شرح المدرسين
Introduction
The early stages of pregnancy are pivotal for ensuring the health and well-being of both the mother and the fetus. Accurate diagnosis and consistent monitoring are crucial during this period. Confirming pregnancy involves a comprehensive approach, incorporating laboratory tests, ultrasound examinations, and thorough clinical assessments.
To confirm the pregnancy:
- Confirm pregnancy by measuring human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in urine and/or serum.
- If there is concern (signs or symptoms) for ectopic pregnancy or early pregnancy loss:
- Obtain ultrasound to confirm a viable intrauterine pregnancy (IUP).
- Monitor with serial ultrasound and/or serum hCG until pregnancy viability and location are confirmed.
Laboratory Findings in Early Pregnancy
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG):
- Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone secreted into the maternal bloodstream shortly after implantation, typically 6 to 10 days post-ovulation, marking the onset of pregnancy. Standard serum hCG tests are commonly used for early detection, offering a reliable indication of pregnancy.
Types of pregnancy tests Urine hCG test Serum hCG test Test description - Qualitative test (less sensitive than quantitative serum pregnancy test)
- May be a quantitative test (high sensitivity) or qualitative test
Timing - Usually detectable beginning the day a menstrual cycle is expected to start (approx. 14 days after fertilization)
- Detectable beginning 6–8 days after fertilization
Indications - Identification of pregnancy in individuals with clinical signs of early pregnancy
- Diagnosis and management of abnormal pregnancy (e.g., suspected ectopic pregnancy, early pregnancy loss, or gestational trophoblastic disease)
- Prenatal genetic testing
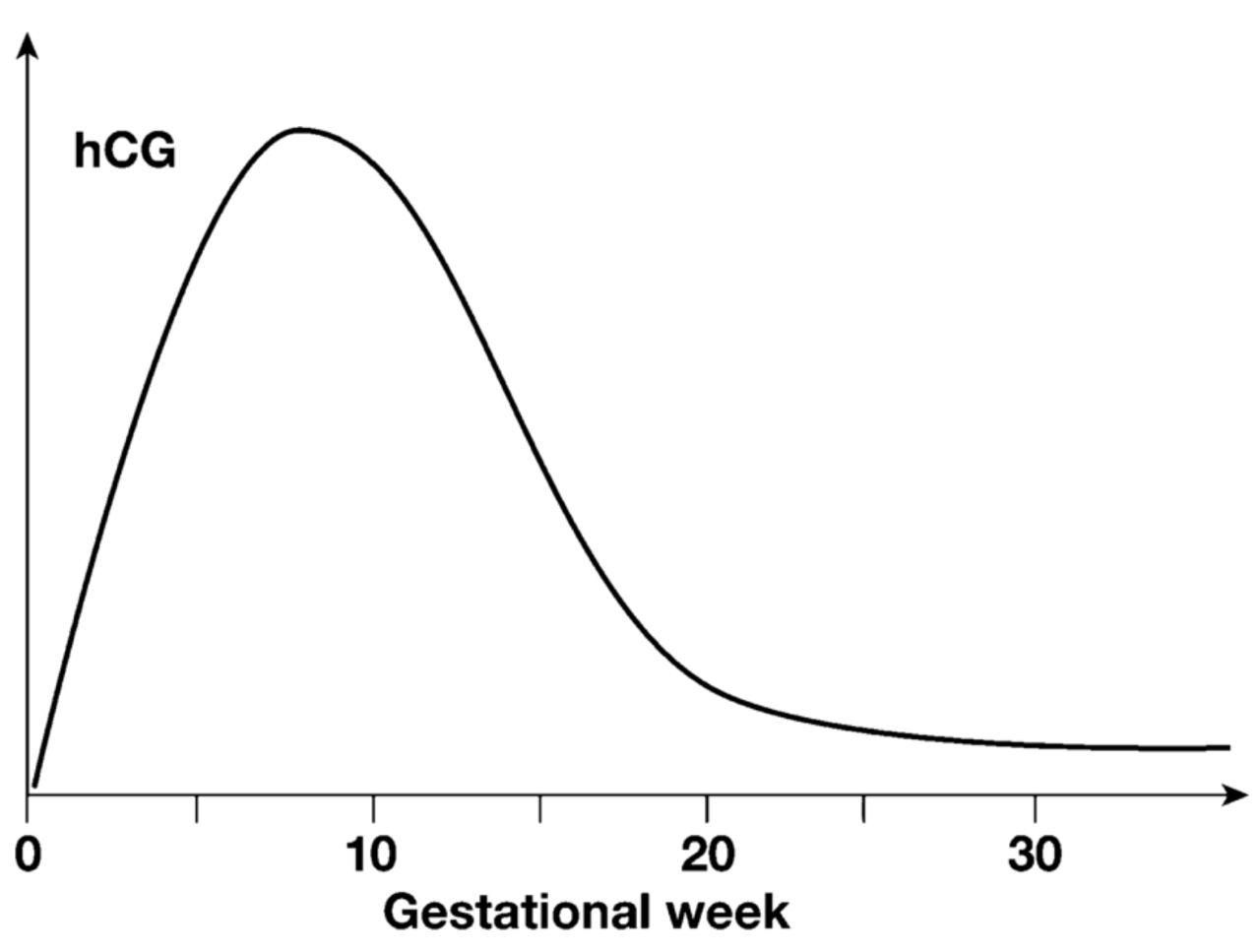
hCG Levels Across Pregnancy
- In the first 30 days following implantation, hCG levels approximately double every 29 to 53 hours, peaking at 8 to 10 weeks of gestation. After reaching the peak, the levels decline but then stabilize until the term. These dynamic changes in hCG concentrations are crucial indicators of the pregnancy's progression and health.
