YourMedPass
أكبر مرجع لامتحان الامتياز الأردني وامتحانات الإقامة
Pseudomembranous colitis
Pseudomembranous colitis is an inflammatory condition of the colon caused by Clostridioides difficile (formerly Clostridium difficile) infection, typically following antibiotic use. The disease is characterized by the formation of yellow-white pseudomembranes on the colonic mucosa. Patients present with watery diarrhea, abdominal pain, and leukocytosis. Diagnosis is confirmed through stool testing for C. difficile toxins or nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT). First-line treatment includes oral fidaxomicin or vancomycin, with surgical intervention reserved for fulminant cases.
Last updated: July 29, 2025
- Pseudomembranous colitis is an acute colonic inflammation caused by toxin-producing Clostridioides difficile bacteria; a gram-positive, anaerobic bacterium
- Characterized by pseudomembrane formation (yellow-white plaques) on colonic mucosa
- Most common cause of healthcare-associated diarrhea
- Occurs primarily after antibiotic disruption of normal colonic flora

- Primary risk factors:
- Recent antibiotic use (within 3 months) ➜ Most important risk factor
- Clindamycin
- Fluoroquinolones
- Broad-spectrum penicillins and cephalosporins
- Advanced age (>65 years)
- Hospitalization or nursing home residence
- Proton pump inhibitor (PPI) use
- Recent antibiotic use (within 3 months) ➜ Most important risk factor
- Additional risk factors:
- Immunosuppression
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Chronic kidney disease
- Previous C. difficile infection
| Important – فكرة سؤال | |
| Post-surgical patient (especially day 5-10) + watery diarrhea + recent antibiotics = High suspicion for C. difficile | تذكر |
- Mechanism:
- Antibiotic disruption of normal colonic flora → C. difficile overgrowth
- Production of toxin A (enterotoxin) and toxin B (cytotoxin)
- Toxins bind to intestinal epithelial cells → disruption of cytoskeleton
- Loss of epithelial barrier function → inflammation and fluid secretion
- Neutrophil recruitment → pseudomembrane formation
- Common symptoms:
- Watery diarrhea (≥3 loose stools/24 hours) ➜ Hallmark symptom
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Fever (15% of cases)
- Anorexia and malaise
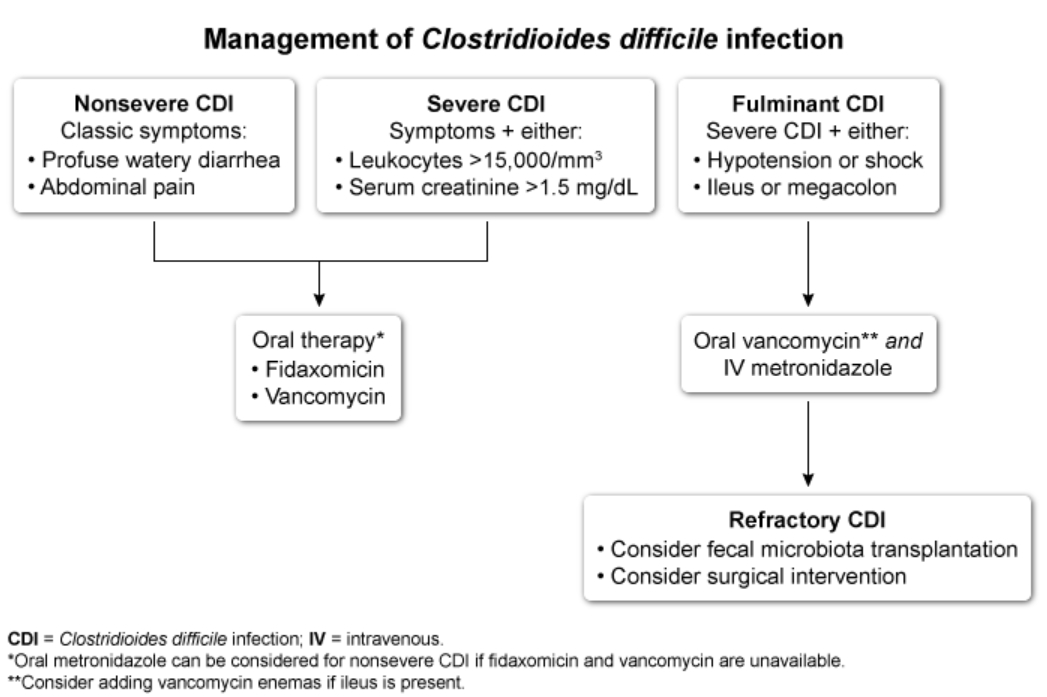
- Disease severity classification:
- Nonsevere: Diarrhea without systemic toxicity
