intoduction
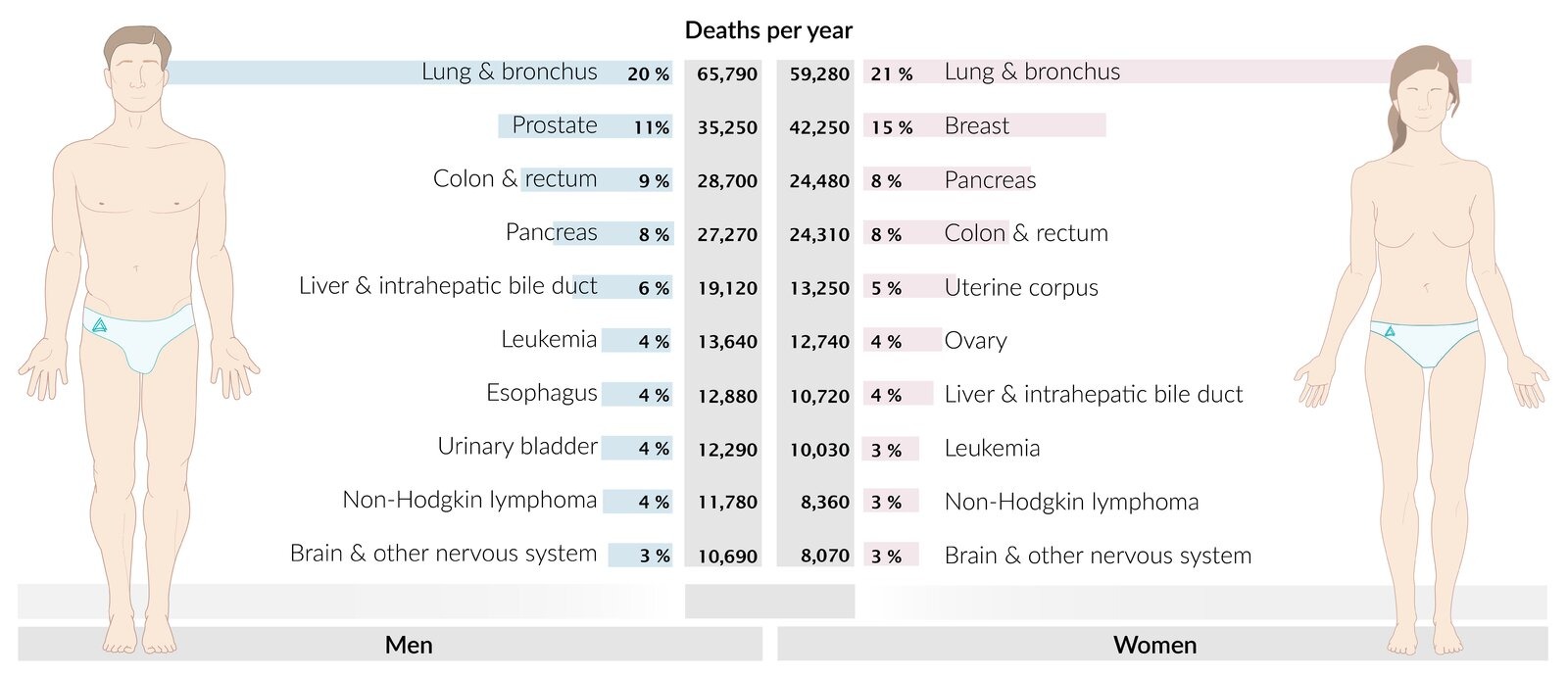
Colon cancer is a malignancy of the colon that typically affects individuals over 50 years old. Understanding its risk factors, presentation, and management is crucial for proper patient care.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Background and Epidemiology
- Colon cancer is a malignancy of the colon
- Most patients are > 50 years old (25% have a positive family history)
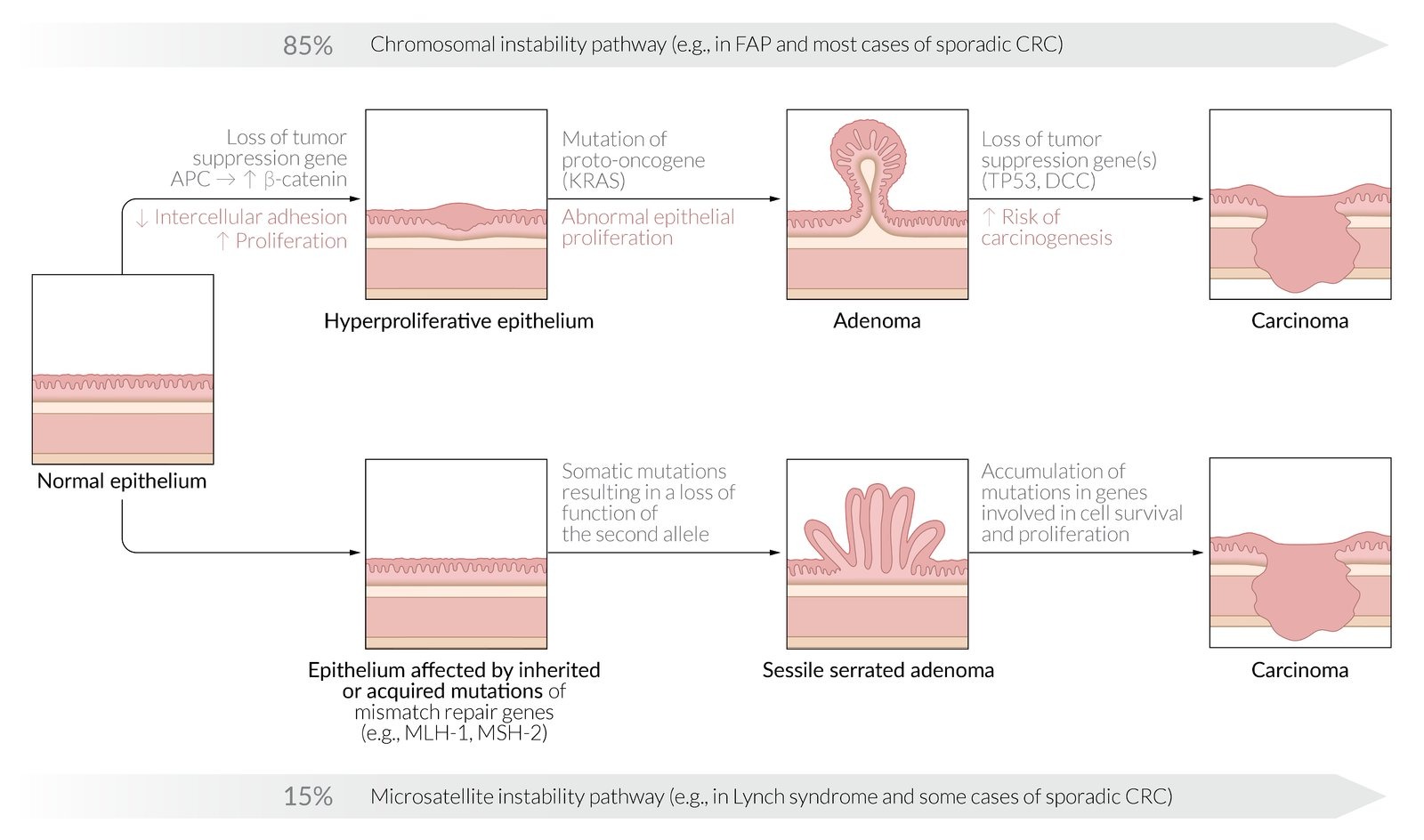
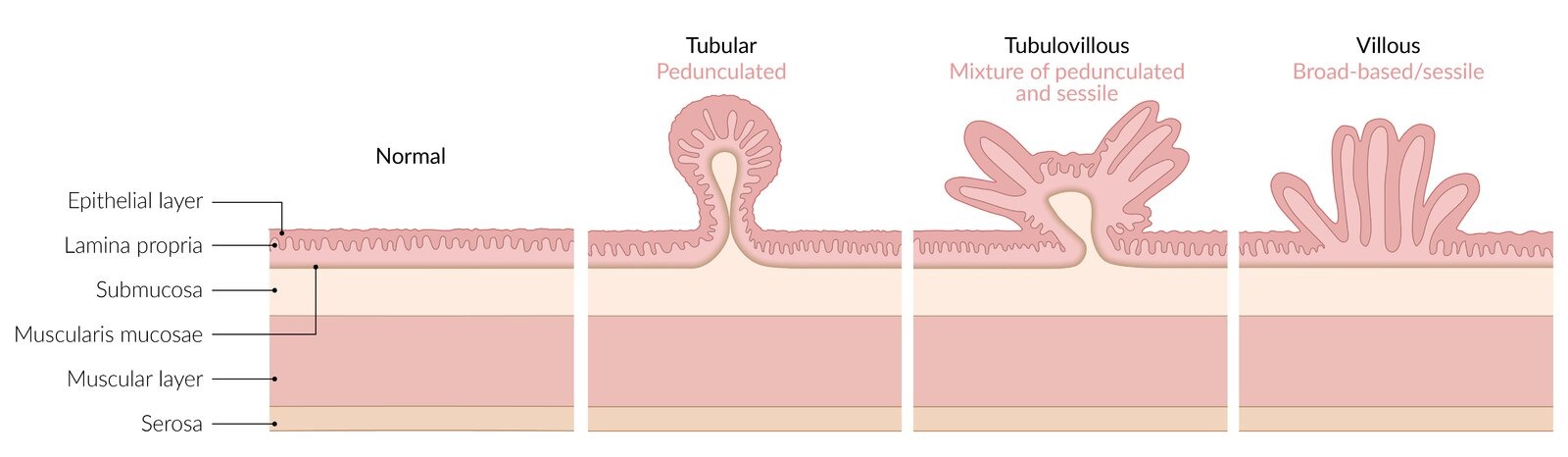
- Risk factors include: adenomatous and serrated polyps, familial cancer syndromes, inflammatory bowel disease, smoking and low fiber diet
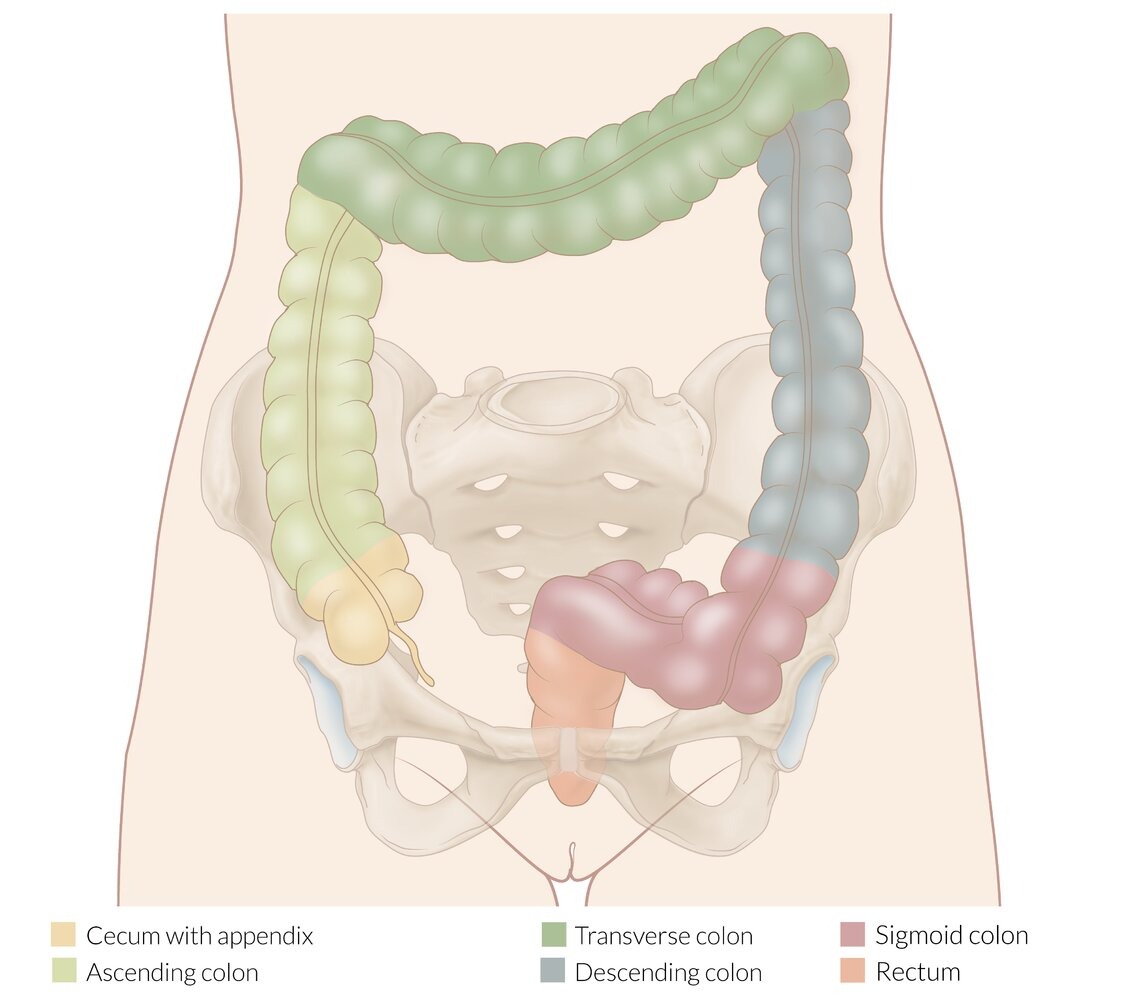
- This malignancy can arise in the right side or left side of the colon
- Clinical presentation is dependent on the location of the tumor
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Risk Factors
Risk Factor Categories