Ultrasound in pregnancy
Recommended for all pregnancies before 22 weeks to:
- Confirm intrauterine pregnancy.
- Confirm gestational age.
- Confirm the number of pregnancy.
- Assess fetal development/screening.
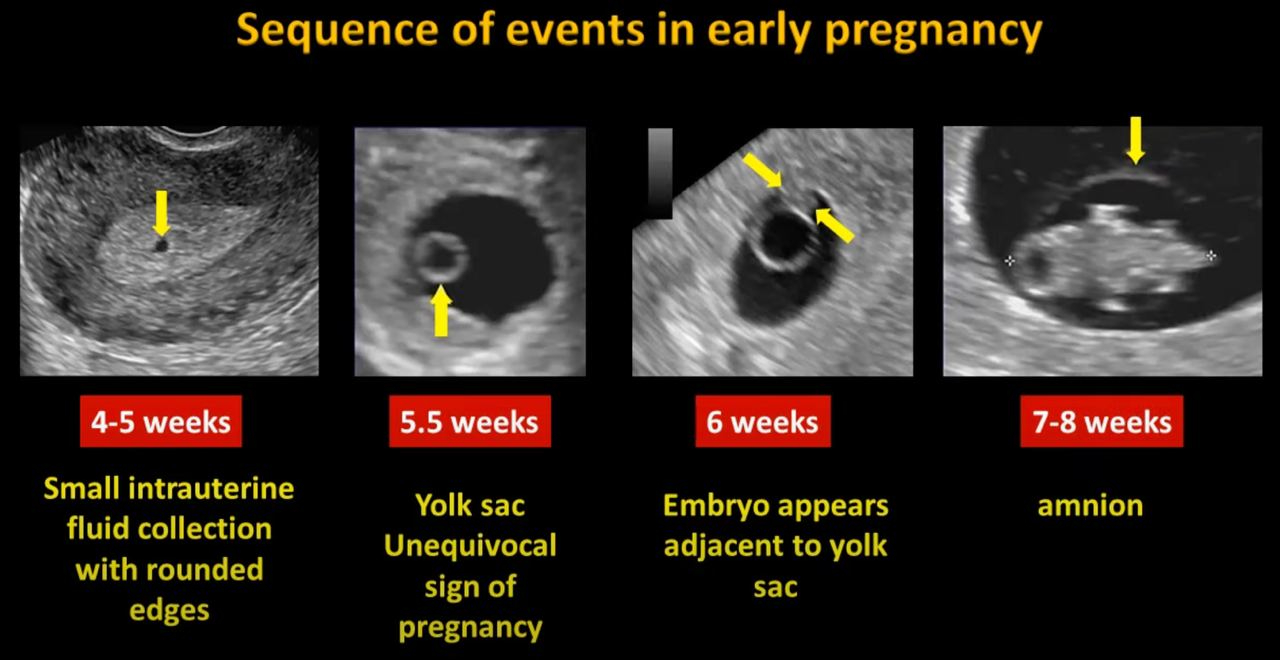
Timing of Gestational Landmarks
- Gestational Sac: The earliest ultrasound indication of pregnancy, detectable around 4.5 to 5 weeks via transvaginal ultrasound. It typically becomes visible when serum hCG levels reach 1500–3000 mIU/mL, providing early confirmatory evidence of an intrauterine pregnancy.
- Yolk Sac: Visible between 5 to 6 weeks of gestation, the yolk sac is essential for the embryo's early development, remaining until approximately 10 weeks.
- Embryonic Cardiac Activity: Observable by 5.5 to 6 weeks, embryonic cardiac activity is a definitive sign of a viable pregnancy, crucial for assessing the health of the developing fetus.
- Measurable Embryo: From 6 weeks, the embryo reaches a size that allows for measurement, aiding in accurate assessment of gestational age and pregnancy viability.