- Severe: WBC >15,000/mm³ OR creatinine >1.5 mg/dL
- Fulminant: Hypotension, ileus, or toxic megacolon
| Important – فكرة سؤال | |
| Recent antibiotic use + watery diarrhea + leukocytosis = Think C. difficile infection | تذكر |
- Initial assessment:
- Clinical suspicion based on risk factors and symptoms
- Laboratory findings: Leukocytosis, hypoalbuminemia
- Stool testing (diagnostic):
- NAAT (Nucleic Acid Amplification Test) (PCR):
- Most sensitive test
- Detects toxin genes
- Cannot differentiate colonization from active infection
- EIA (Enzyme Immunoassay) for toxins:
- High specificity but lower sensitivity
- Detects actual toxin production
- Two-step algorithm: NAAT followed by toxin EIA for confirmation
- NAAT (Nucleic Acid Amplification Test) (PCR):
- Imaging:
- CT abdomen: Colonic wall thickening, "accordion sign"
- Colonoscopy: Shows pseudomembranes (not routinely needed)
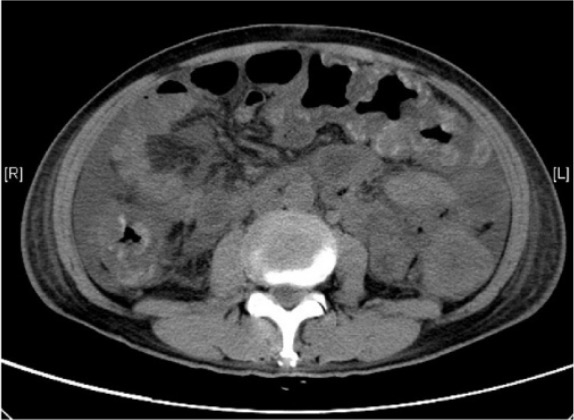
| Important – فكرة سؤال | |
| Stool culture for microscopy and sensitivity is for OTHER causes of diarrhea. For C. difficile, use NAAT/PCR or toxin testing | تذكر |
- General measures:
- Discontinue inciting antibiotic if possible
- Avoid antiperistaltic agents (loperamide)
- Contact isolation
- First-line antibiotics:
- Fidaxomicin PO × 10 days (preferred if available)
- Vancomycin PO × 10 days (NOT IV vancomycin)
- Alternative treatment:
- Metronidazole PO (if fidaxomicin/vancomycin unavailable)
- Fulminant disease:
- High-dose vancomycin PO + metronidazole IV
- Vancomycin enemas if ileus present
- Surgical consultation for possible colectomy
- Recurrent infection:
- Vancomycin taper/pulse regimen
- Fidaxomicin
- Bezlotoxumab (monoclonal antibody)
- Fecal microbiota transplant (multiple recurrences)
| Important – فكرة سؤال | |
|
In pregnancy: Use oral vancomycin, NOT metronidazole (teratogenic) |
تذكر |
- Toxic megacolon
- Colonic dilation >6 cm
- Systemic toxicity
- May require emergency colectomy
- Intestinal perforation
- Septic shock
- Death (mortality 5-10% in severe cases)
- Judicious antibiotic use
- Hand hygiene with soap and water (alcohol-based sanitizers ineffective against spores)
- Contact precautions for infected patients
- Environmental cleaning with sporicidal agents (bleach)
|
Pseudomembranous Colitis - Summary |
|
|
Risk Factors |
|
|
Clinical Features |
|
|
Diagnosis |
|
|
Treatment |
|