سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Background
- Esophageal cancer is a malignancy that arises in the esophagus
- Most cases of esophageal malignant tumors are due to squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma
- Patients usually present with progressive dysphagia (first solids then subsequently liquids) and weight loss
- This cancer is very aggressive due to the lack of serosa in esophageal wall (allows for rapid extension)
| Esophageal Cancer | |
| Subtypes |
|
| Risk Factors |
|
| Symptoms |
|
| Diagnosis |
|
| Treatment |
|
| Cancer | Location | Risk Factors | Prevalence |
| Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Upper 2/3 | Alcohol, Hot Liquids, Caustic Strictures, Smoking, Achalasia, Nitrosamine-Rich Foods | More Common Worldwide |
| Adenocarcinoma | Lower 1/3 | Chronic GERD, Barrett Esophagus, Obesity, Tobacco Smoking | More Common in America |
Version 2
- Definition: Esophageal cancer is a malignant neoplasm arising from the epithelial lining of the esophagus
- ★ Most common histologic types:
- Adenocarcinoma (60-70% in US) - Most common in Western countries
- Squamous cell carcinoma (30-40% in US) - Most common worldwide
- Epidemiology:
- 8th most common cancer worldwide
- Male:Female ratio = 3:1
- Median age: 60-70 years
- Incidence: ~20,640 new cases/year in US (2022)
- ⚠️ Key Point: Very aggressive cancer due to lack of serosa in esophageal wall → rapid local extension and early metastasis
🎯 HIGH-YIELD FACT
Progressive dysphagia (solids → liquids) + weight loss in older patient = Esophageal cancer until proven otherwise