SONOGRAPHIC ASSESSMENT OF GESTATIONAL AGE
Sonographic assessment is a critical tool in estimating the gestational age of a pregnancy. It uses measurements of the gestational sac, embryo, and fetal structures to provide accurate dating. This method is especially useful when the last menstrual period (LMP) is uncertain or unreliable.
- How Gestational Age is Measured?
- Assumptions: Ultrasound estimates rely on the correlation between fetal size (e.g., crown-rump length, Biparital diameter , femur length) and age.
- Exclusions: Measurements that may not represent true age due to conditions like skeletal dysplasia or hydrocephalus are excluded.
- When Ultrasound is Essential?
- Irregular menstrual cycles.
- Unknown or uncertain LMP.
- Conception during hormonal contraceptive use.
- Uterine size inconsistent with LMP.
Ultrasound Techniques
- First Trimester (up to 13+6 weeks):
- Transvaginal Ultrasound (TVS): Provides clear images of early pregnancy structures like the gestational sac, yolk sac, and embryo. Recommended for early pregnancy.
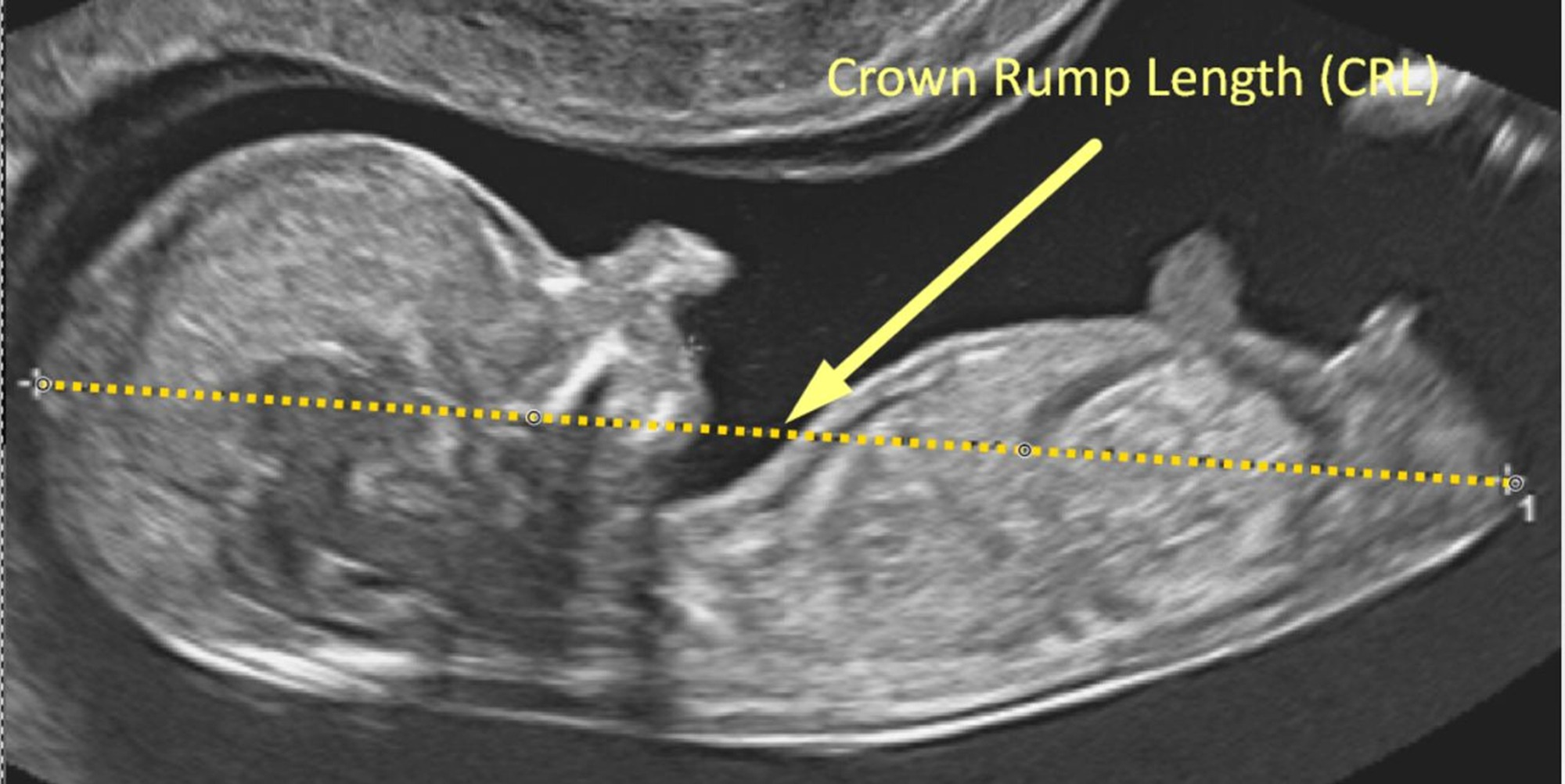
- Crown-Rump Length (CRL): Most accurate measurement for dating.
