شرح المدرسين
Introduction
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Normal Growth Patterns
- Definition: the physical process of increasing in size, mass, or number. In human beings, it’s measured with; weight, height/length, Head circumference.
- Growth is a cornerstone of pediatric care.
- Body tissues and organs grow most rapidly during infancy and adolescence, with these exceptions:
- Brain growth is most rapid during the first 2 years of life.
- Head circumference (HC) increases 10 cm in the 1st year, another 2-3cm in the 2nd year, and 5-6 cm throughout the remainder of childhood.
- Lymphoid tissue volume increases rapidly before puberty and then declines until reaching adult levels.
- Growth of the reproductive organs is slow until puberty.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Weight
- Average weight at birth = 3.4 kg ( 2.5-4.5)
- Full-term infants weight gain patterns:
- 1 Double(2x) their birth weight at 4-5 months
- Triple(3x) their birth weight by 12 months
- Quadruple(4x) their birth weight by 24 months.
- As children grow older, the weight gain continues at a steady but slower rate, averaging about 2-3 kg per year until adolescence, when growth accelerates again during puberty.
- In a prepubertal child, weight gain of < 1 kg /year is cause for concern.
| Average Weight Gain for a Healthy Infant | |
|---|---|
| Age Range | Weight Change |
| First few days after birth | Loss of 10% of birth weight |
| 10–14th day | Regain the lost 10% |
| 0–3 months | 25–30 grams/day |
| 3–6 months | 20–25 grams/day |
| 6–9 months | 15–20 grams/day |
| 9–12 months | 10–15 grams/day |
Important Terminologies on Birth Weight
| Terminology (According to Weight) | |
|---|---|
| Term | Description |
| Extremely Low Birth Weight (ELBW) | Birth weight is less than 1000 grams. |
| Very Low Birth Weight (VLBW) | Birth weight is 1000–1500 grams. |
| Low Birth Weight (LBW) | Birth weight is 2000–2500 grams. |
| Normal Birth Weight (NBW) | Birth weight is between 2.5–4.2 kg (some resources up to 4.5 kg). |
| Macrosomia | Birth weight is above 4.2 kg (some resources beyond 4.0 kg). |
| Terminology (Weight According to Gestational Age) | |
| Term | Description |
| Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR) | Baby’s growth inside the womb is not as expected for gestational age. |
| Small for Gestational Age (SGA) | Birth weight is <10th percentile for gestational age. |
| Appropriate for Gestational Age (AGA) | Birth weight is between 10th–90th percentile for gestational age. |
| Large for Gestational Age (LGA) | Birth weight is >90th percentile for gestational age. |
Calculating the Average Weight at Different Ages
| Formulas for Calculating Average Weight in Children (by Age) | |
| Age Group | Formula |
| 0–1 year | Average Weight = 0.5 × Age (months) + 4 |
| 1–5 years | Average Weight = 2 × Age (years) + 8 |
| 6–12 years | Average Weight = 3 × Age (years) + 7 |
Practice Questions
- What is the estimated average weight for a 7 month old baby?
- Weight= 0.5*7+4= 7.5 kg.
- What is the estimated average weight for an 8 year old child?
- Weight= 2*8+8= 24 kg.
- What is the estimated average weight for a 12 year old child?
- Weight= 3*12+7= 43 kg.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Height/Length
- Average full-term newborn length at birth = 50 cm (45-55 cm).
- Full term infants height/length gain patterns:
- Birth length (height) increases 50% by1 year of age.
- Birth length (height) doubles by 4 years of age.
- Birth length (height) triples by 13 years of age.
- After 4 years of age, average height increase is 2 inches (5cm) per year until adolescence.
- If the increase is less than that in a prepubertal child, it is considered a concerning linear growth pattern that needs further evaluation.
| Note | |
|
Length is the height of children under 2 years old, measured while lying supine. Standing height is measured for children above 2 years of age. |
ملاحظة |
| Average Height/Length Gain for a Healthy Infant | |
|---|---|
| Age | Average Height |
| At birth | 50 cm |
| 6 months | 68 cm |
| 1 year | 75 cm |
| 2 years | 87 cm |
| 4 years | 100 cm |
Calculating Midparental height (MPH)
- While environmental, genetic, nutritional, and hormonal elements all affect growth, the most influential factors pertain to a child’s parents.
