سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Background
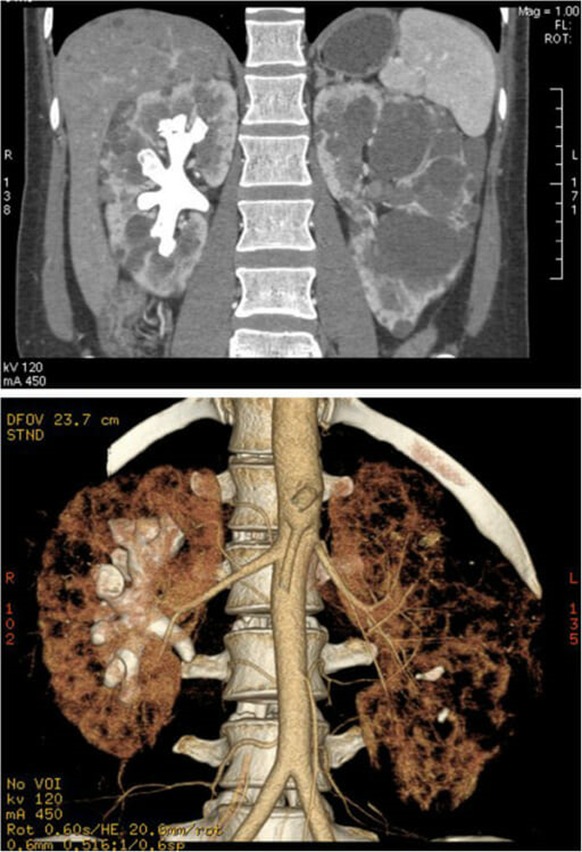
- Nephrolithiasis describes the formation of all types of urinary stones (calculi) in the kidney
- Renal stones are formed secondary to substance precipitation affecting the kidney and the ureter
- Risk factors include: dehydration and high sodium, hyperuricemia and low potassium diets
- Renal stones are more common in men
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
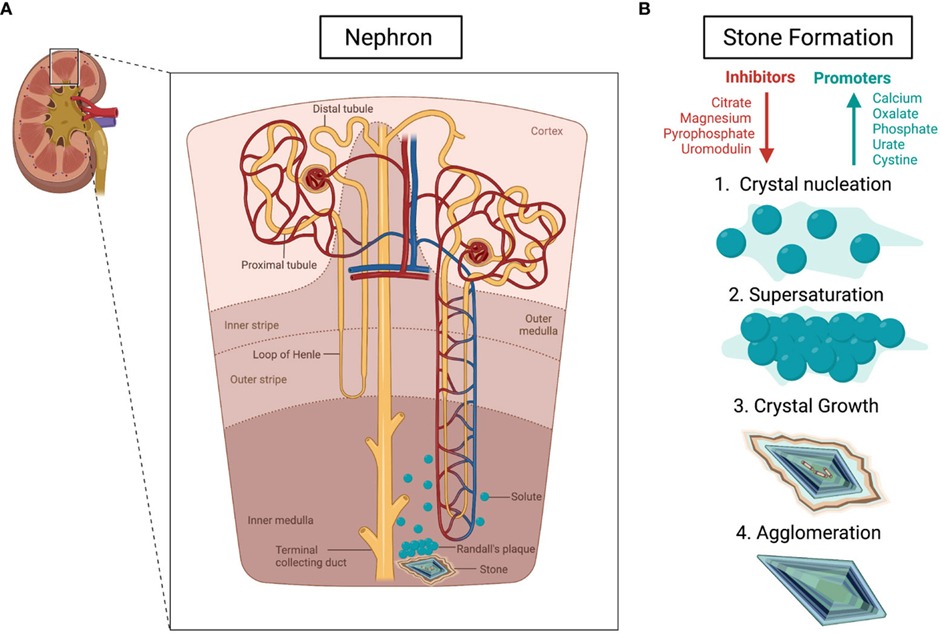
Risk factors
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Hypocitraturia
- Hyperoxaluria
- Indwelling catheter
- Urinary tract infections
- Malabsorption (eg, Crohn’s disease)
