YourMedPass
أكبر مرجع لامتحان الامتياز الأردني وامتحانات الإقامة
Hyperaldosteronism
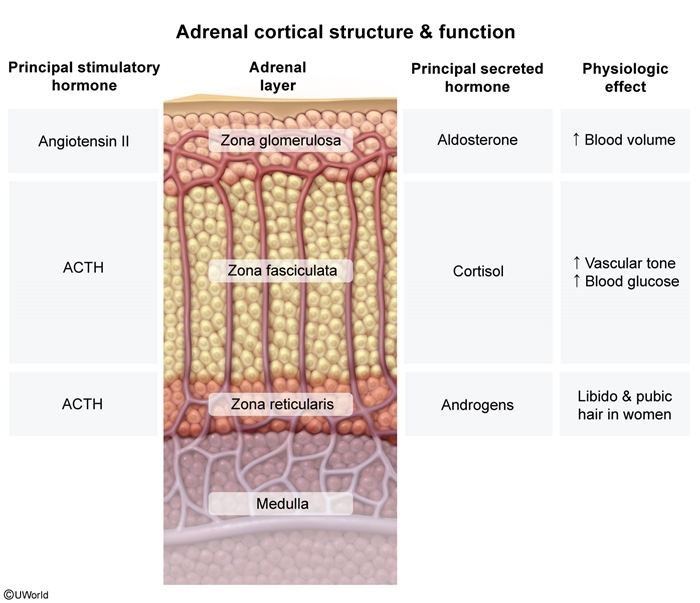
Hyperaldosteronism is defined as the increased secretion of aldosterone from the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex. Hyperaldosteronism may be primary (resulting from autonomous secretion), or secondary (resulting from physiological secretion due to stimulation of the RAAS). Classically, hyperaldosteronism presents with hypertension, hypokalemia, and metabolic alkalosis, although recent studies have suggested that hypokalemia is less common than originally thought in primary hyperaldosteronism. Patients with hypertension who are treatment resistant and/or associated with hypokalemia should be screened for hyperaldosteronism by determining their plasma aldosterone concentration and plasma renin activity. Confirmatory tests and an abdominal CT scan are required to conclusively diagnose primary hyperaldosteronism. Management involves the use of aldosterone receptor antagonists and surgical excision of any aldosterone-secreting tumors.
Last updated: July 20, 2025
Definition: Primary hyperaldosteronism is characterized by autonomous overproduction of aldosterone from the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex, independent of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS).
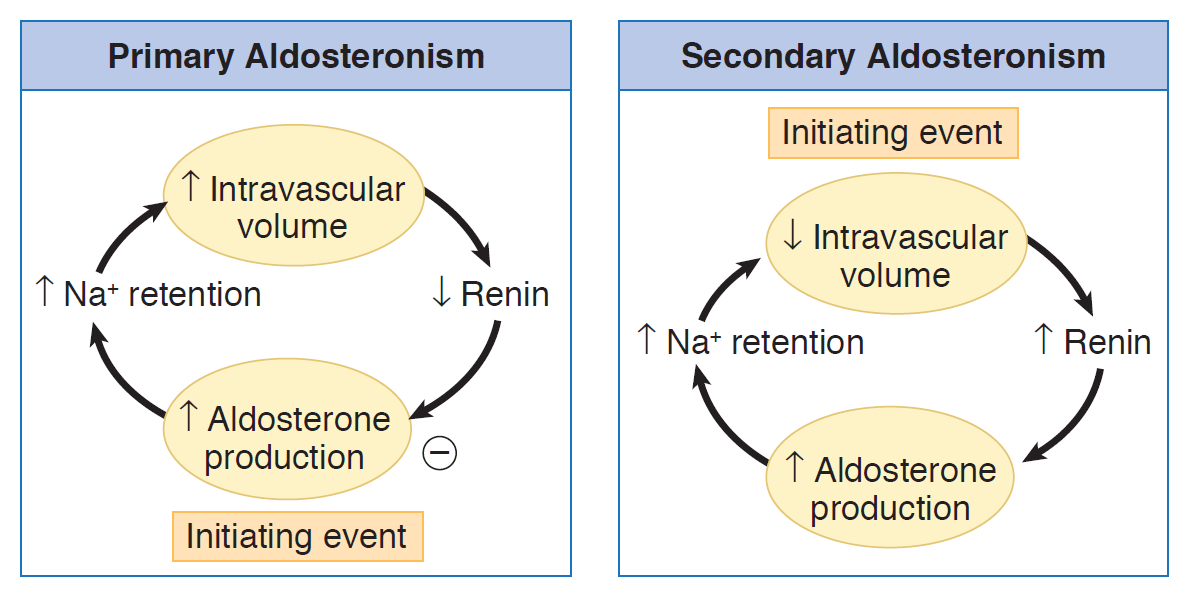
- Primary hyperaldosteronism: autonomous (renin-independent) secretion of aldosterone
- Secondary hyperaldosteronism: physiological oversecretion of aldosterone that occurs in response to overstimulation of the RAAS, triggered by decreases in renal blood flow.