Types and Classification
| Feature | Adenocarcinoma ★ | Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
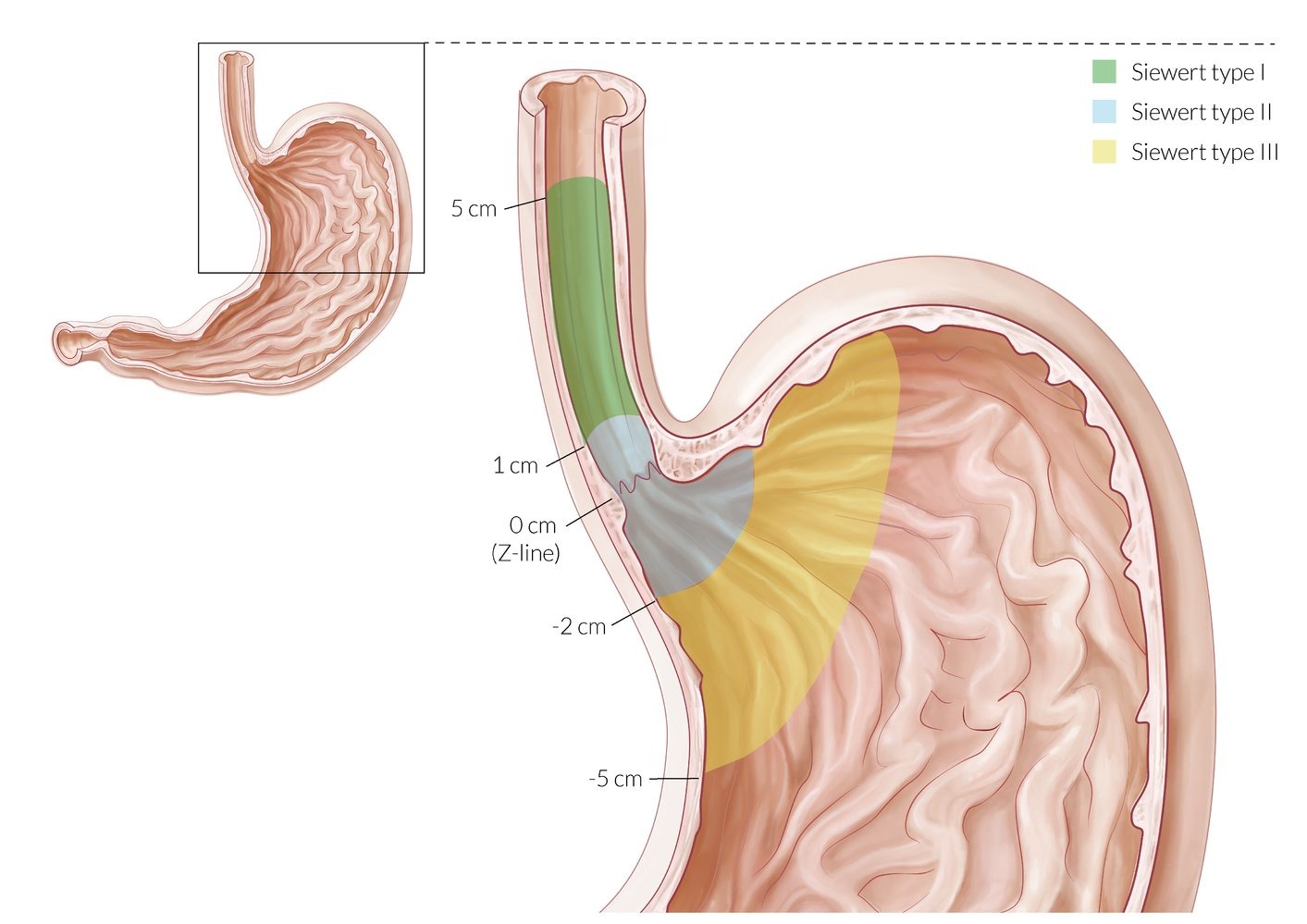
| Location | Distal 1/3 of esophagus Gastroesophageal junction |
Upper 2/3 of esophagus Middle > upper > lower |
| ★ Most Common in | Western countries (US, Europe) | Worldwide (Asia, Africa) |
| ★ Key Risk Factors |
|
|
| Pathogenesis | Normal squamous → Metaplasia (Barrett) → Dysplasia → Adenocarcinoma | Normal squamous → Dysplasia → Carcinoma |
| Demographics | White males > others | African Americans > whites |
💡 MEMORY AID
"ABCDEF" for Adenocarcinoma risk factors:
- Acid reflux (GERD)
- Barrett esophagus
- Cigarettes
- Diet (processed foods)
- Excess weight (obesity)
- Fat (central adiposity)
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Clinical presentation
- Symptom
- Progressive dysphagia
- Unintentional weight loss
- Epigastric or retrosternal pain
- Hoarseness
Version 2
★ CLASSIC PRESENTATION
Elderly male (60-70 years) with:
- Progressive dysphagia (solids → liquids) - Most common symptom
- Unintentional weight loss - Second most common
- Odynophagia (painful swallowing)
Additional Clinical Features:
- Local symptoms:
- Retrosternal chest pain/burning
- Regurgitation of undigested food
- Halitosis
- Advanced disease:
- Hoarseness - recurrent laryngeal nerve involvement
- Chronic cough - tracheoesophageal fistula
- Hematemesis/melena - tumor bleeding
- Iron deficiency anemia - chronic blood loss
- Horner syndrome - sympathetic chain involvement
