YourMedPass
أكبر مرجع لامتحان الامتياز الأردني وامتحانات الإقامة
Diffuse Esophageal Spasm
Diffuse esophageal spasm (DES) is an esophageal motility disorder characterized by uncoordinated, simultaneous contractions of the esophageal smooth muscle. Unlike normal peristalsis, these contractions occur spontaneously throughout multiple segments of the esophagus, preventing proper food passage. Patients typically present with intermittent chest pain that can mimic cardiac angina and dysphagia to both solids and liquids. The chest pain is often triggered by hot or cold beverages and emotional stress.
Diagnosis is established through esophageal manometry showing simultaneous, non-peristaltic contractions with normal lower esophageal sphincter (LES) relaxation. Barium swallow may reveal the characteristic “corkscrew” or “rosary bead” appearance during spasms. Treatment focuses on reducing esophageal smooth muscle contractions with calcium channel blockers as first-line therapy, followed by nitrates or tricyclic antidepressants if needed.
Last updated: July 25, 2025
- Diffuse esophageal spasm (DES) is a primary esophageal motility disorder characterized by simultaneous, uncoordinated contractions of the esophageal body تقلصات متزامنة وغير منسقة في جسم المريء
- These abnormal contractions prevent normal peristaltic waves, causing difficulty in food passage
- The condition affects middle-aged adults (typically 40-60 years) with equal gender distribution
- Often associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and anxiety disorders
- Can present with chest pain severe enough to mimic myocardial infarction ألم صدري يشبه النوبة القلبية
- Primary (Idiopathic): Most cases have no identifiable cause
- Associated conditions:
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) - present in up to 50% of cases
- Anxiety and depression اضطرابات القلق والاكتئاب
- Emotional stress الضغط النفسي
- Triggers ➜ Important for exam:
- Hot or cold beverages المشروبات الساخنة أو الباردة
- Carbonated drinks
- Red wine
- Acidic foods
- Emotional stress
| Important – فكرة سؤال | |
| Temperature extremes (hot/cold beverages) are classic triggers for DES symptoms - this helps differentiate it from other causes of chest pain | تذكر |
- Impaired inhibitory innervation:
- Loss of nitric oxide (NO) producing neurons in myenteric plexus
