causes bowel wall edema, and hemorrhage.
- This may be complicated with bowel ischemia, and infarction.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Clinical Presentation
- Sudden onset of cramps/colicky abdominal pain (pain occurs in intervals followed by periods of calm).
- Vomiting.
- Stools may be normal or have currant jelly appearance, because of intestinal ischemia and mucosal sloughing.
- Sausage-shaped mass may be palpated in the abdominal right upper quadrant.
- May have abdominal distention.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
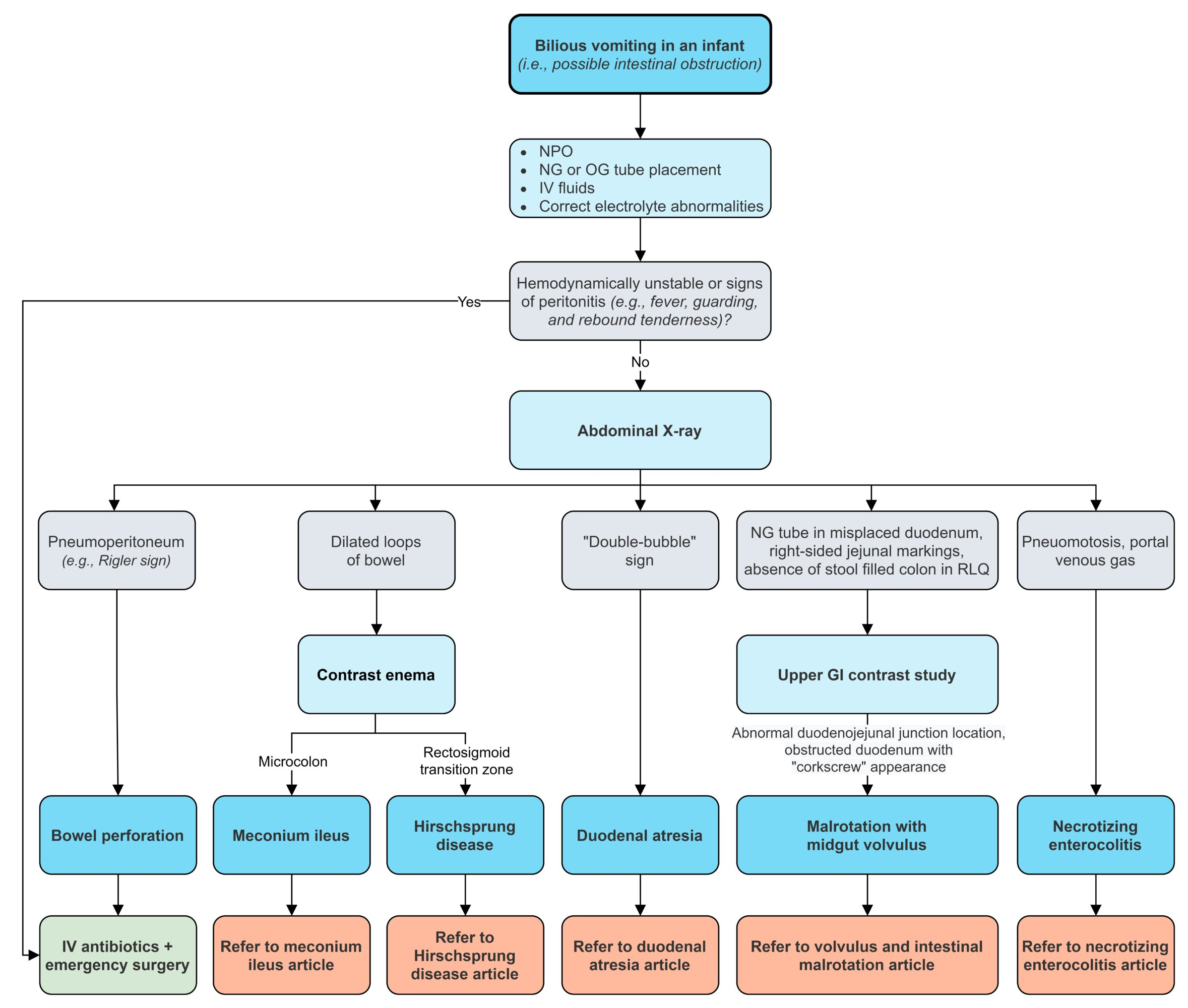
Diagnosis
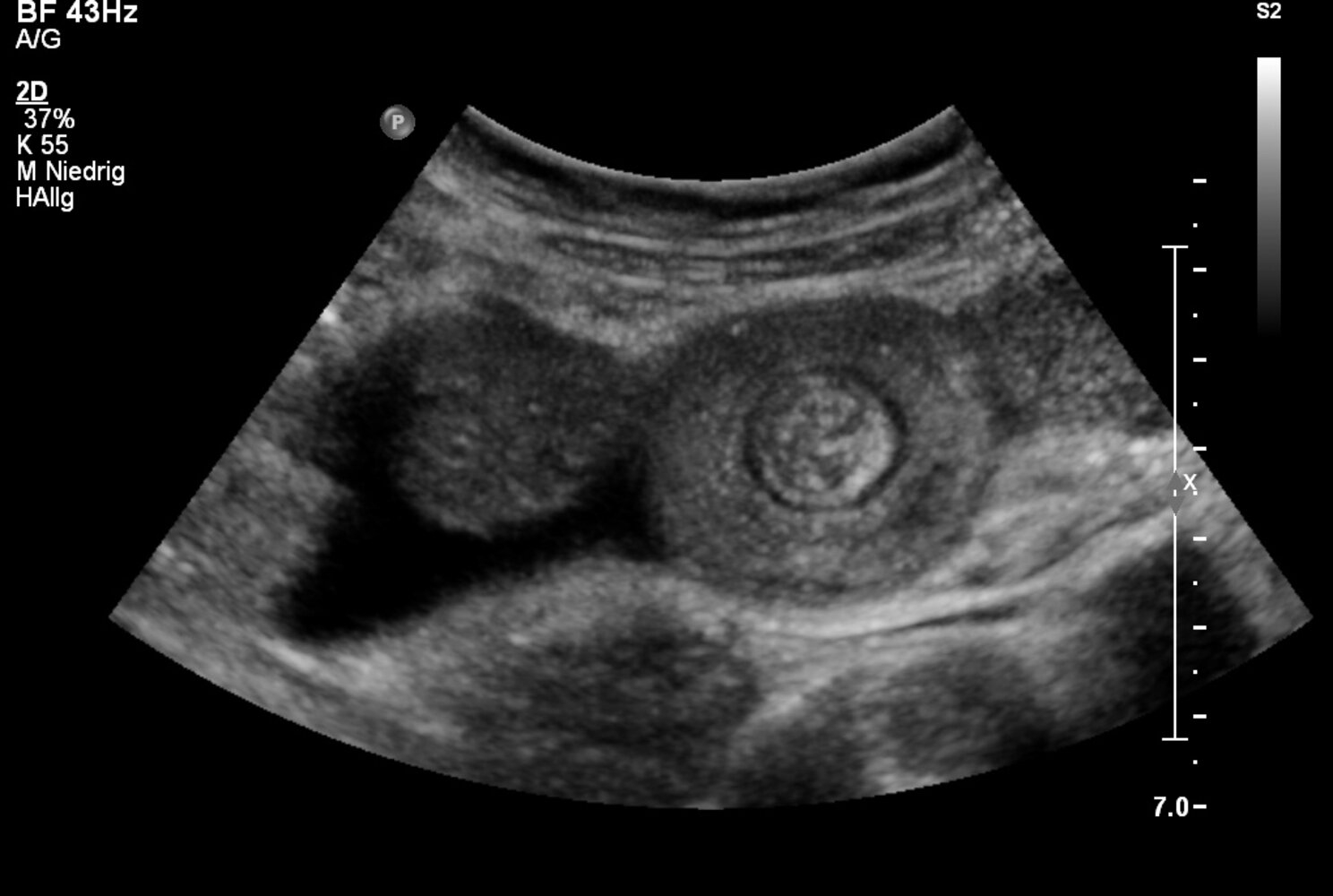
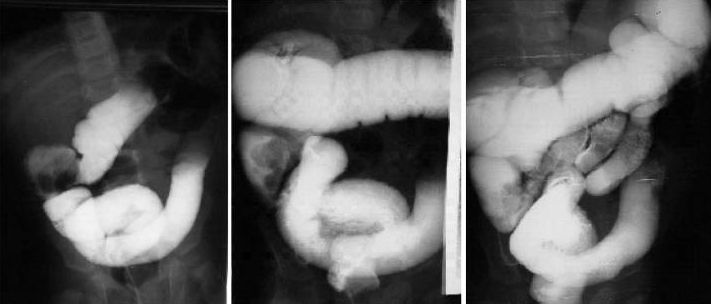
- Ultrasound may show small bowel obstruction (donut sign).
- Abdominal radiography may show small bowel obstruction (air fluid levels).
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Differential Diagnosis
- Intestinal atresia.
- Midgut volvulus.
- Gastroenteritis.
- Appendicitis.