| Risk factors for colon cancer | |
| Lifestyle factors |
|
| Medical/family history |
|
| Protective factors |
|
Hereditary Cancer Syndromes
| Common Hereditary Cancer Syndromes | |
|---|---|
| Syndrome | Associated Neoplasms |
| Lynch syndrome |
|
| Familial adenomatous polyposis |
|
| Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome |
|
| Multiple endocrine neoplasm type 1 |
|
| Multiple endocrine neoplasm type 2 |
|
| BRCA1 and BRCA2 |
|
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Clinical Presentation
- Location-Based Symptoms
- Right-Sided Cancers (Cecum, Ascending Colon)
- Exophytic mass
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Weight loss
- Often silent until advanced
- Left-Sided Cancers (Descending, Sigmoid)
- Infiltrating mass
- Partial obstruction
- Colicky pain
- Hematochezia
- Change in bowel habits
- Right-Sided Cancers (Cecum, Ascending Colon)
- Common Presentations
- Asymptomatic (discovered on screening)
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Change in stool caliber
- Alternating bowel habits
- Obstruction
- Association with Streptococcus bovis
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Diagnosis
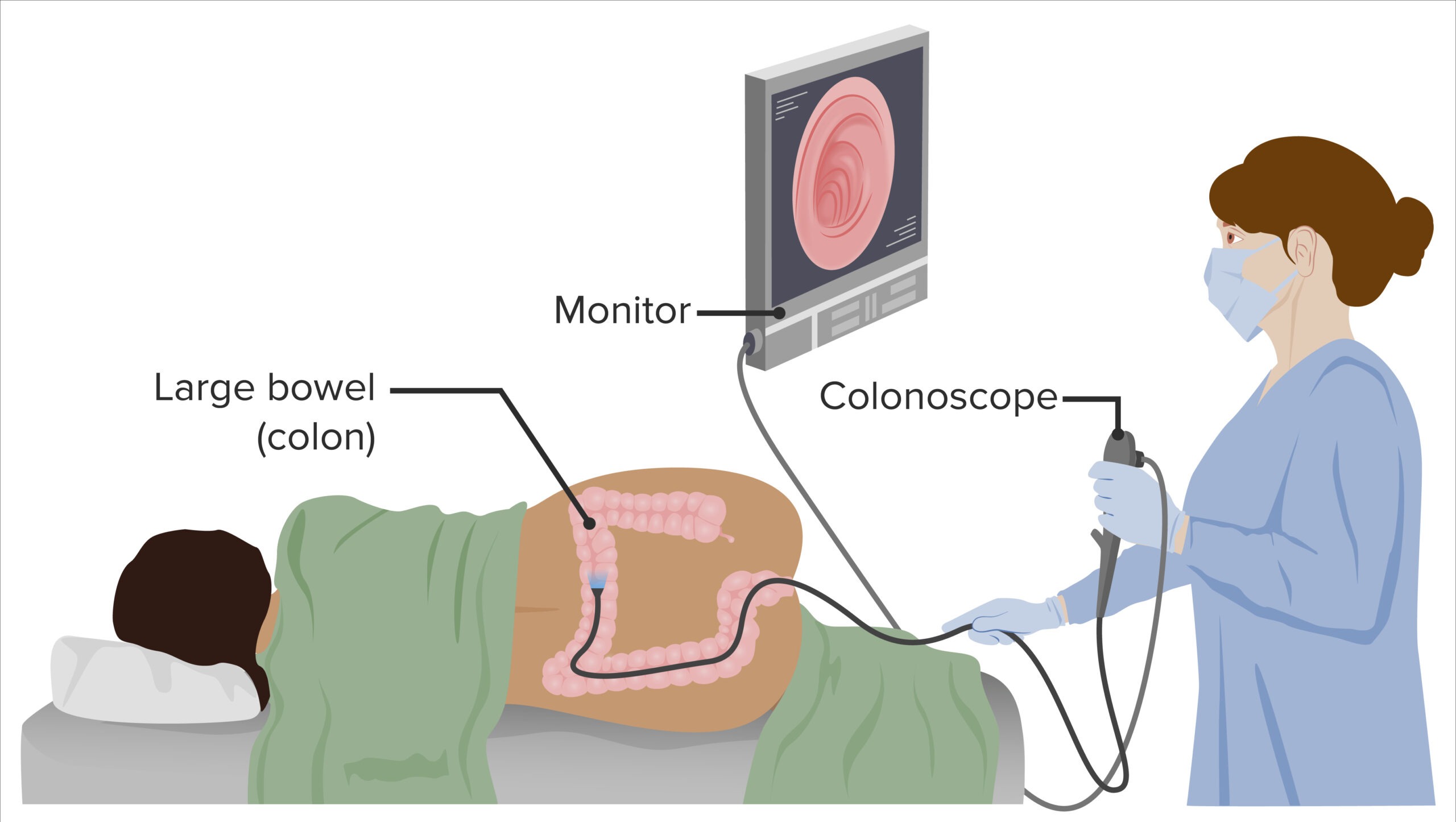
- Colonoscopy and biopsy (begins at age 50 and then repeated every 10 years) → (gold standard)
- “Apple core” lesion is seen on barium enema X-ray
- CEA tumor marker: good for monitoring recurrence (should not be used for screening)
- Fecal occult blood testing (FOBT) can also be used
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Staging
TNM Simplified
| Colorectal Cancer Staging | |
|---|---|
| Stage | Location |
| Stage 1 |
|
| Stage 2 |
|
| Stage 3 |
|
| Stage 4 |
|
| Staging Evaluation for Rectal Adenocarcinoma | |
| Tumor markers |
|
| Imaging |
|
| Endoscopy/Direct Visualization |
|
