Summary
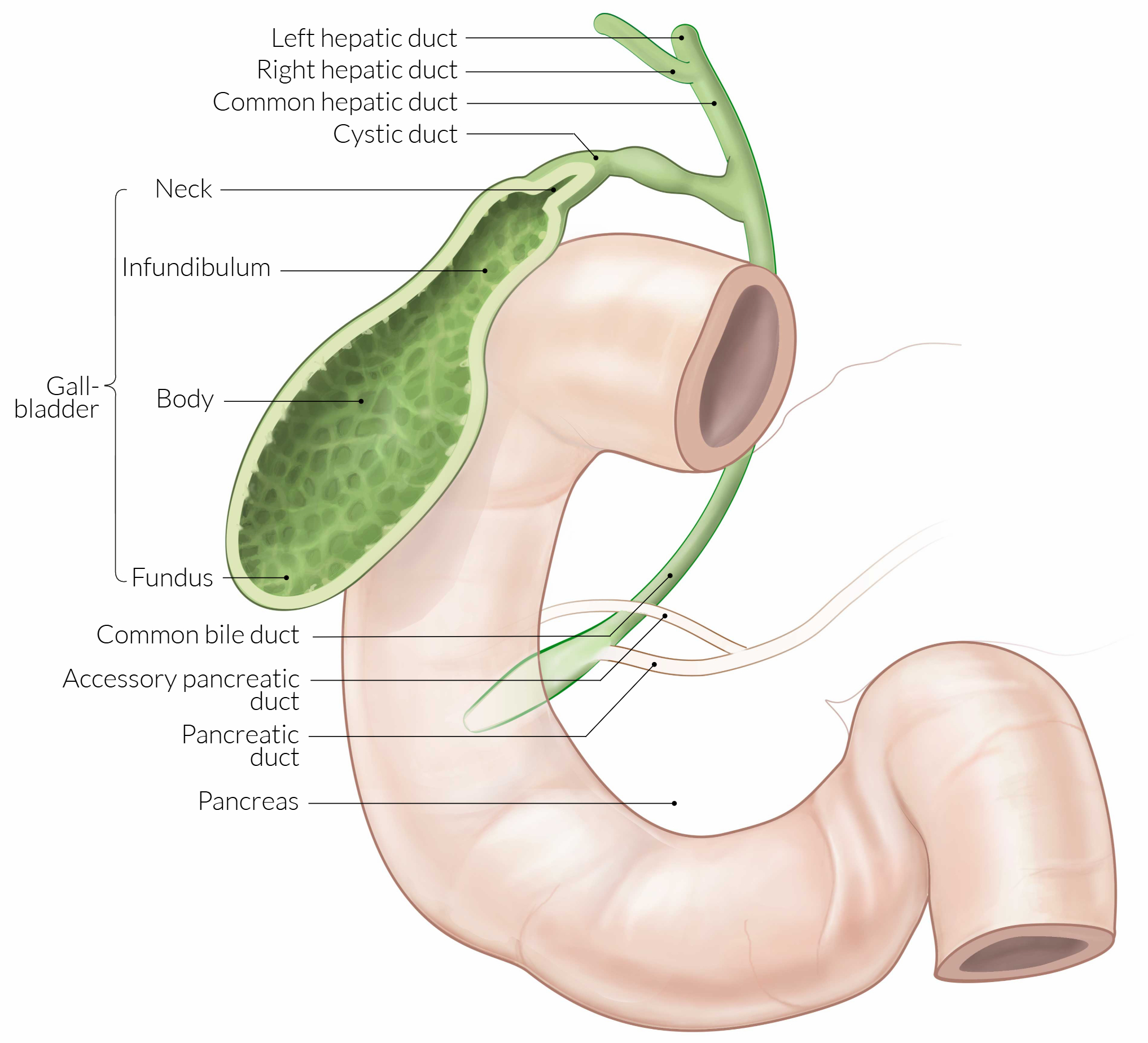
The gallbladder is a pear-shaped, hollow organ located on the inferior surface of the liver that serves as a reservoir for bile storage and concentration. Anatomically positioned at the intersection of the right 9th costal cartilage and lateral border of the rectus abdominis muscle, it has a normal capacity of approximately 50 mL but can accommodate up to 300 mL when the cystic duct is obstructed. The organ consists of a fundus, body, neck, and sometimes a Hartmann's pouch—a common site for gallstone impaction.