- Adult heights of both parents,along with their patterns of growth in childhood, influence their child’s growth velocity and ultimate height.
- A child’s final adult height normally falls within 2 standard deviations (SDs) (i.e., 4 inches or 10 cm) above or below the calculated MPH.
| Formulas for Calculating Midparental Height in Children (in cm) | |
| Sex | Formula |
| Girls | (Paternal Height + Maternal Height − 13) / 2 (SD = ±8.5) |
| Boys | (Paternal Height + Maternal Height + 13) / 2 (SD = ±10) |
Practice Questions
- What is the estimated average adult height for a 12 year old boy, knowing that his father's height is 175 cm, and his mother's height is 165 cm?
- Answer:
- Midparental Height for a boy formula = Paternal Height+maternal Height+13)/2
- Boy’s estimated height= (175+165+13)/2
- Boys’s estimated height =176.5 cm
- What is the estimated average adult height for an 8 year old female , knowing that her father's height is 180 cm, and her mother’s height is 165 cm?
- Answer:
- Midparental Height for a girl formula = Paternal Height+maternal Height-13)/2
- Girl’s estimated height= (175+165-13)/2
- Boys’s estimated height =163.5 cm
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Head Circumference (HC)
- Average Head Circumference at birth = 34-35 cm.
- The fastest rate of head growth occurs between 0 and 2 months, averaging 0.5 cm/week.
- From birth to 6 months, the HC increases by approximately 9–10 cm (43-44 cm).
- From birth to 1 year, the HC increases by approximately 12–14 cm (46–49 cm).
- By 12 months, the brain has completed half its postnatal growth and is 75% of adult size.
Anterior and Posterior Fontanelles
| Anterior Fontanelle | Posterior Fontanelle | |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Diamond-shaped | Triangular-shaped |