- Decreased endogenous NO synthesis → loss of smooth muscle relaxation
- Imbalance between excitatory (cholinergic) and inhibitory (NO, VIP) neurotransmitters
- Result:
- Simultaneous, non-peristaltic contractions تقلصات متزامنة غير تمعجية
- High-amplitude contractions in multiple esophageal segments
- Normal LES function (unlike achalasia)
- Intermittent symptoms due to episodic nature of spasms
- Chest pain ألم الصدر ➜ Most common symptom
- Retrosternal, squeezing quality
- Can radiate to back, arms, jaw (mimics angina)
- Triggered by hot/cold beverages, stress
- Episodes last seconds to minutes (occasionally hours)
- Not related to exertion عدم الارتباط بالمجهود البدني
- May respond to nitroglycerin (confusing with cardiac pain)
- Dysphagia عسر البلع
- Intermittent, not progressive
- For both solids AND liquids للأطعمة الصلبة والسوائل معاً
- Sensation of food "sticking" in chest
- Other symptoms:
- Regurgitation (less common than in achalasia)
- Globus sensation الإحساس بكتلة في الحلق
- Heartburn (if associated GERD)
| Note | |
| DES presents with dysphagia to BOTH solids and liquids from the beginning, while mechanical obstruction typically starts with solids only | ملاحظة |
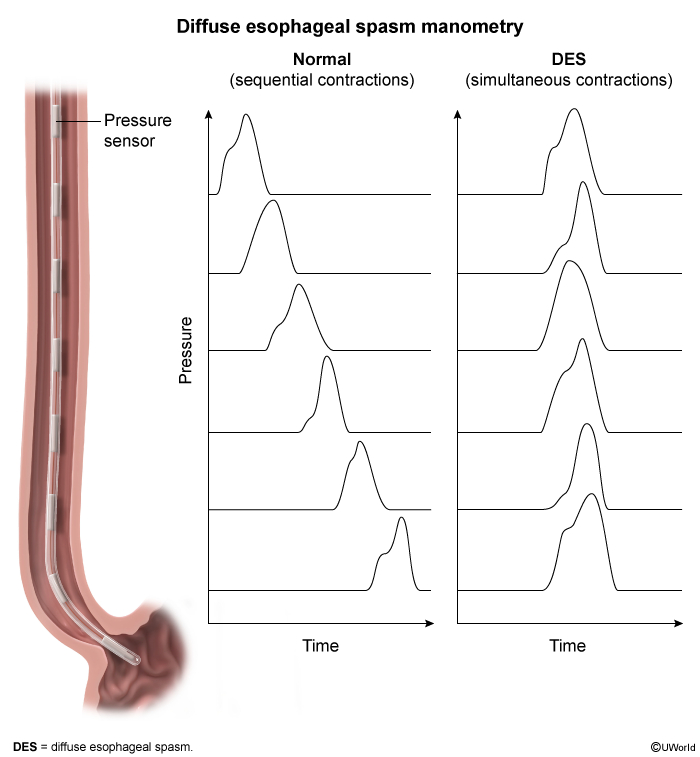
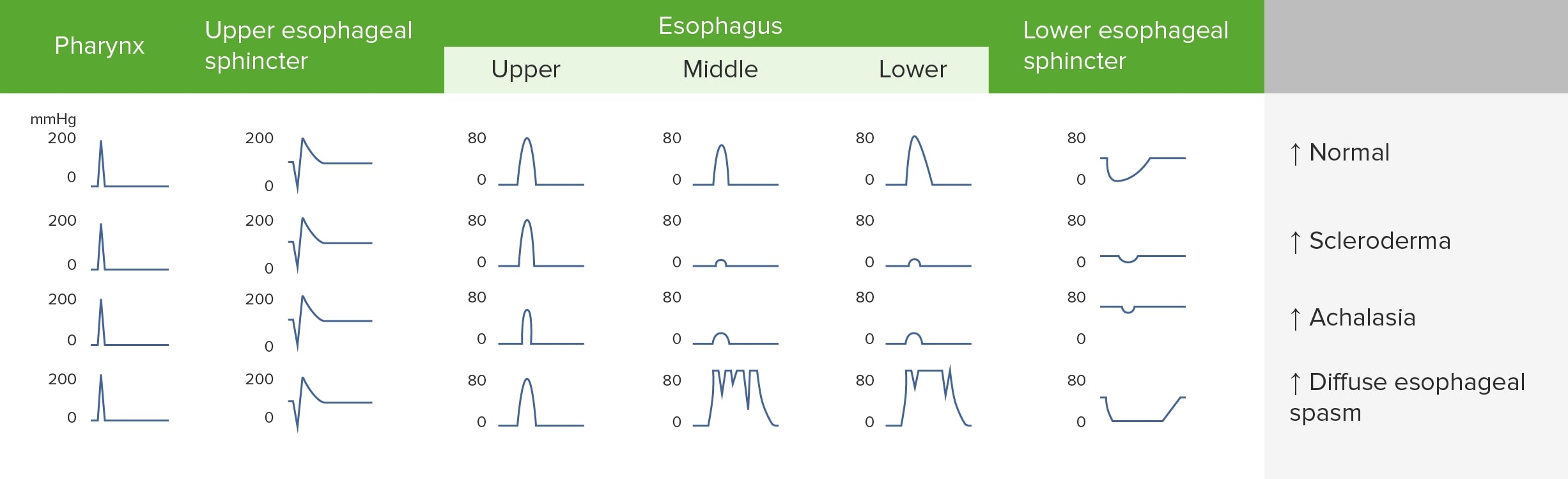
- Esophageal Manometry ➜ Gold standard diagnostic test
- Shows simultaneous, repetitive, non-peristaltic contractions
- ≥20% of swallows with simultaneous contractions (Chicago Classification)
- High amplitude contractions (>30 mmHg)
- Normal LES relaxation (differentiates from achalasia)
- Barium Esophagram
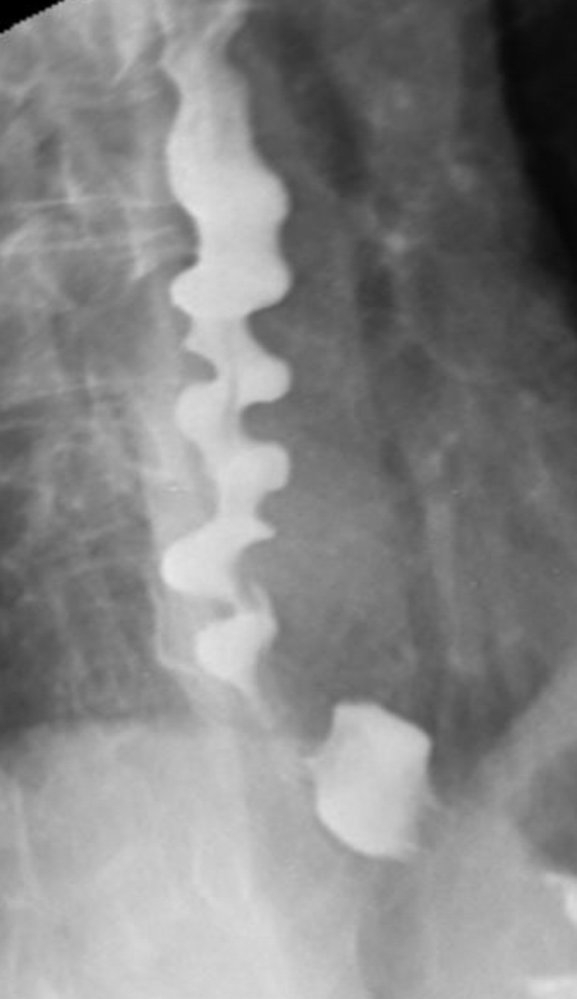
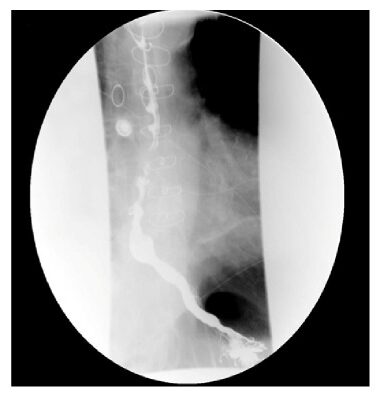
- "Corkscrew" or "rosary bead" appearance المظهر اللولبي
- Only visible during spasm episodes
- Not sensitive or specific (seen in only 30-50% of cases)
- Upper Endoscopy
- Usually normal
- Important to rule out mechanical obstruction, malignancy
- May show esophagitis if concurrent GERD
- Cardiac workup (to exclude cardiac causes):
- ECG, cardiac enzymes, stress test
- Often done first due to chest pain presentation
- الأفكار المهمة والأسئلة المتكررة:
- الفحص الأدق هو Esophageal Manometry
- المظهر اللولبي "Corkscrew" في الأشعة مميز لكن غير موجود دائماً
- يجب استبعاد الأسباب القلبية أولاً بسبب تشابه الأعراض
- الــ LES طبيعي على عكس Achalasia
- First-line therapy:
- Calcium channel blockers (e.g., diltiazem, nifedipine)