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Surveillance After Treatment
| Surveillance After Colon Cancer Resection | |
| Stage 1 |
|
| Stage 2 & 3 |
|
| Stage 4 |
|
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Treatment
- Whenever possible, patients with adenocarcinoma of the colon should be offered surgical resection
- When metastatic spread is confined to the liver, the surgical resection of both the hepatic mass and the primary tumor can be curative and increases long term survival
- Combined chemotherapy and radiation are used for inoperable rectal adenocarcinoma as well as anal squamous cell carcinoma. However, radiation therapy is typically avoided in tumors proximal to the rectum (radiation enteritis can be severe)
| Surgical Approaches | |
|---|---|
| Location | Procedure |
| Right Colon |
|
| Left Colon |
|
| Sigmoid |
|
| Rectum |
|
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Follow-up
- Surveillance Schedule
- CEA every 3-6 months for 2 years
- CT scan annually for 5 years
- Colonoscopy at 1 year, then 3-5 years
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Clinical Pearls
- Key Remember Points
- Never ignore iron deficiency anemia
- Location affects presentation
- Early detection is crucial
- Regular screening saves lives
- Common Exam Topics
- Right vs left sided symptoms
- Staging workup
- Screening guidelines
- Surgical options
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Screening
- Average Risk
- Start at age 45
- Colonoscopy every 10 years
- Annual FIT test alternative
- High Risk
- Start 10 years before index case
- More frequent intervals
- Consider genetic counseling
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
احصل على التجربة الكاملة
اشترك للوصول لفيديوهات الشرح التفصيلي والبطاقات التعليمية التفاعلية وأسئلة الممارسة مع تتبع التقدم.
فيديوهات الشرح
بطاقات تفاعلية
أسئلة ممارسة
اشترك الآن