| Site | at the junction of the frontal and parietal bones. | at the junction of the occipital and parietal bones. |
| Closure Age | 12–18 months. | 6–8 weeks of age (approximately 2-3 months). |
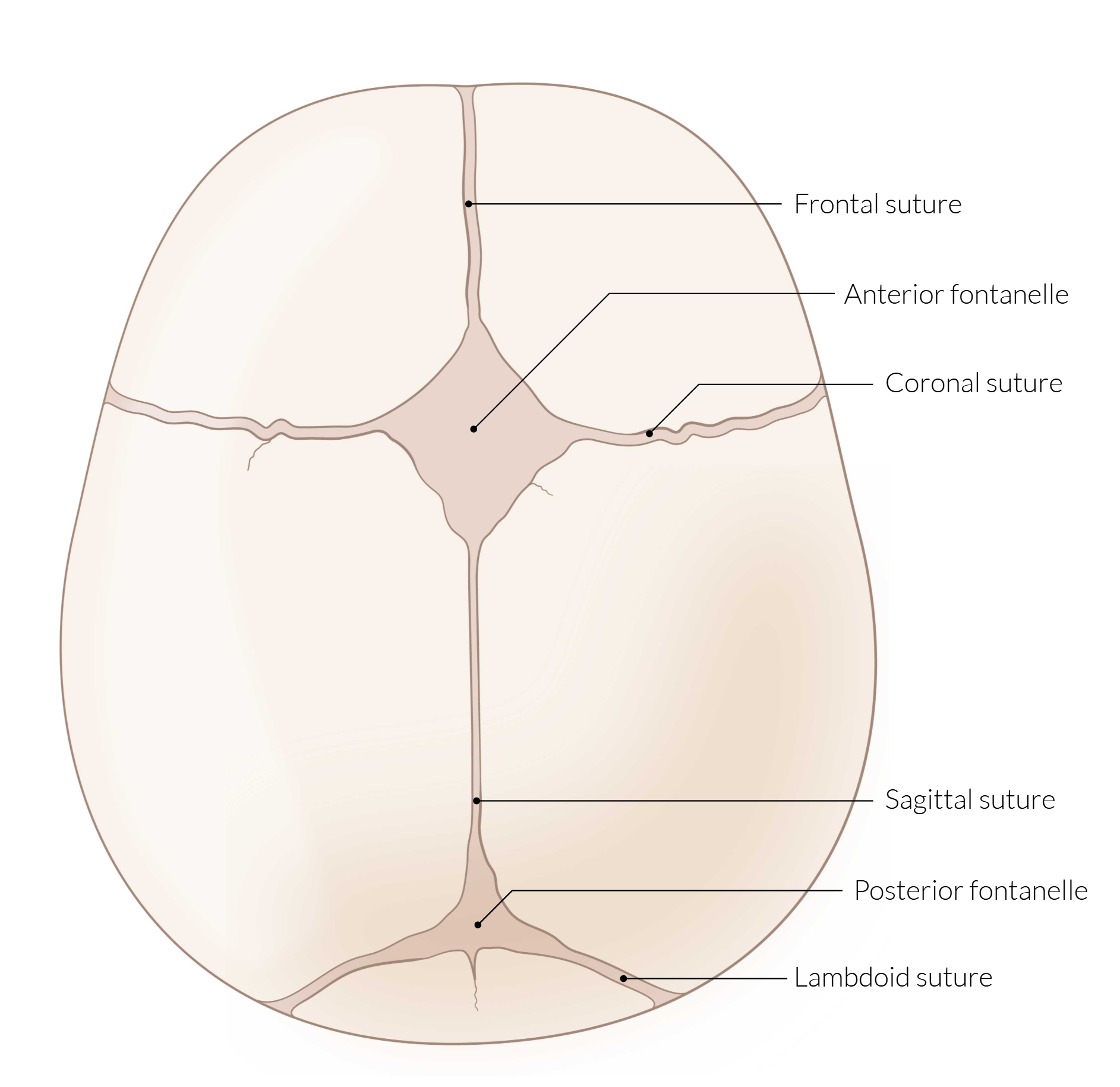
Early and Delayed Closure of Fontanelles
- Causes of Early Closure (Premature Closure)
- Primary Craniosynostosis
- Premature fusion of one or more cranial sutures, leading to abnormal head shapes
- Secondary Craniosynostosis
- Genetic Disorders
- Microcephaly
- Hyperthyroidism
- Hypercalcemia
- Head Injury
- Primary Craniosynostosis
- Causes of Delayed Closure
- Physiological
- Prematurity
- Nutritional Deficiency (Rickets, Malnutrition)
- Endocrine Disorders (Hypopituitarism, Congenital hypothyroidism, Hypophosphatemia)
- Increase Intracranial Pressure (Hydrocephalus)
- Genetic Disorders (Down’s syndrome, Achondroplasia, Osteogenesis imperfecta)
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Body Mass Index (BMI)
- Body Mass Index (BMI) is a numerical value calculated using a person's weight in kilograms divided by the square of their height in meters (kg/m²).
- In pediatrics, BMI is adjusted for age and sex to account for developmental changes and growth patterns, and it is typically expressed as a percentile on growth charts.
| Formulas For Calculating BMI | |
| BMI = Weight (kg) / Height (m²) | |
| Interpretation | Description |
| Underweight | BMI of less than 5th percentile |
| Normal weight | BMI between 5th – 85th percentile |
| Overweight | BMI more than 85th percentile |
| Obesity | BMI more than 95th percentile |
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
احصل على التجربة الكاملة
اشترك للوصول لفيديوهات الشرح التفصيلي والبطاقات التعليمية التفاعلية وأسئلة الممارسة مع تتبع التقدم.
فيديوهات الشرح
بطاقات تفاعلية
أسئلة ممارسة
اشترك الآن