- CRL: The longest straight-line measurement from the top of the embryo's head (cephalic pole) to the bottom (rump).
- Calculation:
- Gestational age (in days) = CRL (mm) + 42 (for CRL <25 mm).
- Beyond CRL of 84 mm, use other measurements like BPD or HC
- Second and Third Trimesters:
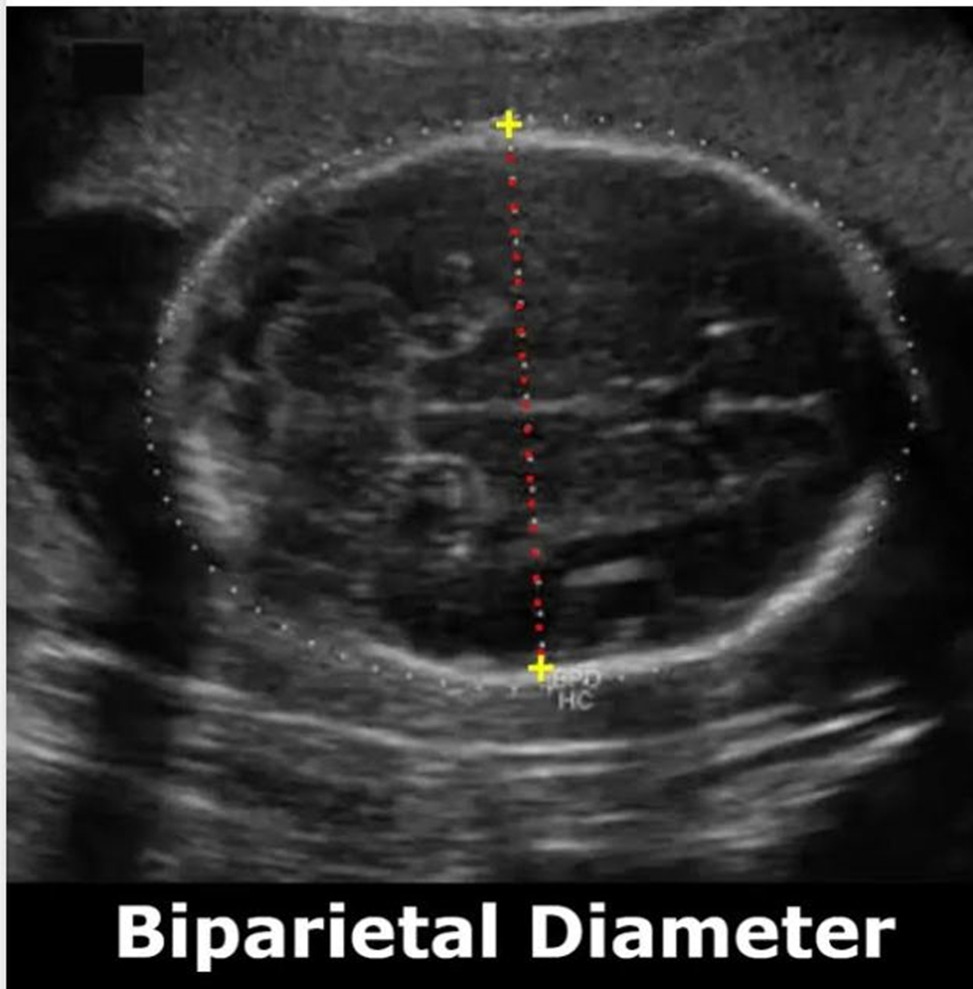
- Transabdominal Ultrasound (TAS): Used for fetal biometry as the uterus enlarges.
- Measurements include head circumference (HC), biparietal diameter (BPD), femur length (FL), and abdominal circumference (AC).
Accuracy of US
| Gestational age (weeks+days) based on the first day of LMP | Change LMP-based EDD to ultrasound-based EDD if ultrasound-based gestational age differs from LMP-based gestational age by more than: |
|---|---|
| ≤8+6 | 5 days |
| 9+0 to 13+6 | 7 days |
| 14+0 to 15+6 | 7 days |
| 16+0 to 21+6 | 10 days |
| 22+0 to 27+6 | 14 days |
| ≥28+0 | 21 days |
احصل على التجربة الكاملة
اشترك للوصول لفيديوهات الشرح التفصيلي والبطاقات التعليمية التفاعلية وأسئلة الممارسة مع تتبع التقدم.