- Low fluid intake
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Clinical features
- Colicky flank pain radiating to groin or lower abdomen
- Dysuria
- Urgency and frequency
- Hematuria
- Unilateral flank/ lower abdominal tenderness
- Costovertebral angle (CVA) tenderness
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
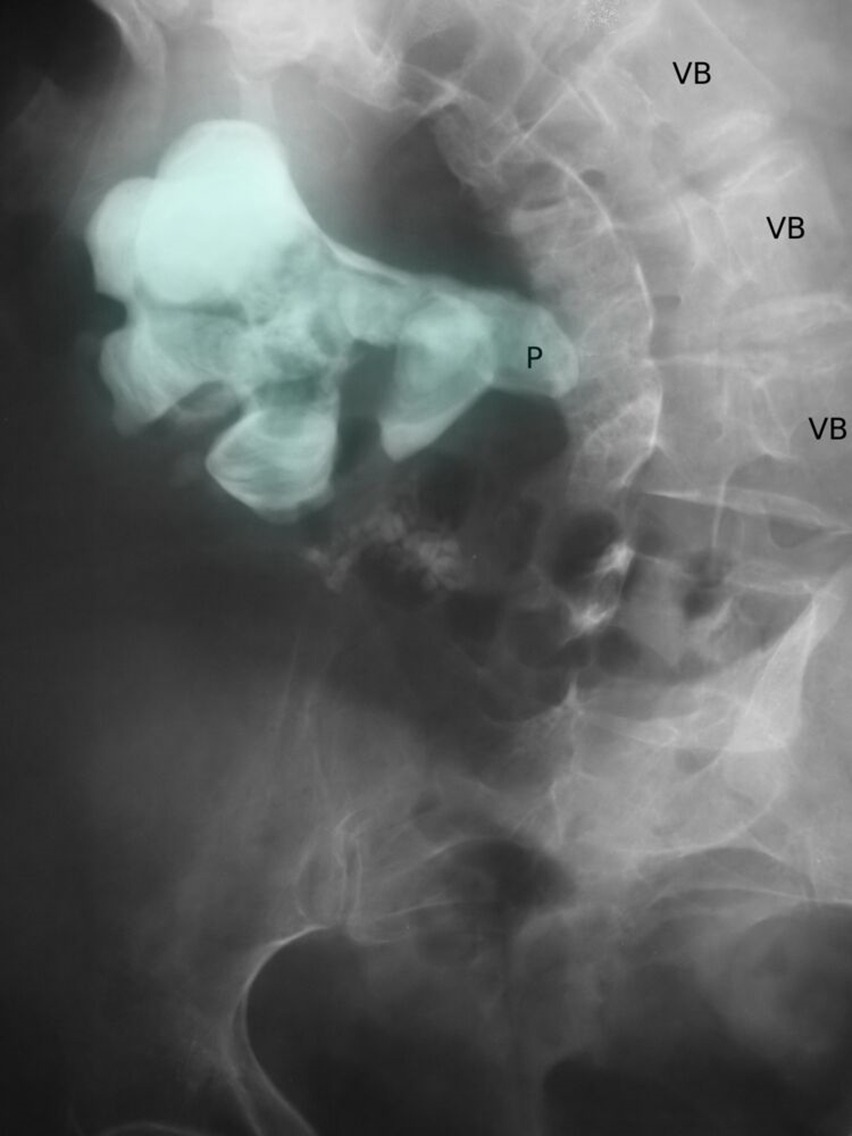
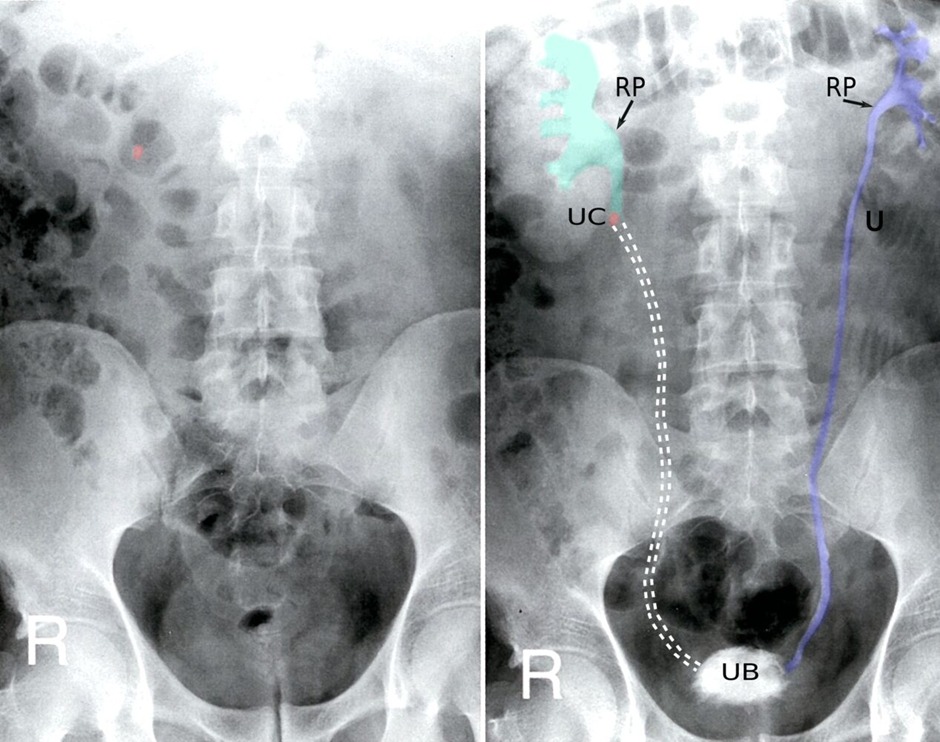
Diagnosis
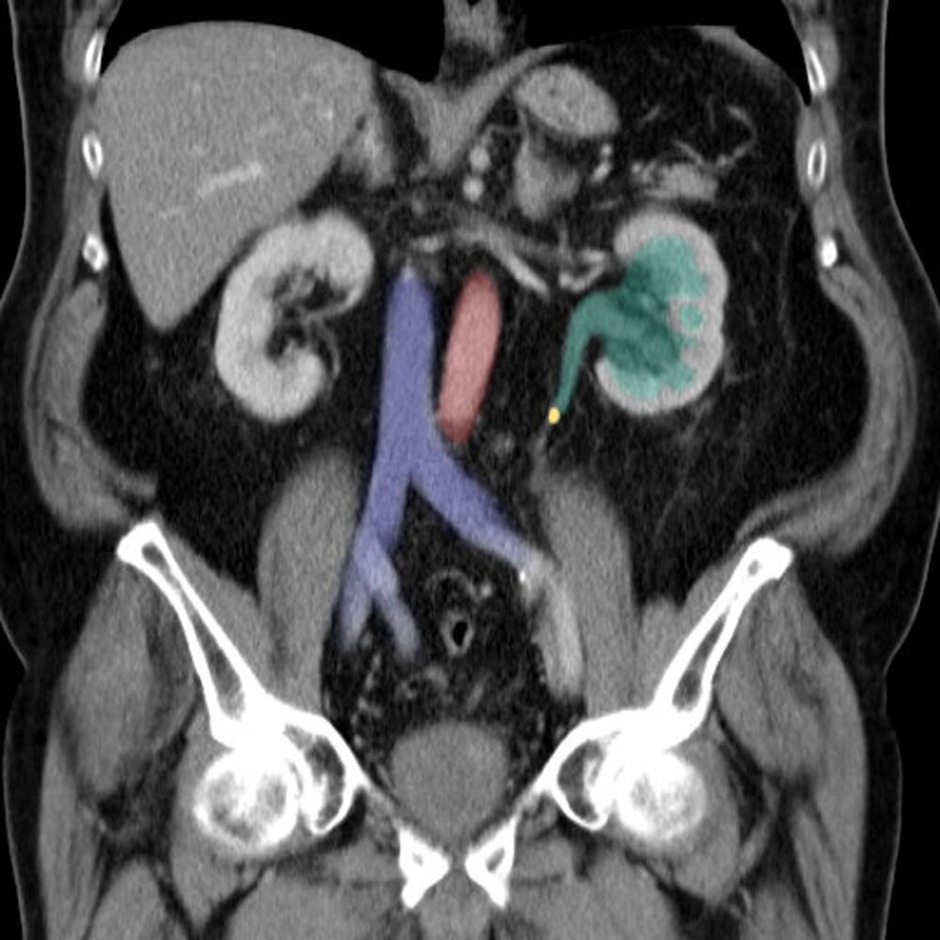
Imaging
- Renal ultrasound (in patients who are pregnant and children)
- Non-contrast computerised tomography (CT)
Labs
- Serum: creatinine, Uric acid and ionized calcium
- Urinalysis/dipstick (urine pH)
- Stone composition analysis
