Definition
- Definition: Caesarean Section is a surgical procedure for delivering a baby through incisions in the mother's abdomen and uterus.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Advantages and Disadvantages
- Advantages:
- Safest birth method for certain maternal or fetal health complications.
- Rare occurrence of fetal birth trauma.
- Disadvantages:
- Potential for postoperative complications.
- Extended recovery period.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Indications
Maternal indications
- Primary cesarean delivery
- Placenta praevia totalis
- Refractory HELLP syndrome (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count), severe preeclampsia
- Severe uterine abnormalities (e.g., myoma) of the mother
- Maternal skeletal deformities
- Relative:
- Severe maternal disease (e.g., cardiopulmonary disorders, uncontrolled diabetes mellitus)
- Maternal HIV infection
- Severe stress reactions
- Elective cesarean delivery
- Possible indications :
- Fetal head is disproportionately large compared to the maternal pelvis.
- Breech presentation in a nullipara or multiple pregnancy
- Suspected absolute fetal macrosomia
- Secondary cesarean delivery (after PROM and/or onset of phase 1)
- Prolonged labor in:
- Premature birth
- Intraamniotic infection
- Abnormal fetal position (e.g., breech presentation, longitudinal position)
- Maternal exhaustion; ineffective contractions
- Prolonged labor in:
- Emergency cesarean delivery
- Immediate threat to life of mother
- Severe vaginal bleeding of unknown etiology (suspected placental separation)
- Suspected uterine rupture
Fetal indications
- Primary cesarean delivery
- Fetal growth retardation with circulatory depression
- Premature birth, if further risk factors are present, e.g., infection
- Fetal malformations that hinder a natural birth (e.g., severe hydrocephalus)
- Multiple pregnancy with a significant difference in fetal weight
- Emergency cesarean delivery
- Immediate threat to life of fetus
- Pathological CTG (particularly persistent, severe fetal bradycardia)
- Fetal acidosis
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Contraindications
- There are no absolute contraindications to cesarean birth.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Timing
- Planned primary cesarean birth at term should be performed in the 39thweek of gestation rather than in the 37th or 38th week.
- Medically/obstetrically indicated cesarean births are performed when clinically indicated.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Procedure/Application
- Preoperative Antibiotic Prophylaxis: A single intravenous dose of a narrow-spectrum antibiotic, such as cefazolin, is recommended.
- Procedure Steps:
