Summary
Normal puberty is a physiological process marking the transition to sexual maturity, typically lasting 2–5 years and occurring between ages 8–13 in girls. It involves sequential hormonal changes, beginning with adrenarche and gonadarche, followed by thelarche, pubarche, and culminating in menarche. Tanner staging is used to assess pubertal development based on breast and pubic hair growth. Precocious puberty refers to early onset of these changes—before age 8 in girls—classified as central (gonadotropin-dependent) or peripheral (gonadotropin-independent). Diagnosis involves hormonal testing and imaging, and treatment targets the underlying cause, with GnRH agonists for central forms and hormone antagonists for peripheral types.
Normal puberty
- Definition: Puberty is the physiological process of sexual maturation involving the development of secondary sexual characteristics, reproductive capability, and the transition from childhood to adulthood.
Parameter Girls Boys Normal age range 8–13 years 9–14 years ★ Average onset 11 years 13 years Duration 2–5 years 2–5 years Menarche age 10–16 years (mean: 13) N/A - Pubertal physiology:
- Adrenarche (First Phase)
- Definition: Activation of adrenal androgen production
- Age of onset: 6-8 years (both sexes)
- Clinical features:
- Axillary and pubic hair growth
- Body odor (apocrine gland activation)
- Acne development
- Oily skin
- Key Point: Independent of hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis
- Gonadarche (HPG Axis Activation)
- Definition: Activation of hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis
- Mechanism: Pulsatile GnRH secretion → ↑FSH and LH → gonadal hormone production
- Hormonal changes:
- Girls: ↑Estradiol from ovaries
- Boys: ↑Testosterone from testes
- Thelarche (Girls) / Testicular Enlargement (Boys)
- Girls - Thelarche:
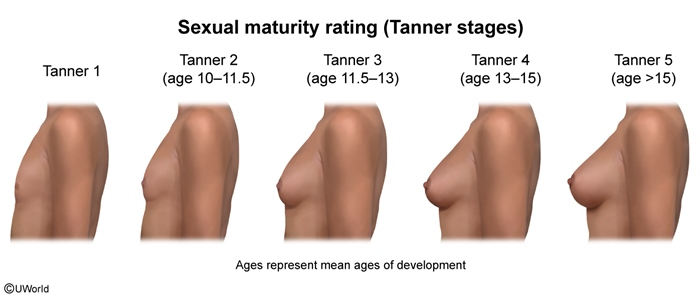
- ★ First sign of puberty in girls
- Age: 8-11 years (average 10.5)
- Breast bud development (Tanner stage 2)
- Boys - Testicular enlargement:
