سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Background
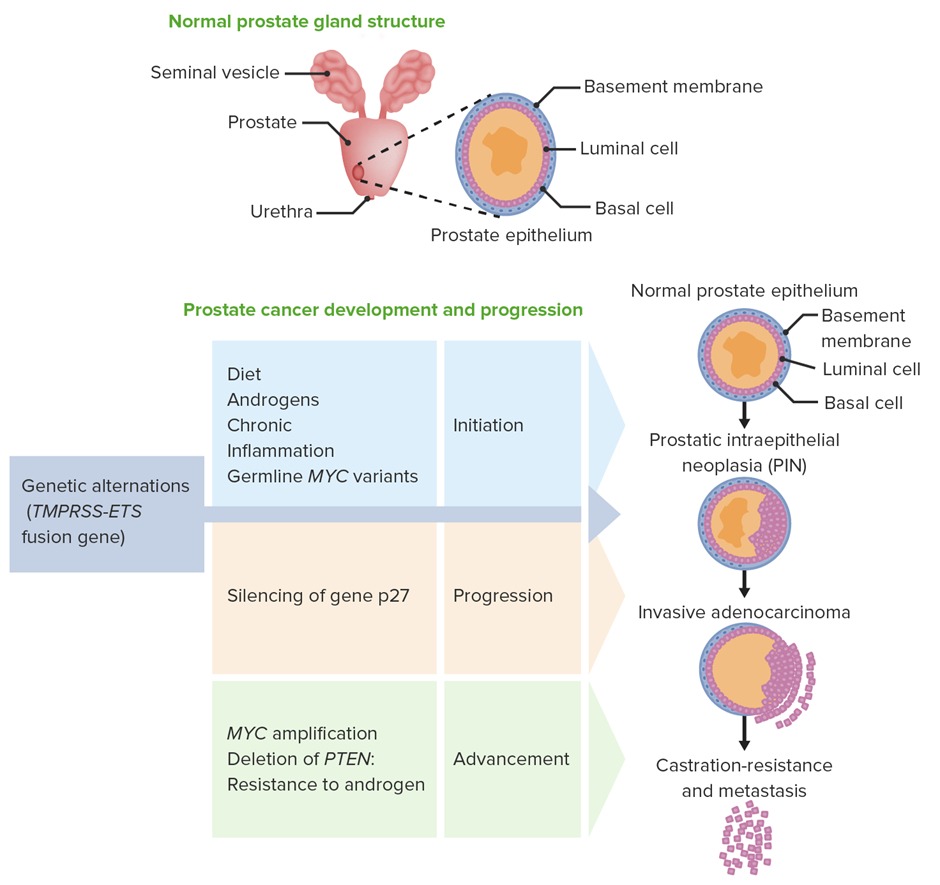
- Prostatic cancer is a malignancy arising from the prostate gland (mostly adenocarcinoma)
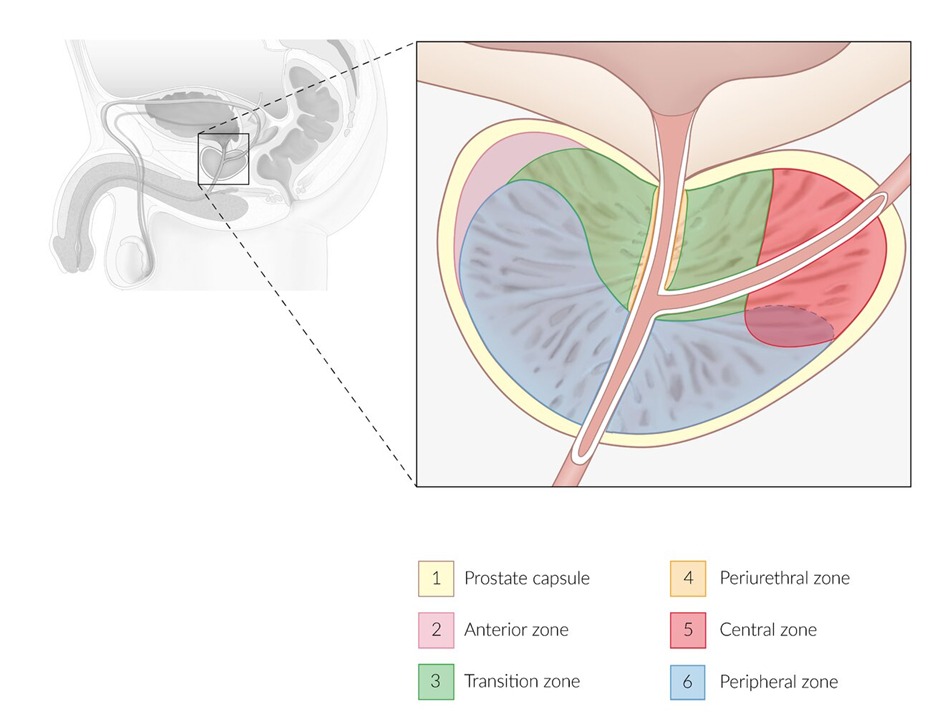
- It arises most commonly in the posterior lobe (peripheral zone)
- Risk factors include; increasing age ( > 50-60 years of age), family history or black race
- It is frequently diagnosed by Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) increase and a biopsy (transrectal ultrasound guided multiple biopsies)
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Clinical features
- It often presents with;
- Asymptomatic in most cases
- Lower urinary tract symptoms (urinary retention)
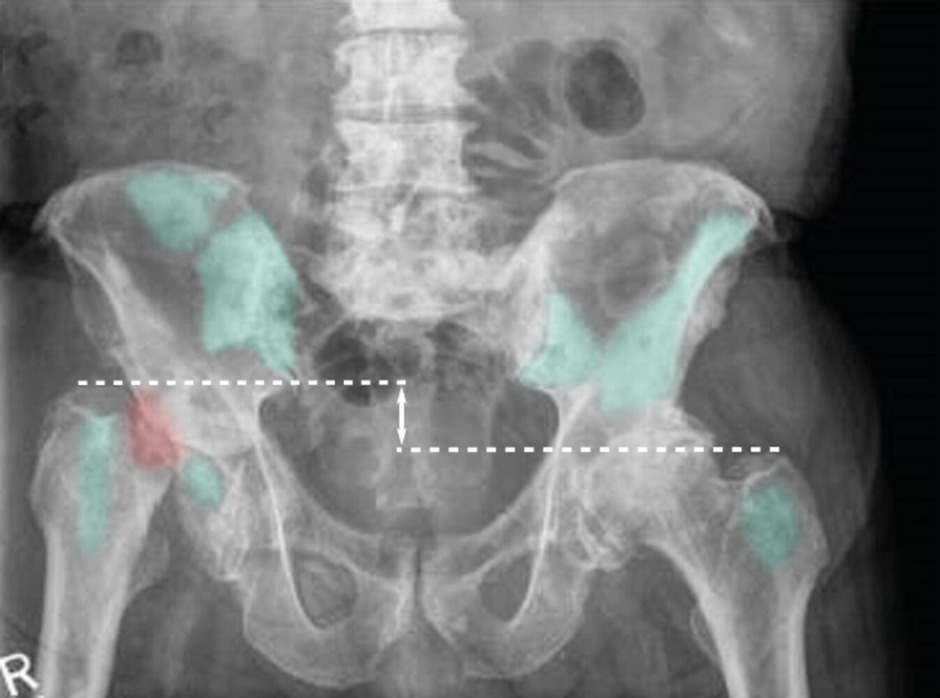