- Reduce smooth muscle contractility
- Decrease amplitude and frequency of contractions
- 60-70% response rate
- Calcium channel blockers (e.g., diltiazem, nifedipine)
- Second-line options:
- Nitrates (sublingual or long-acting)
- Relax smooth muscle
- Side effects may limit use
- Tricyclic antidepressants (low dose)
- Especially if concurrent anxiety/depression
- May have visceral analgesic effects
- Peppermint oil النعناع
- Natural smooth muscle relaxant
- Nitrates (sublingual or long-acting)
- Additional management:
- Proton pump inhibitors (if concurrent GERD)
- Avoid triggers (hot/cold beverages, stress)
- Stress management, psychological support
- Refractory cases:
- Botulinum toxin injection (endoscopic)
- Temporary effect (3-6 months)
- Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) or surgical myotomy
- Reserved for severe, incapacitating symptoms
- Controversial efficacy
- Botulinum toxin injection (endoscopic)
| Important – فكرة سؤال | |
|
Calcium channel blockers are the first-line treatment for DES. Remember that nitrates can also help (which is why DES pain can be confused with cardiac pain) حاصرات قنوات الكالسيوم هي العلاج الأول. تذكر أن النترات تساعد أيضاً وهذا سبب الخلط مع ألم القلب |
تذكر |
| Comparison of Esophageal Motility Disorders | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Feature | DES | Achalasia | Nutcracker Esophagus |
| Primary symptom | Chest pain | Progressive dysphagia | Chest pain |
| Dysphagia | Intermittent, solids + liquids | Progressive, solids + liquids | Occasional |
| LES function | Normal | Impaired relaxation | Normal |
| Manometry | Simultaneous contractions | Aperistalsis + ↑LES pressure | High amplitude, coordinated |
| Barium swallow | "Corkscrew" | "Bird beak" | Usually normal |
- Prognosis:
- Generally benign course
- Symptoms may wax and wane
- No increased risk of esophageal cancer
- Quality of life can be significantly affected
- Complications:
- Weight loss (due to eating avoidance)
- Psychological distress from chronic symptoms
- Misdiagnosis leading to unnecessary cardiac procedures
- Treatment failure is common (30-40% of patients)
| Diffuse Esophageal Spasm | |
|---|---|
| Pathophysiology |
|
| Clinical presentation |
|
| Diagnosis |
|
| Management |
|
| DES = Diffuse Esophageal Spasm; LES = lower esophageal sphincter. | |