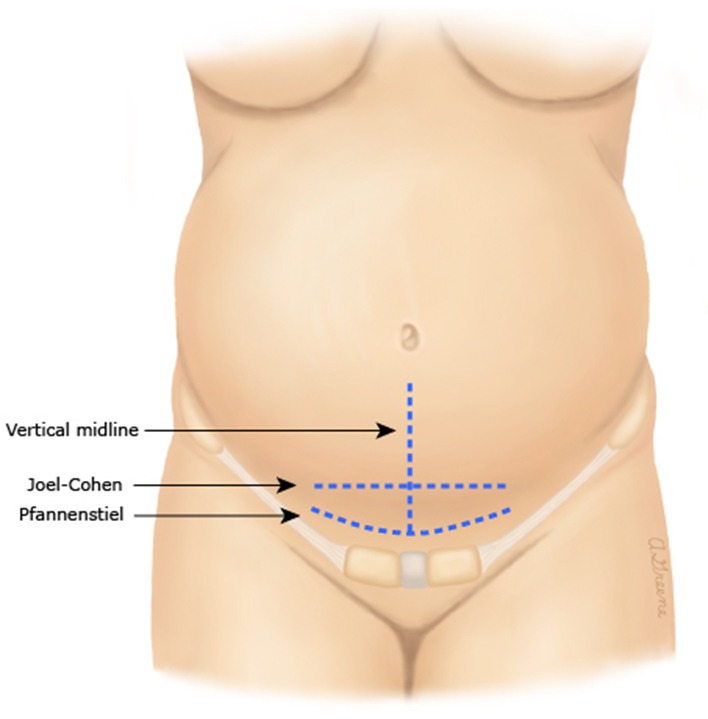
- Skin incision
Type of Incision Description Advantages Disadvantages Pfannenstiel - Slightly curved, 2 to 3 cm above the symphysis pubis
- Better cosmetic outcomes , Lower risk of hernia formation , Potentially less postoperative pain
- May not provide adequate exposure for all situations
Joel-Cohen - Straight, 3 cm below the anterior superior iliac spine line
- Lower rates of fever , Less postoperative pain and analgesia use , Less blood loss , Shorter operating time and hospital stay, Better cosmetic than vertical
- Requires more skill for adequate exposure
Vertical Midline - Vertical incision from the umbilicus to the pubic symphysis
- Can be extended for better access , Causes less bleeding and superficial nerve injury, Faster abdominal entry
- Higher risk of postoperative complications such as hernia , Less favorable cosmetically
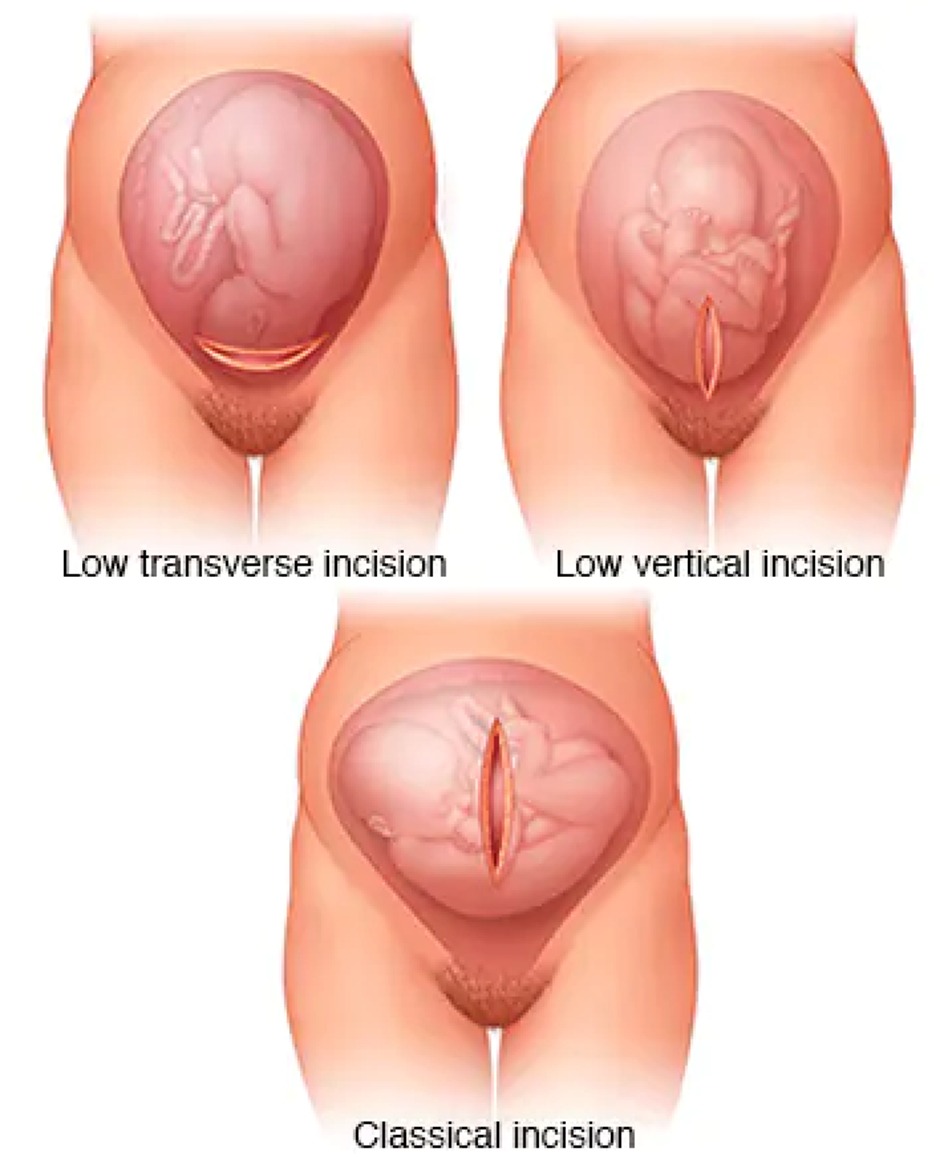
- Hysterotomy (uterine incision)
Type of Incision Location Advantages Disadvantages Indications Transverse Lower uterine segment - Less blood loss
- Less need for bladder dissection
- Easier reapproximation
- Lower risk of rupture in subsequent pregnancies
- Preferred for future pregnancy and trial of labor
- Limited ability for lateral extension without risking major blood vessel laceration
- May require "J" or inverted "T" extension for a larger incision
- Most cesarean births
- Patients planning another pregnancy
Low Vertical Lower uterine segment - Appears as strong as the low transverse incision
- Can be used when a larger incision is needed without the risk of lateral vessel laceration
- Risk of extension into bladder, cervix, or vagina
- Difficult to ensure it remains confined to lower segment
- Poorly developed lower uterine segment with anticipated normal intrauterine manipulation
- Lower uterine segment pathology precluding a transverse incision
Classical Upper uterine segment/fundus - Allows delivery in situations with pathology in the lower uterine segment or when extensive intrauterine manipulation is expected
- Useful for delivery of very large fetuses or in postmortem delivery
- Higher frequency of uterine dehiscence/rupture in subsequent pregnancies (4-9%)
- Associated with more maternal morbidity
- Extremely preterm breech presentation, back down transverse lie
- Large leiomyoma, anterior placenta previa or accreta
- Densely adherent bladder
- Delivery of a very large fetus
- Fetal extraction, cord clamping, and manual placental removal
- Wound closure
- Skin incision
- Procedure Steps:
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Postpartum care
- Prophylaxis Against Hemorrhage: Oxytocin is routinely administered to prevent hemorrhage.