- ★ First sign of puberty in boys
- Age: 9-14 years (average 11.5)
- Testicular volume >4 mL (normal prepubertal: 1-3 mL)
- Girls - Thelarche:
- Growth Spurt
- Peak height velocity:
- Girls: 11.5 years (6-12 cm/year)
- Boys: 13.5 years (7-14 cm/year)
- Mechanism: Estrogen → ↑Growth hormone → ↑IGF-1
- Duration: ~2 years
- Peak height velocity:
- Pubarche
- Definition: Onset of pubic hair growth
- Age: Usually follows thelarche/testicular enlargement by 6-12 months
- Hormone: Primarily androgen-dependent
- Menarche (Girls) / Voice Changes (Boys)
- Girls - Menarche:
- Age: 10-16 years (mean: 13 years)
- Timing: Usually 2-3 years after thelarche
- Important: Initial cycles often anovulatory for 6-18 months
- Boys - Voice changes:
- Age: 13-15 years
- Mechanism: Testosterone → laryngeal growth
- Girls - Menarche:
- Adrenarche (First Phase)
- Female: adrenarche → gonadarche → thelarche → growth spurt→ pubarche → menarche
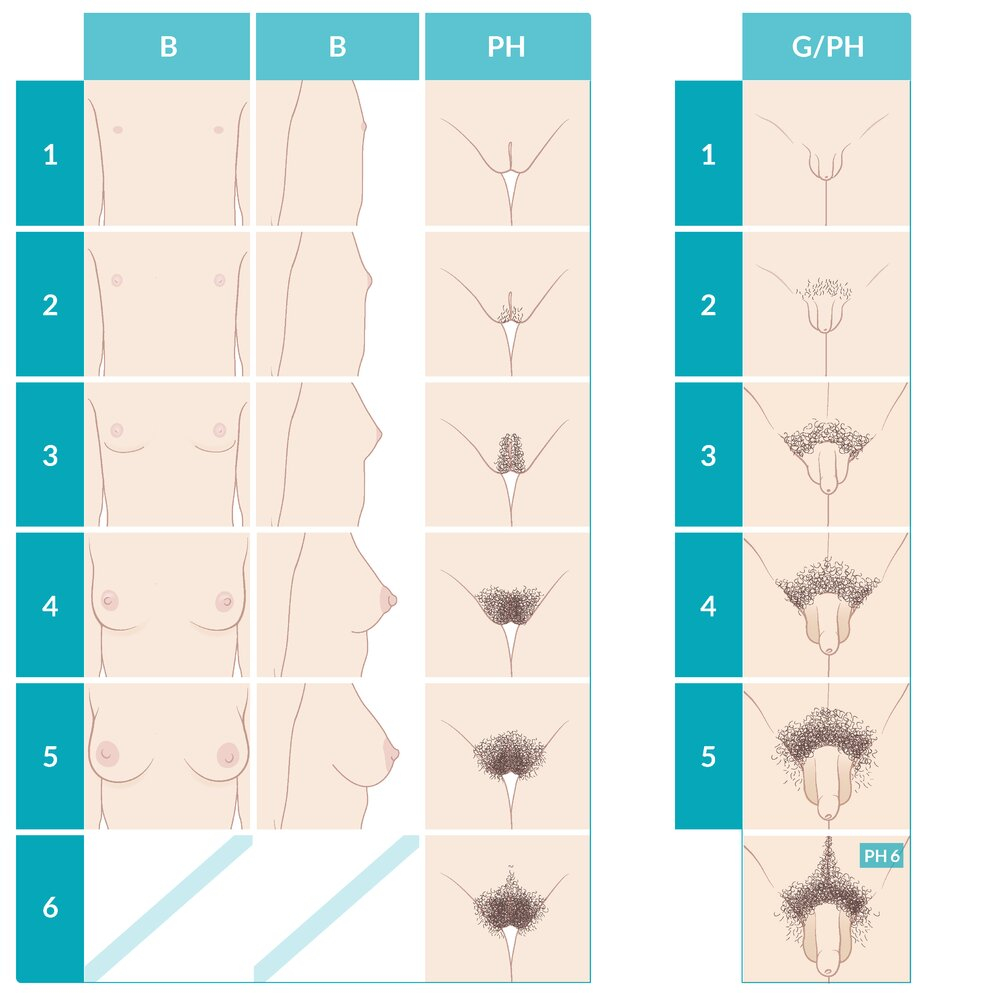
Pubertal changes -Tanner stage-
| Tanner Stages Table | |||
| Stage | Breast Development | Pubic Hair | Age Range |
| 1 | Prepubertal – papilla elevation only | No pubic hair | <8 years |
| 2 | Breast buds – small mound formation, areolar enlargement | Sparse, lightly pigmented hair on labia majora | 8–11 years |
| 3 | Further breast enlargement, no separation of contours | Dark, coarse, curly hair over mons pubis | 9–12 years |
| 4 | Secondary mound – areola and nipple form separate mound | Adult-type hair, no spread to medial thighs | 10–14 years |
| 5 | Adult contour – areola recedes to breast contour | Adult distribution extending to medial thighs, not up linea alba | 12–16 years |
| Note | |
| Tanner staging is the gold standard for assessing pubertal development. It evaluates breast development and pubic hair in girls, and genital development and pubic hair in boys. | ملاحظة |
Precocious puberty
- Definition: A condition in which onset of pubertal development begins earlier than normal population — typically before age 8 in girls and before age 9 in boys.