- Cervical lymphadenopathy - metastatic disease
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Diagnosis
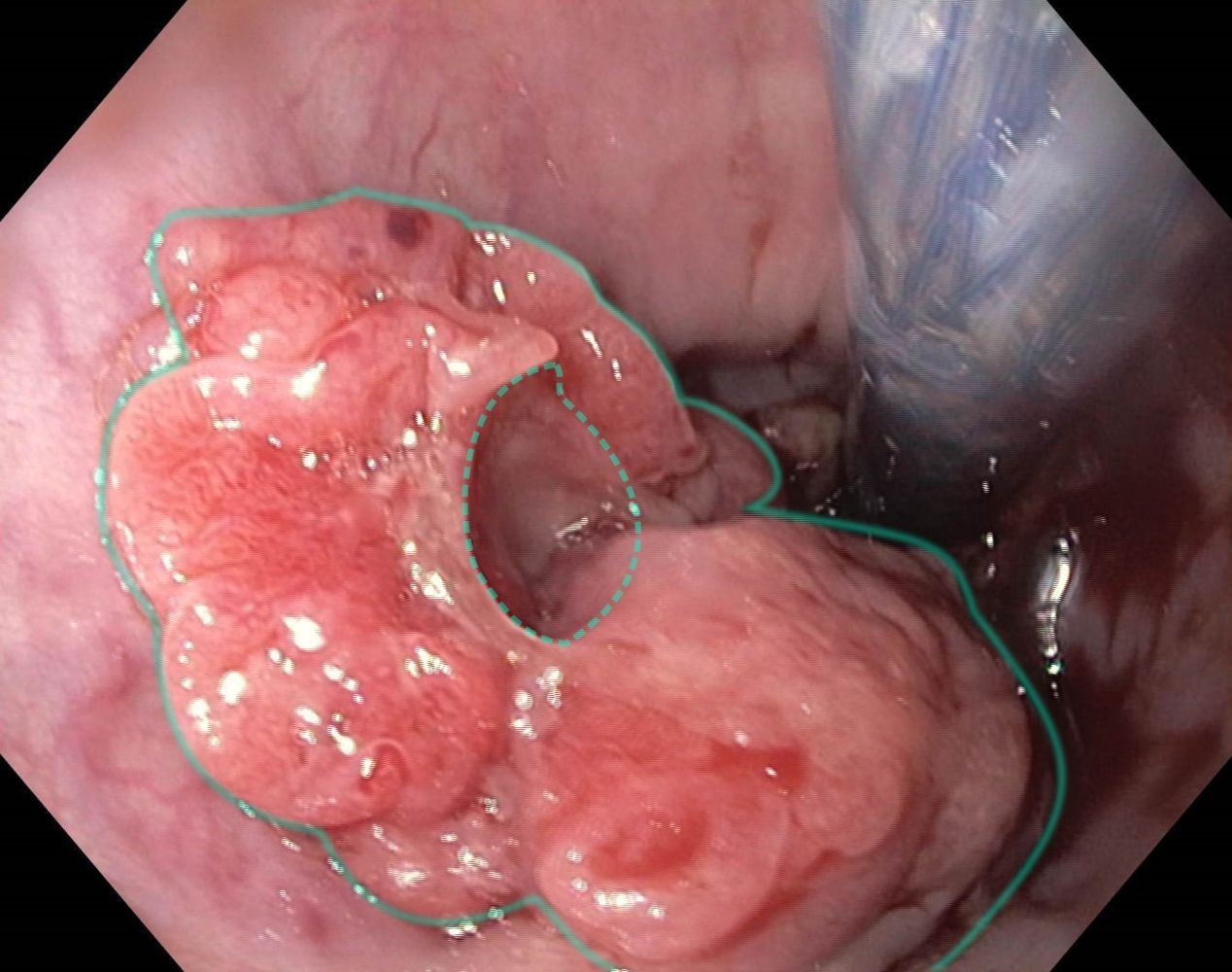
- Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy (to allow for direct visualisation)
Version 2
🔍 DIAGNOSTIC APPROACH
- ★ Best initial test: Upper endoscopy (EGD) with biopsy
- Direct visualization
- Tissue diagnosis (gold standard)
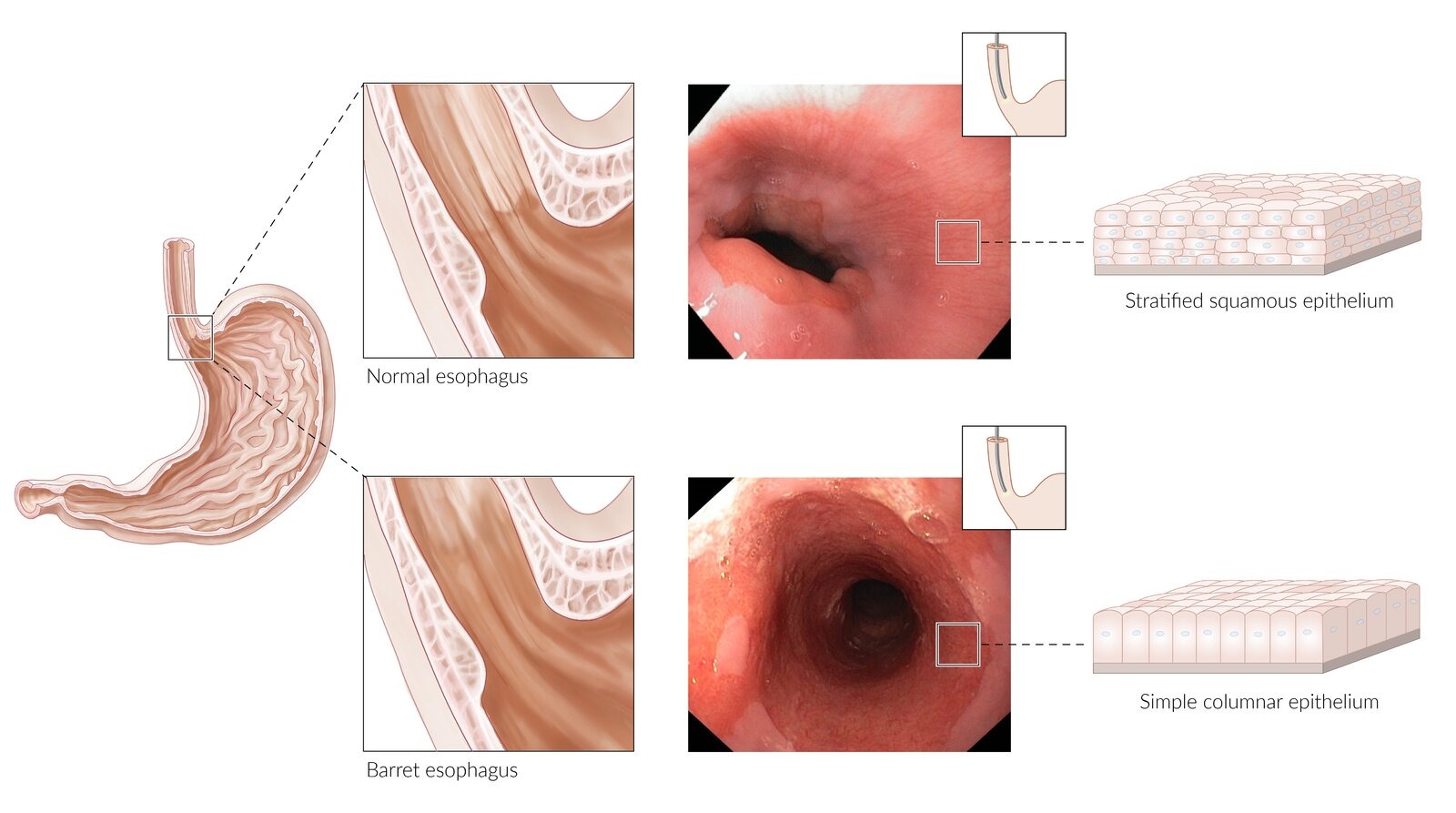
- Can assess for Barrett esophagus
- Staging workup (if cancer confirmed):
- CT chest/abdomen - distant metastases
- ★ Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) - Most accurate for T and N staging
- PET/CT - detect occult metastases
- Bronchoscopy - if upper third tumor (rule out tracheal invasion)
Alternative Initial Tests (if endoscopy unavailable):
- Barium swallow: Shows "apple core" lesion or irregular filling defect
- CT scan: Can show esophageal wall thickening
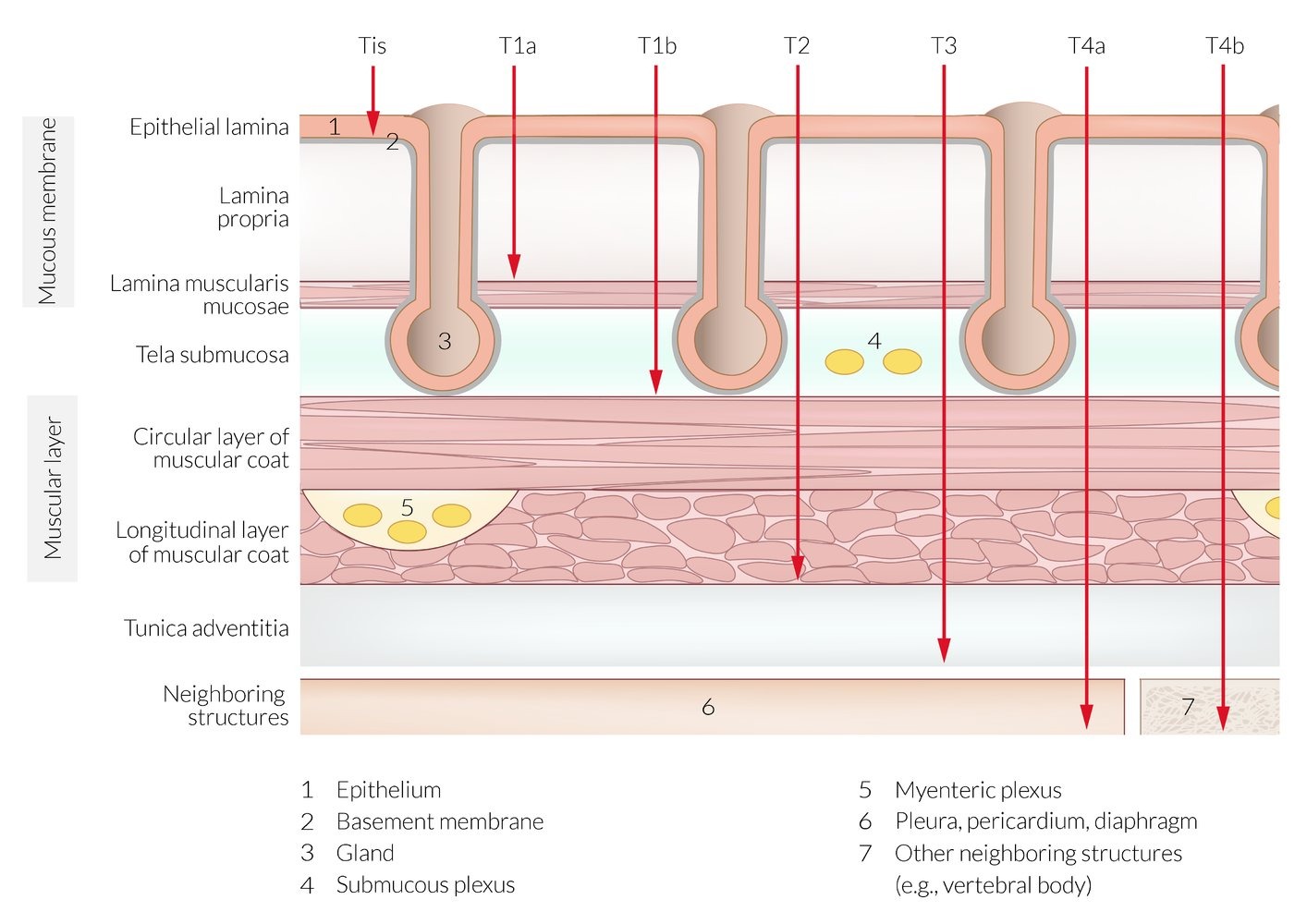
Histopathology:
| Type | Microscopic Features |
| Adenocarcinoma |
|
| Squamous Cell |
|
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Differential diagnosis
- Gastrointestinal reflux disease (GERD)
Version 2
| Condition | Key Distinguishing Features | Test to Differentiate |
| GERD | Heartburn, no dysphagia to solids, responds to PPI | Trial of PPI, endoscopy if refractory |
| Achalasia | Dysphagia to solids AND liquids from onset, regurgitation | Esophageal manometry (absent peristalsis) |
| Esophageal stricture | History of GERD/caustic ingestion, gradual onset | Barium swallow, endoscopy |