- Thromboembolism prophylaxis: Evaluation of thrombosis risk is essential to determine the type, dose, and duration of prophylaxis needed.
- Analgesia: A multimodal, opioid-sparing approach is used, incorporating regular acetaminophen and NSAIDs.
- Bladder Catheter: If used, the catheter is removed as soon as possible postpartum
- Activity and Diet: Early Ambulation, Initiate oral intake within six hours post-delivery
- Wound Care: Dressings removed 6 to 24 hours post-application; showering allowed 48 hours after surgery completion.
- Breastfeeding and Skin-to-Skin Contact: Initiated ideally in the delivery room
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Complications
- Fever: Common early post-cesarean causes include endometritis, respiratory tract infections, and pyelonephritis. Uncommon causes for persistent or late-onset fever may include septic pelvic thrombophlebitis, pelvic abscess, and drug fever.
- Endometritis
- Wound Complications
- Hemorrhage
- Surgical Injury
- Venous Thromboembolism (VTE)
- Anesthetic Complications
- Ileus and Colonic Pseudo-Obstruction
- Septic Pelvic Thrombophlebitis and Ovarian Vein Thrombophlebitis
- Fetal and Neonatal Risks: Include iatrogenic prematurity, birth trauma, transient tachypnea of the newborn (TTN), and respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), especially after scheduled cesarean births.
Long-term Risks Associated with Cesarean Birth
- Abnormal Placentation
- Uterine Rupture
- Scar Complications
- Adhesions and Bowel Obstruction
- Subfertility
- Unexplained Stillbirth
- Preterm Birth
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
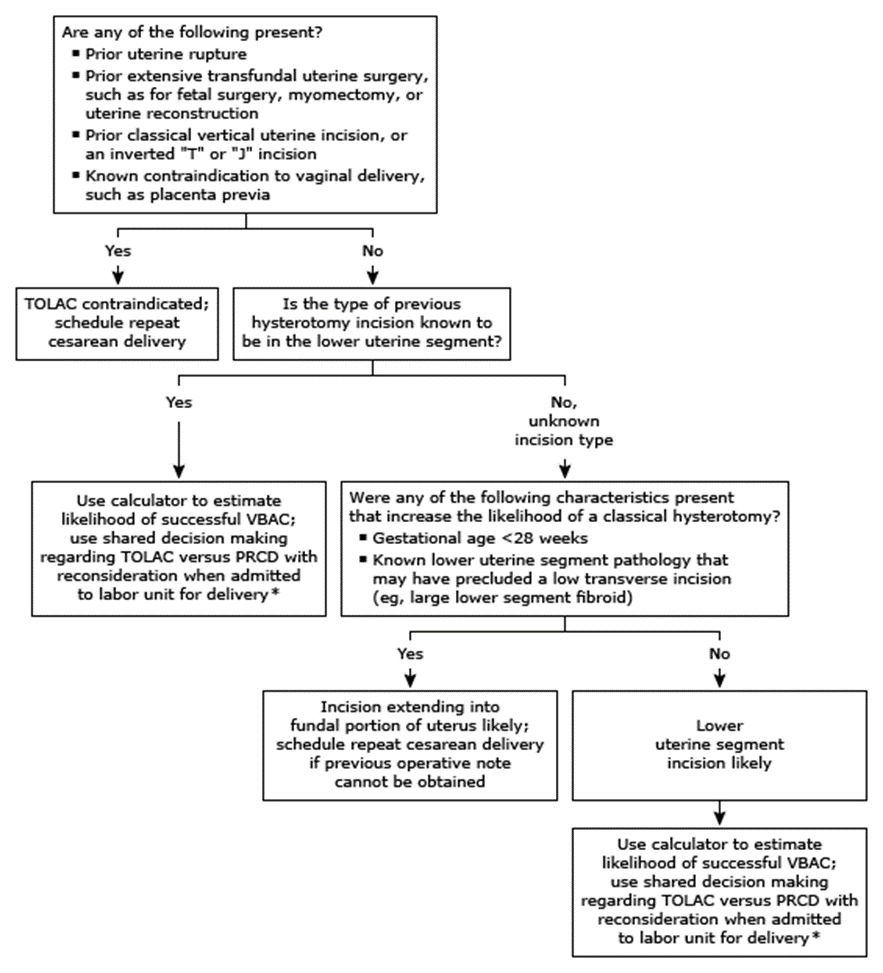
Subsequent Deliveries
- Options: Trial of labor after cesarean (TOLAC) or planned repeat cesarean birth (PRCB).
- Decision-Making: Should be patient-centered, considering the resources for cesarean birth, potential complications, patient preferences, past birthing experiences, and the probability of successful VBAC.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
احصل على التجربة الكاملة
اشترك للوصول لفيديوهات الشرح التفصيلي والبطاقات التعليمية التفاعلية وأسئلة الممارسة مع تتبع التقدم.
فيديوهات الشرح
بطاقات تفاعلية
أسئلة ممارسة
اشترك الآن