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Differential diagnosis
- Urinary tract infections
- Acute pyelonephritis
- Hernia
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Treatment
Medical treatment
- Analgesia, bed rest, and intravenous fluids (first line in uncomplicated nephrolithiasis < 10 mm)
- Alpha blockers or calcium channel blockers (relaxes the ureter)
Surgical treatment
- Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (preferred for renal stones < 2 cm - Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (preferred for renal > 2 cm)
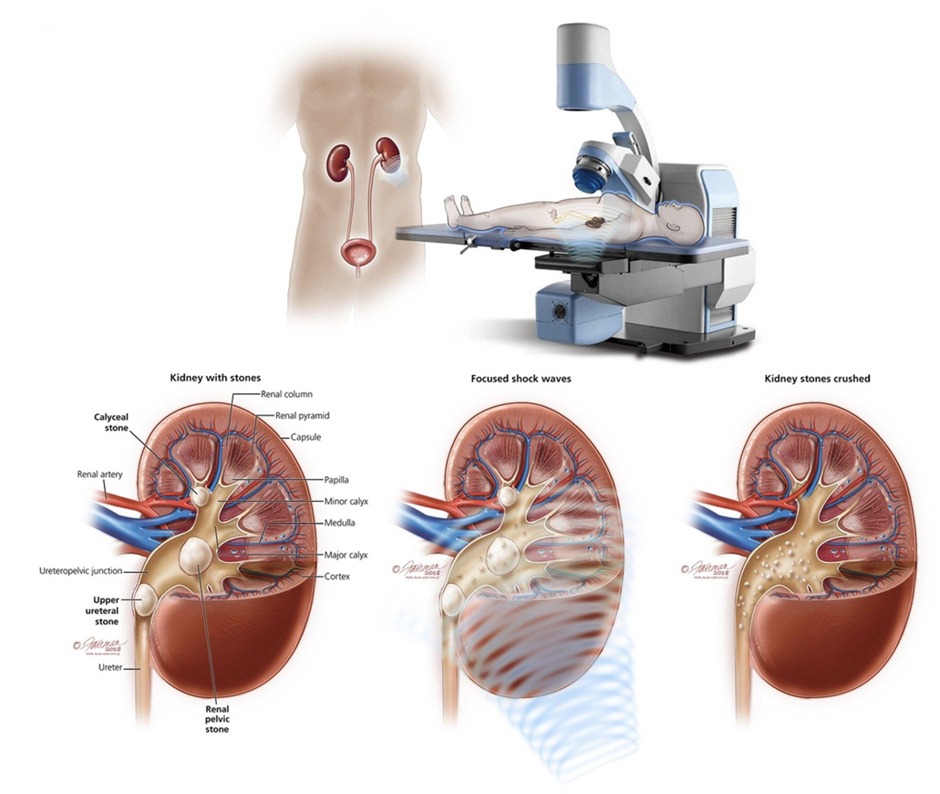
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Complications
- Ureteral obstruction
- Ureteral stricture