The gallbladder receives its blood supply primarily from the cystic artery, a branch of the right hepatic artery that courses through Calot's triangle. Its unique histological structure lacks a muscularis mucosa and submucosa, distinguishing it from other gastrointestinal organs. The primary functions include bile storage, concentration (5-10 fold), mucus secretion, and slight acidification of bile. Understanding gallbladder anatomy is crucial for recognizing clinical conditions such as cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, and potential surgical complications.
Anatomy & Location
- Position: Intraperitoneal organ located on the visceral surface of the liver
- Lies in the gallbladder fossa between right and left hepatic lobes (segments IVb and V)
- Attached to liver by peritoneum except at the gallbladder bed
- Surface landmark: Found at the intersection of:
- Right 9th costal cartilage
- Lateral border of rectus abdominis muscle
- This point becomes tender in acute cholecystitis (Murphy's sign) علامة مورفي
- Relations:
- Superior: Liver (segments IVb and V)
- Inferior: Transverse colon, duodenum (first and second parts)
- Posterior: Gastroduodenal artery
Gross Anatomy
- Shape & Size:
- Pear-shaped sac شكل الكمثرى
- Length: 7-10 cm
- Width: 3 cm at widest point
- Capacity:
- Normal: ~30-50 mL
- Can distend up to 300 mL if cystic duct obstructed
- Parts of gallbladder:
- Fundus:
- Rounded, blind end
- Projects beyond inferior liver margin
- Related to anterior abdominal wall at 9th costal cartilage
- Body:
- Main storage area
- In contact with visceral surface of liver
- Infundibulum:
- Funnel-shaped area between body and neck
- Neck:
- S-shaped, narrows to become cystic duct
- Contains spiral valves of Heister
- Hartmann's pouch جيب هارتمان:
- Small outpouching at junction of neck and infundibulum
- Most common site for gallstone impaction الموقع الأكثر شيوعاً لانحشار الحصوات
- Fundus:
Microscopic Anatomy (Histology)
- Wall layers (from lumen outward):
- Mucosa:
- Simple columnar epithelium with microvilli
- Numerous folds (rugae) when gallbladder is empty
- Contains mucus-secreting goblet cells
- Lamina propria:
- Loose connective tissue
- No muscularis mucosa (unlike GI tract)
- Muscularis propria:
- Smooth muscle fibers in irregular arrangement
- Responsible for gallbladder contraction
- Perimuscular layer:
- Connective tissue with vessels, nerves, lymphatics
- Serosa/Adventitia:
- Serosa: covers free surface (peritoneum)
- Adventitia: where attached to liver bed
- Mucosa:
- Special features:
- Spiral valves of Heister:
- Located in cystic duct and neck
- Maintain patency and regulate bile flow
- Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses:
- Deep invaginations of mucosa into muscle layer
- Can be sites of inflammation in chronic cholecystitis
- Spiral valves of Heister:
Blood Supply & Lymphatics
- Arterial supply:
- Cystic artery:
- Usually arises from right hepatic artery
- Divides into superficial and deep branches
- Courses through Calot's triangle مثلث كالو
- Calot's triangle boundaries:
- Medial: Common hepatic duct
- Inferior: Cystic artery
- Superior: Inferior surface of liver
- Critical anatomical landmark during cholecystectomy
- Cystic artery:
- Venous drainage:
- Small veins drain directly into liver bed (portal system)
