شرح المدرسين
Summary
Hypoparathyroidism is defined as reduced parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels due to poor function of the parathyroid glands . The cause of hypoparathyroidism is most commonly iatrogenic following neck surgery, but it can also be associated with genetic or autoimmune disorders as well as infiltrative diseases causing destruction of the normal parathyroid tissue. Deficiency of PTH results in hypocalcemia , which leads to increased neuromuscular excitability and osteosclerosis , as well as cardiac and neuropsychiatric manifestations. Treatment is based on calcium and vitamin D supplementation.
Causes
- Iatrogenic (most common cause):
- Thyro/parathyroidectomy
- Neck dissection
- Radiation
- Idiopathic/familial hypoparathyroidism
- Autoimmune parathyroid destruction: autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1
- Genetic: DiGeorge syndrome (triad of: conotruncal cardiac anomalies, hypoplastic thymus (→ T cell immunodeficiency), and hypocalcemia (from parathyroid hypoplasia)
- Infiltrative disease of the parathyroid glands :
- Hemochromatosis
- Wilson’s disease
Clinical features
Acute manifestations
- Symptoms of hypocalcemia, such as tetany (see "Clinical features of hypocalcemia.")
Chronic
- Basal-ganglia calcifications:
- Parkinsonism
- Dementia
- Coarse, brittle hair and dry skin
- Tetanic cataracts (paradox intraocular lens calcification)
- Decreased insulin secretion
- Osteosclerosis, cortical thickening, craniofacial abnormalities
- Dental abnormalities when hypocalcemia is present in early childhood
- Idiopathic familial hypoparathyroidism may be associated with immune disorder and moniliasis.

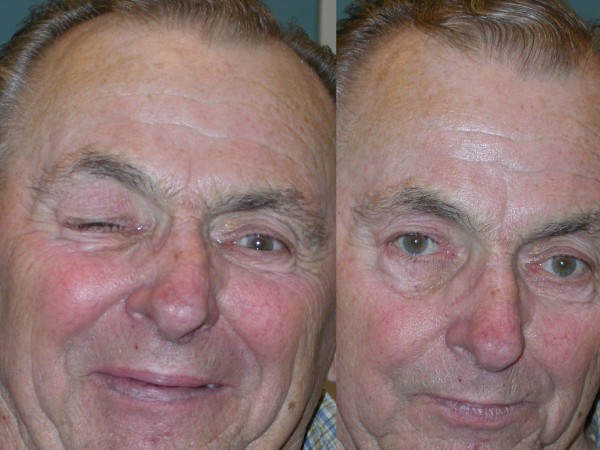
Diagnosis
History:
- Recent neck surgery/ thyroidectomy / parathyroidectomy
- Family history
- Genetic syndromes
Physical exam:
- Chvostek’s sign: Tapping on the facial nerve in the area of the cheek results in the twitching of the mouth musculature.
- Trousseau’s sign: muscle spasms of the hand (“claw”) after BP-cuff inflation of the arm
- Dry, puffy skin
- Alopecia , thin/brittle hair
Laboratory studies:
- ↓ Serum PTH levels
- ↓ Ca and ↑ phosphate levels in serum
- ↓ Phosphate levels in urine
- Urine Ca level can be low or high depending on the degree of serum Ca correction.
- Document normal levels of serum magnesium , creatinine , and 25-hydroxyvitamin D
Differential Diagnosis
- Pseudohypoparathyroidism : an autosomal dominant disorder with end-organ resistance to PTH secondary to a mutation in G protein (GNAS). Parathyroid hormone is secreted normally, but kidneys and bones are resistant to its effects, which leads to hypocalcemia , hyperphosphatemia , and increased serum PTH levels. Treatment is with Ca and vitamin D supplementation.
- Secondary hyperparathyroidism : secondary elevation of serum PTH due to hypocalcemia usually associated with CKD . Diagnosis is established based on elevated PTH levels in the setting of hypocalcemia and hyperphosphatemia . Management is focused on treating the underlying disease.
- Hypomagnesemia : low serum magnesium levels. Hypomagnesemia causes hypocalcemia by impairing PTH release in response to low serum Ca levels as well as by inducing bone PTH resistance . Hypocalcemia responds promptly to the restoration of normal magnesium levels.
Treatment
- Treat underlying disease
- Calcium and vitamin D supplementation
- Recombinant human PTH can reduce the amount of supplemental calcium and vitamin D required.
البطاقات التعليمية
البطاقة من 50
تتبع الإجابات يتطلب اشتراك
Iatrogenic causes following neck surgery are the most common cause of hypoparathyroidism
Specific iatrogenic causes include:
- Thyroidectomy
- Parathyroidectomy
- Neck dissection
- Radiation therapy
تتبع الإجابات يتطلب اشتراك
تتبع الإجابات يتطلب اشتراك
احصل على التجربة الكاملة
اشترك للوصول لفيديوهات الشرح التفصيلي والبطاقات التعليمية التفاعلية وأسئلة الممارسة مع تتبع التقدم.
