شرح المدرسين
Introduction
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Definition
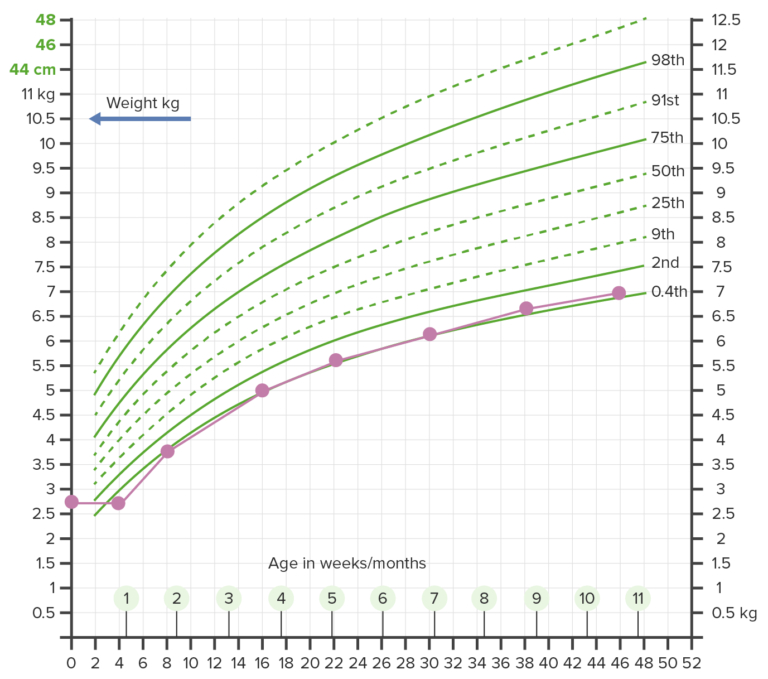
- Cessation of weight gain after a period of stable growth that manifests as weight below the 3rd percentile for age, Weight for height below the 5th percentile.
- Failure to thrive is growth that has fallen, crossing 2 major percentile curves in a short time.
- Any change below the 5th percentile suggests a child is at risk for FTT.
| Definition of Failure to Thrive (FTT) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Number of Points on Growth Chart | Failure to Thrive Characteristics | |
| 1 point |
|
|
| Series of points |
|
|
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Presentation
- The degree of FTT is best evaluated by measuring weight and height (the weight height ratio) at multiple points over time.
Typically, FTTis first characterized by a decrease in weight for age while height and HC are preserved. - Progressive FTT due to chronic malnutrition can also result in loss of height.
- In the absence of wasting, abnormal linear growth would not suggest FTT.
| Note | |
| In FTT, the first growth parameter that shows a fall off is the weight curve, then the height curve, and finally the head circumference curve. | ملاحظة |
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Risk Factors
- Organic risk factors: prematurity, congenital malformations, neuromuscular disorders, abnormal suck/swallow coordination, intrauterine infections, exposure to drugs and/or otherntoxins.
- Nononorganic (psychosocial) risk factors: familial dysfunction, maternal depression, poverty, and low food security
- Poverty remains the major risk factor for FTT.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Etiology
- FTT can be divided into 2 main categories:
- Inadequate intake (calories not offered by an adult or calories not ingested by the infant)
- Altered metabolism (calories not retained or used by the infant or increased metabolic need compared to caloric intake)
| Causes of FTT | ||
|---|---|---|
| Inadequate intake |
|
|
| Excessive calorie loss |
|
|
| Excessive calorie consumption |
|
|
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Clinical Picture
- If severe psychosocial FTT is present→ gaze disturbances—“wary watchfulness” or total avoidance of eye contact, apathetic withdrawal,developmental delays in language and social behavior.
- Wasting of subcutaneous tissue, especially lateral buttocks, thighs, and upper arms
- Alopecia.
- Dermatitis.
- Kwashiorkor or marasmus.
- Specific physical findings suggestive of organic etiologies can be noted.
| Note | |
| If only weight parameter is affected → Mostly due to inadequatecaorie intake. If Both weight and height are below the 5th percentile→ suspect endocrinological disorder. If weight,height, and HC are all affected→ suspect IUGR, genetic disorders. |
ملاحظة |
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Diagnosis
Consider laboratory studies in a stepwise fashion, based on history and physical exam, which may include:
- Urine analysis and urine culture; urine-reducing substances.
- CBC with differential.
- Stool test for reducing substances.
- Fecal fat.
- Electrolytes.
- BUN and creatinine.
- Serum transaminases.
- Total protein and albumin.
- Thyroid function studies.
- Sweat chloride.
- Review of newborn screen (Serum amino acids, urine organic acid screen, serum ammonia.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Treatment
- Organic FTT: Treat the underlying medical condition, along with nutritional rehabilitation.
- Non-Organic FTT: Provide nutritional education and psychosocial interventions, involve social services if neglect is suspected.
- Mixed FTT: Address both medical and psychosocial factors.
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
احصل على التجربة الكاملة
اشترك للوصول لفيديوهات الشرح التفصيلي والبطاقات التعليمية التفاعلية وأسئلة الممارسة مع تتبع التقدم.
فيديوهات الشرح
بطاقات تفاعلية
أسئلة ممارسة
اشترك الآن