- Meckel’s diverticulum.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
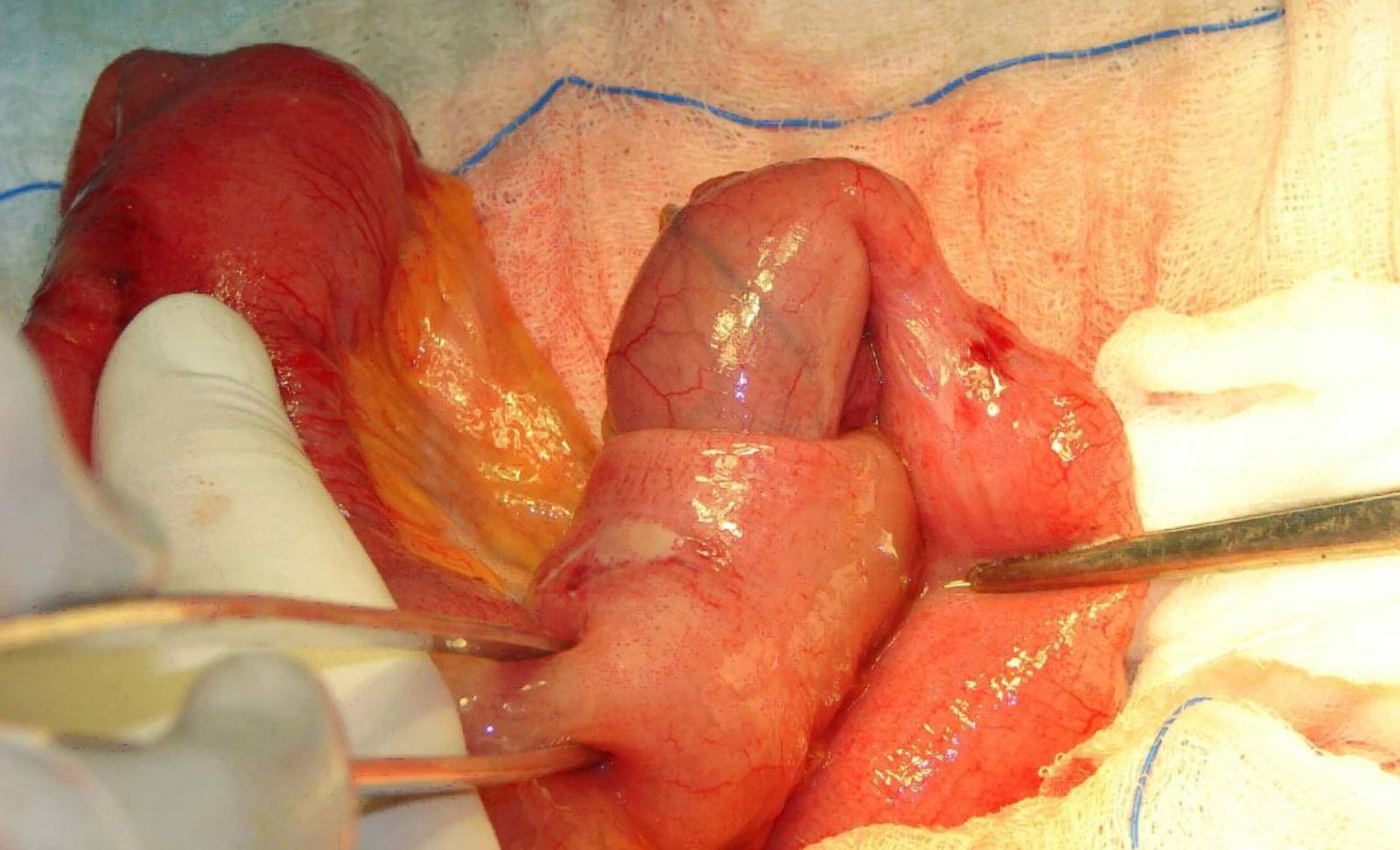
Treatment
- Air or contrast enemas (under ultrasound guidance) can successfully reduce the intussusception in 80-90%.
- If the contrast enema fails to reduce the intussusception, or if the child has signs of peritonitis or pneumoperitoneum, operative reduction is indicated.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Complications
- The risk of recurrence is 5% after contrast reduction and 1% after surgical repair.
- Bowel necrosis.
- Bowel perforation.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
احصل على التجربة الكاملة
اشترك للوصول لفيديوهات الشرح التفصيلي والبطاقات التعليمية التفاعلية وأسئلة الممارسة مع تتبع التقدم.
فيديوهات الشرح
بطاقات تفاعلية
أسئلة ممارسة
اشترك الآن