| Esophageal web/ring | Intermittent dysphagia, especially with meat | Barium swallow, endoscopy |
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Treatment
- Medical management
- Chemoradiation
- Surgical management
- Endoscopic mucosal resection (stage 1-2-3)
- Esophagectomy or esphagogastrectomy (in case of high-grade dysplasia that cannot be adequately treated with endoscopic resection)
Version 2
⚕️ TREATMENT ALGORITHM
Based on staging:
- Early disease (T1a, mucosal only):
- ★ Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR)
- Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD)
- Localized disease (T1b-T3, N0-1):
- ★ Neoadjuvant chemoradiation → Esophagectomy (preferred)
- Alternative: Primary esophagectomy → adjuvant therapy
- Locally advanced (T4 or N2-3):
- ★ Definitive chemoradiation
- Consider surgery if good response
- Metastatic disease:
- Palliative chemotherapy
- Esophageal stenting for obstruction
- Radiation for bleeding/pain
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Complication
- Esophageal obstruction
Version 2
- ★ Most common complication: Esophageal obstruction
- Progressive dysphagia
- Malnutrition
- Aspiration pneumonia
- Local invasion complications:
- Tracheoesophageal fistula - coughing with swallowing
- Aortoesophageal fistula - massive hematemesis (fatal)
- Pericardial effusion - cardiac tamponade
- Treatment complications:
- Post-esophagectomy: Anastomotic leak (most feared), stricture, dumping syndrome
- Radiation: Esophagitis, stricture, pneumonitis
⚠️ WARNING - RED FLAGS