- It can metastasize to the bone (Osteoblastic metastases in bone may develop in late stages, as indicated by lower back pain and increase serum ALP and PSA)
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Diagnosis
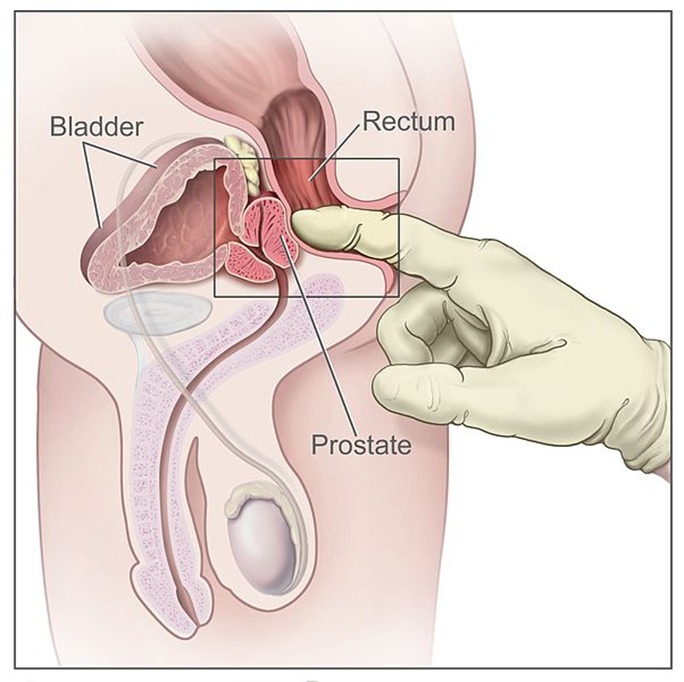
- Digital rectal examination (DRE)
- Serum labs
- Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is not specific for malignancy (can be elevated in benign prostatic hyperplasia)
- Alkaline phosphatase (suggestive of bony metastases)
- Invasive studies
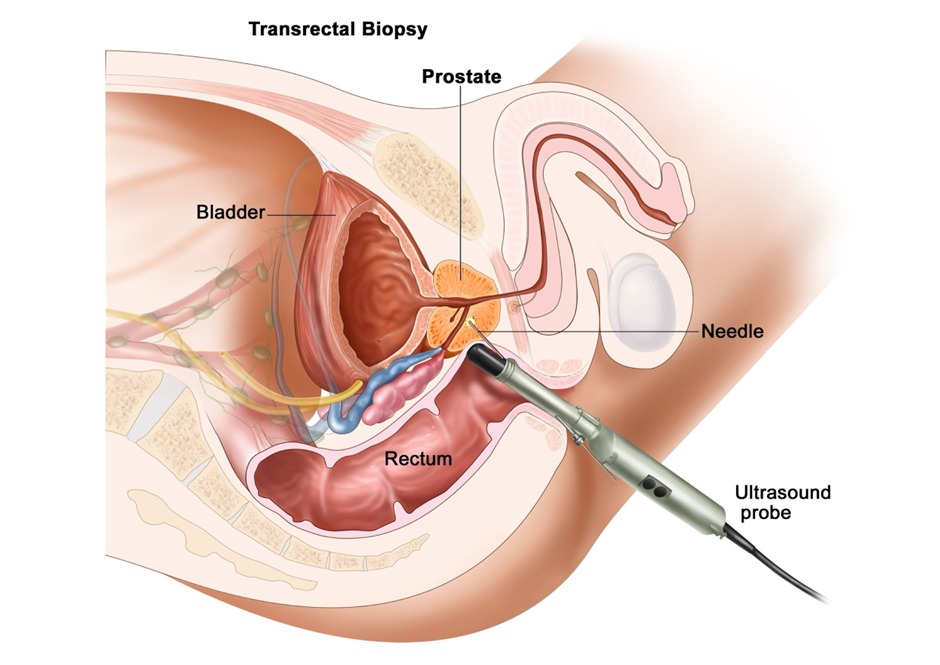
- Transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) guided multiple biopsies
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
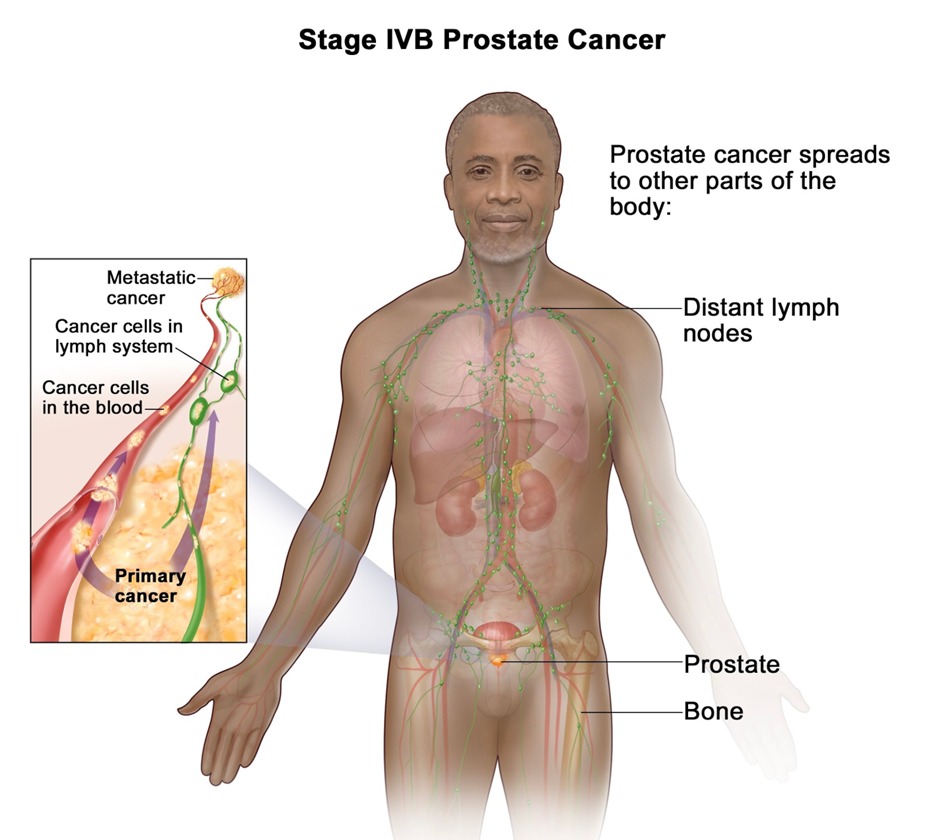
Prostate cancer staging
| Prostate cancer stages | |
| Stage 1 (localised) |
|
| Stage 2 (localised) |
|
| Stage 3 (Locally, advanced) |
|
| Stage 4 (Metastatic/Advanced) |
|