- Classification:
- Central precocious puberty:
- Pathophysiology
- Gonadotropin-dependent precocious puberty
- Early activation of hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis → ↑GnRH → ↑LH/FSH → ↑sex hormones
- Causes: idiopathic (most common), CNS lesions (25%, most commonly is craniopharyngioma), systemic condition like (tuberous sclerosis, neurofibromatosis).
- Note: most common cause in girls is idiopathic (85-90%) while in boys is CNS lesions (60%)
- Clinical picture: normal symmetric development of secondary sexual characteristics but at an early age.
- Diagnosis:
- Lab:
- Serum LH and FSH: increased
- GnRH stimulation test (gold standard, increase in LH levels after GnRH administration)
- Estradiol level: increased
- Imaging:
- X-ray of the nondominant hand and wrist (increase bone age)
- MRI/CT of the brain with contrast if increased LH is confirmed (to rule out CNS lesions).
- Lab:
- Treatment:
- GnRH agonist (e.g., leuprolide, buserelin, goserelin).
- Treat underlying cause
- Pathophysiology
- Peripheral precocious puberty
- Pathophysiology
- Gonadotropin-independent precocious puberty, peripheral pseudopuberty
- Autonomous sex hormone production → negative feedback → ↓LH/FSH
- Causes: HCG-producing tumors (granulosa cell tumors and follicular cysts), congenital adrenal hyperplasia, McCune Albright syndrome (increase estrogen production), and exogenous estrogen exposure
- Clinical picture: not following the normal secondary sexual development.
- Diagnosis:
- Lab:
- FSH and LH decreased
- GnRH stimulation test (no increase in LH levels after GnRH administration)
- Imaging:
- X-ray (accelerated bone growth)
- Pelvic/abdominal ultrasound
- Adrenal CT/MRI if indicated
- Treatment:
- Treat underlying cause
- Androgen or estrogen antagonist therapy.
- Surgical intervention: For tumors
- Lab:
- Pathophysiology
- Central precocious puberty:
| Note | |
|
🎯 TOP 5 MUST-KNOW FACTS
|
ملاحظة |
Delayed puberty
- Definition: Absent breast development by age 13 OR absent menstruation by age 14 OR within 3 years of breast development
- Causes:
- Constitutional delay of puberty (most common cause, physiological cause)
- Genetic disorders (ex. Turner syndrome)
- Hypergonadotropic hypogonadism
- Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (ex. Kallman syndrome “genetic cause”)
- Certain chronic disorders (eg, diabetes mellitus, inflammatory bowel disorders, renal disorders, CF, anemia)
- Autoimmune disorders (eg, Hashimoto thyroiditis)
- Basic Pathophysiology
Delayed Puberty: Levels of Dysfunction Level of Dysfunction Mechanism LH/FSH Levels Sex Hormone Levels Constitutional Delay Normal but delayed HPG axis maturation Low (prepubertal) Low Hypogonadotropic Hypothalamic/pituitary dysfunction Low Low Hypergonadotropic Primary gonadal failure High Low - Diagnosis:
- Best initial test: Bone age X-ray (left hand/wrist)
- Most important labs: LH, FSH, estradiol (girls), genetic testing
- Initial Laboratory Workup
Hormonal Evaluation in Delayed Puberty Test Purpose Normal Values Interpretation ★ LH, FSH Classify hypo vs hypergonadotropic Prepubertal: <2 IU/L High = primary gonadal failure Testosterone (boys) Assess gonadal function Prepubertal: <50 ng/dL Low with high LH/FSH = primary failure Estradiol (girls) Assess ovarian function Prepubertal: <20 pg/mL Low with high LH/FSH = ovarian failure Prolactin Rule out prolactinoma <25 ng/mL Elevated suggests pituitary adenoma TSH, T4 Rule out hypothyroidism TSH: 0.5–5.0 mIU/L Hypothyroidism can delay puberty
- Treatment:
- Constitutional delay of puberty: reassurance
- Treat the underlying cause
- May include hormone therapy (e.g., testosterone, estrogen)
احصل على التجربة الكاملة
اشترك للوصول لفيديوهات الشرح التفصيلي والبطاقات التعليمية التفاعلية وأسئلة الممارسة مع تتبع التقدم.