- Coughing with swallowing → Suspect tracheoesophageal fistula
- Massive hematemesis in esophageal cancer patient → Aortoesophageal fistula (surgical emergency)
- New hoarseness → Recurrent laryngeal nerve involvement
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Prevention and Screening - was not included in the first version
🛡️ PREVENTION STRATEGIES
- Primary prevention:
- Smoking cessation
- Limit alcohol consumption
- Weight loss if obese
- GERD management with PPIs
- ★ Screening recommendations:
- Barrett esophagus surveillance:
- No dysplasia: Every 3-5 years
- Low-grade dysplasia: Every 6-12 months
- High-grade dysplasia: Every 3 months or treat
- Consider screening in: White males >50 with chronic GERD (>5 years) + ≥2 risk factors
- Barrett esophagus surveillance:
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Quick Review Box - was not included in the first version
📚 MUST-KNOW FACTS FOR EXAMS
- ★ Most common type in US: Adenocarcinoma (lower 1/3)
- ★ Most common type worldwide: Squamous cell carcinoma (upper 2/3)
- ★ Classic presentation: Progressive dysphagia (solids → liquids) + weight loss
- ★ Most important risk factor for adenocarcinoma: Barrett esophagus
- ★ Most important risk factors for SCC: Alcohol + tobacco (synergistic)
- ★ Best initial test: Upper endoscopy with biopsy
- ★ Most accurate staging test: Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)
- ★ Treatment of choice for resectable disease: Neoadjuvant chemoRT → surgery
- ★ Why aggressive spread? Lack of serosa in esophageal wall