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Differential diagnosis
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Treatment
- Treatment is dependent on pathological features, metastasis, and the patient’s life expectancy
- Androgen deprivation therapy (if a patient is already on maintenance GnRH therapy, external beam radiation therapy is used to treat symptomatic metastasis)
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
Supplementary tables
- Table 1: laboratory investigations for prostate cancer workup
Test parameter Significance CBC - Anaemia, pancytopenia due to bone marrow involvement or chronic diseases
PSA - Elevated levels may indicate prostate cancer
Alkaline Phosphatase - Bone metastasis
Electrolytes - Kidney function, bladder obstruction
Liver function tests, Albumin - Ability to treat with anti-androgen medication
LDH - Prognostic value in metastatic disease; elevated levels associated with lower overall survival in castrate-sensitive and castrate-resistant prostate cancer
- Table 2: comparison of benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Prostate cancer Risk factors - Age > 50 years
- Age > 40 years, African American and positive family history
Affected part - Central portion (transitional zone)
- Usually peripheral zone of prostate but can be anywhere
Examination - Symmetrically enlarged and smooth prostate
- Can have elevated PSA
- Asymmetrically enlarged, nodules and firm prostate
- Markedly elevated PSA
سجل دخولك لإضافة ملاحظات خاصة لكل قسم
· اشترك الآن
احصل على التجربة الكاملة
اشترك للوصول لفيديوهات الشرح التفصيلي والبطاقات التعليمية التفاعلية وأسئلة الممارسة مع تتبع التقدم.
فيديوهات الشرح
بطاقات تفاعلية
أسئلة ممارسة
اشترك الآن