- Cystic vein (when present) → portal vein
- Lymphatic drainage:
- Cystic lymph node (Lund's node or node of Mascagni):
- Located at neck of gallbladder
- First node in lymphatic drainage
- May be enlarged in cholecystitis
- Drains to → hepatic nodes → celiac nodes
- Cystic lymph node (Lund's node or node of Mascagni):
Innervation
- Sympathetic:
- From celiac plexus (T5-T9)
- Decreases gallbladder contraction
- Increases sphincter tone
- Parasympathetic:
- Vagus nerve (hepatic branch)
- Stimulates gallbladder contraction
- Relaxes sphincter of Oddi
- Sensory innervation:
- Via sympathetic fibers
- Referred pain: Right scapular region (via phrenic nerve C3-C5)
Physiology & Functions
- Bile storage:
- Stores 30-50 mL of bile between meals
- Receives ~500-1000 mL bile daily from liver
- Bile concentration:
- Absorbs water and electrolytes (Na+, Cl-, HCO3-)
- Concentrates bile 5-10 fold
- Active transport mechanisms in epithelium
- Mucus secretion:
- ~20 mL/day from tubuloalveolar glands
- Protects epithelium from concentrated bile
- Bile acidification:
- H+ secretion lowers pH slightly
- Helps prevent calcium precipitation
- Regulation of gallbladder function:
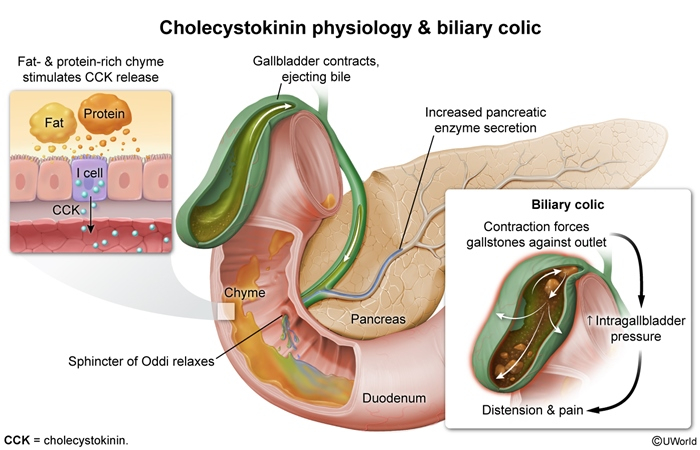
- Cholecystokinin (CCK):
- Released from duodenal I-cells in response to fats/proteins
- Causes gallbladder contraction
- Relaxes sphincter of Oddi
- Neural control:
- Vagal stimulation during cephalic phase
- Local reflexes via enteric nervous system
- Cholecystokinin (CCK):
Clinical Correlations
- Murphy's sign:
- Inspiratory arrest during palpation of RUQ
- Indicates acute cholecystitis
- Courvoisier's law:
- Palpable, non-tender gallbladder + jaundice = likely malignant obstruction
- Gallstones rarely cause palpable gallbladder
- Ducts of Luschka:
- Accessory bile ducts draining directly from liver to gallbladder
- Present in 10-30% of individuals
- Risk of bile leak if not identified during cholecystectomy
- Critical view of safety in cholecystectomy:
- Two arteries entering gallbladder
- No other structures crossing hepatocystic triangle
- Clear view of liver bed
Table Summary
| Gallbladder Anatomy & Physiology - Quick Review | |
|---|---|
| Feature | Key Points |
| Location | • Inferior liver surface (segments IVb & V) - 9th costal cartilage + lateral rectus border - Intraperitoneal organ |
| Parts | • Fundus → Body → Infundibulum → Neck - Hartmann's pouch (stone impaction site) |
| Capacity | • Normal: 30-50 mL - Can expand to 300 mL if obstructed |
| Histology | • Simple columnar epithelium with goblet cells - No muscularis mucosa/submucosa - Spiral valves of Heister in neck/cystic duct |
| Blood Supply | • Cystic artery (from right hepatic) - Courses through Calot's triangle - Venous drainage to liver/portal system |
| Innervation | • Sympathetic: celiac plexus (T5-T9) - Parasympathetic: vagus nerve - Referred pain to right shoulder (C3-C5) |
| Functions | • Store bile (30-50 mL) - Concentrate bile (5-10x) - Secrete mucus (20 mL/day) - Acidify bile slightly |
| Clinical Points | • Murphy's sign in cholecystitis - Courvoisier's law for malignancy - Watch for ducts of Luschka in surgery - Hartmann's pouch = stone impaction |
احصل على التجربة الكاملة
اشترك للوصول لفيديوهات الشرح التفصيلي والبطاقات التعليمية التفاعلية وأسئلة الممارسة مع تتبع التقدم.