- Hydronephrosis
- Urinary tract infection
- Pyelonephritis
- Renal deterioration
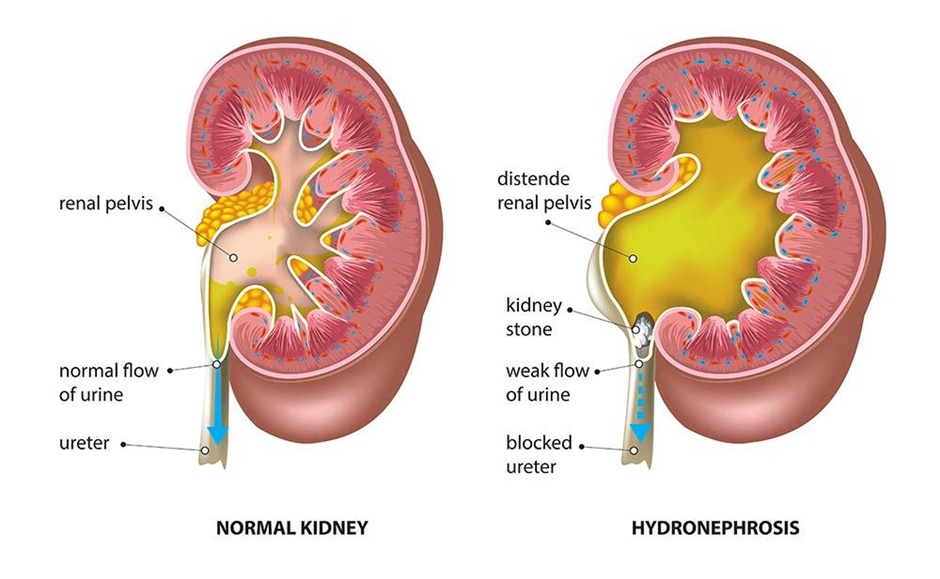
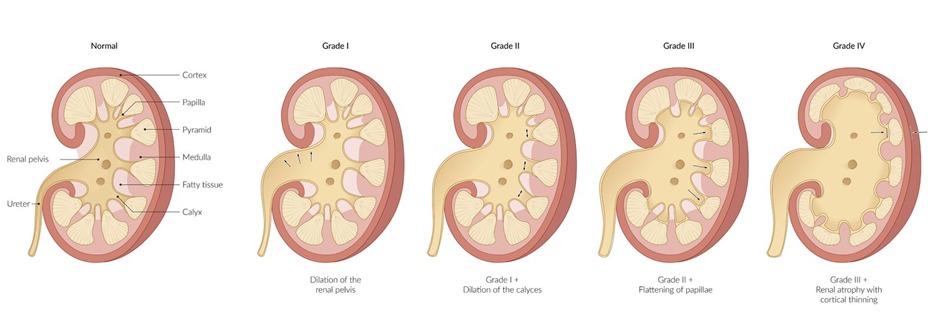
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Supplementary tables
- Table 1: Content, pH and imaging findings for primary renal stones
| Content | pH | X-ray findings | CT findings |
| Calcium | Calcium oxalate (Low pH)/ Calcium phosphate (High pH) | Radiopaque | Radiopaque |
| Ammonium magnesium phosphate | High pH | Radiopaque | Radiopaque |
| Uric acid | Low pH | Radiolucent | Minimally visible |
| Cystine | Low pH | Radiolucent | Sometimes visible |
- Table 2: Stone type, urine crystal and notes
| Stone type | Urine crystal | Notes |
| Calcium oxalate | Envelope/dumbell |
|
| Calcium phosphate | Wedge shaped prism |
|
| Ammonium magnesium phosphate (struvite) | Coffin lid |
|
| Uric acid | Rhomboid or rosettes |
|
| Cystine | Hexagonal |
|
- Table 3: Dietary interventions for calcium stones
| Dietary interventions for calcium stones | ||
| Intervention | Mechanism | |
| Increase | Calcium |
|
| Fluid |
|
|
| Citrate |
|
|
| Fruits and vegetables |
|
|
| Decrease | Sodium |
|
| Animal protein |
|
|
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
احصل على التجربة الكاملة
اشترك للوصول لفيديوهات الشرح التفصيلي والبطاقات التعليمية التفاعلية وأسئلة الممارسة مع تتبع التقدم.
فيديوهات الشرح
بطاقات تفاعلية
أسئلة ممارسة
اشترك الآن