- ★ Prognosis: Poor (5-year survival ~20%)
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Clinical Pearls - was not included in the first version
💎 CLINICAL PEARLS
- Dysphagia patterns:
- Mechanical obstruction (cancer): Solids → liquids
- Motility disorder (achalasia): Solids AND liquids from start
- Barrett esophagus: Increases adenocarcinoma risk 30-40x (0.5% annual risk)
- Alcohol + tobacco: Multiplicative (not additive) risk for SCC
- "Hot dog dysphagia": Think esophageal web/ring, not cancer
- Iron deficiency anemia in elderly male: Always rule out GI malignancy
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Common Exam Questions - was not included in the first version
📝 EXAM QUESTION PATTERNS
- Classic vignette #1: "65-year-old man with 30-year history of GERD presents with progressive dysphagia and 20-lb weight loss" → Adenocarcinoma
- Classic vignette #2: "55-year-old man with history of heavy alcohol and tobacco use presents with dysphagia and hoarseness" → Squamous cell carcinoma
- Next best step questions:
- Dysphagia + weight loss → Upper endoscopy with biopsy
- Confirmed cancer → CT chest/abdomen for staging
- Resectable tumor → Neoadjuvant therapy
- Risk factor associations:
- Barrett → Adenocarcinoma
- Achalasia → Squamous cell
- Plummer-Vinson → Squamous cell
- Caustic injury → Squamous cell
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
احصل على التجربة الكاملة
اشترك للوصول لفيديوهات الشرح التفصيلي والبطاقات التعليمية التفاعلية وأسئلة الممارسة مع تتبع التقدم.
فيديوهات الشرح
بطاقات تفاعلية
أسئلة ممارسة
اشترك الآن