| Key Concept | |
|
ملاحظة |
| Etiology of Hyperaldosteronism | ||
| Type | Etiology | Clinical Features |
| Primary hyperaldosteronism |
|
|
| Secondary hyperaldosteronism |
|
|
Overview: The Role of Aldosterone
Aldosterone is a mineralocorticoid hormone that serves as the body's primary regulator of sodium and water balance. Its fundamental purpose is to increase blood pressure through three key mechanisms:
- ↑ Sodium reabsorption → ↑ Water retention → ↑ Blood volume
- ↑ Potassium excretion
- ↑ Hydrogen ion excretion
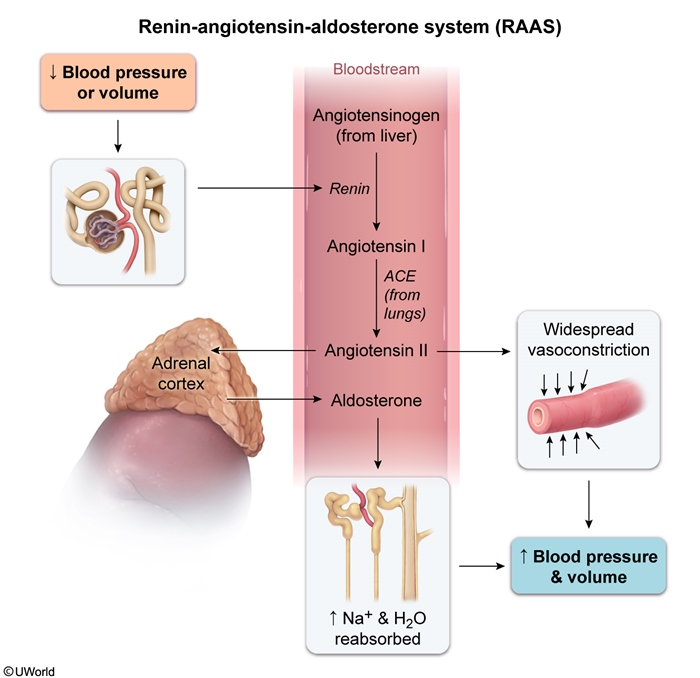
Normal Physiology: The RAAS Cascade
Step 1: Initiation
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) activates when the body senses:
- ↓ Blood pressure or ↓ Effective blood volume
- ↓ Sodium delivery to the distal tubule
- ↑ Sympathetic nervous system activity
Step 2: The Cascade
- Juxtaglomerular cells (kidney) → Release RENIN
- Renin converts Angiotensinogen (liver) → Angiotensin I
- ACE (lungs) converts Angiotensin I → ANGIOTENSIN II
- Angiotensin II stimulates Zona Glomerulosa → ALDOSTERONE
Step 3: Direct Aldosterone Stimulation
Two primary stimuli directly trigger aldosterone release:
- Angiotensin II (via RAAS)
- Hyperkalemia (direct effect on zona glomerulosa)
Net Effects of Aldosterone Action
| Parameter | Effect | Mechanism |
| Blood Pressure | ↑↑ | Volume expansion from Na+/H2O retention |
| Serum Na+ | ↑ | Enhanced renal reabsorption |
| Serum K+ | ↓ | Increased renal excretion |
| Serum pH | ↑ | H+ excretion (metabolic alkalosis) |
Pathophysiology of Hyperaldosteronism
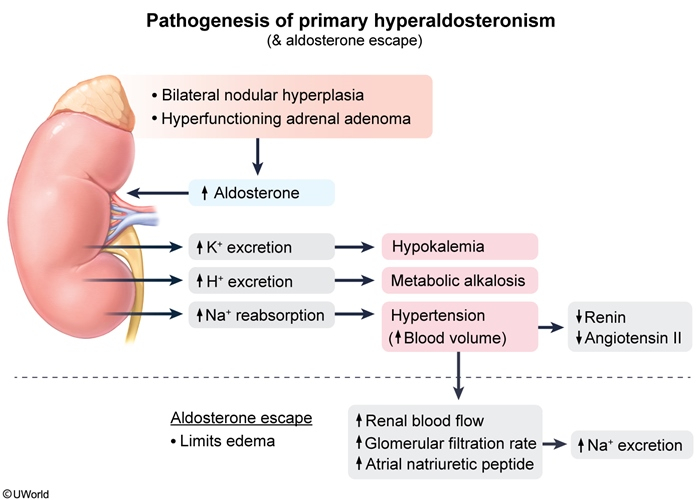
Primary Hyperaldosteronism: Autonomous Secretion
- Key Concept: The adrenal gland produces aldosterone independently of physiologic stimuli
- Sequence of Events:
-
- Autonomous aldosterone production (adenoma or hyperplasia)
- Excessive Na+ and water retention → Hypertension
- Negative feedback suppresses renin → ↓ PRA (key diagnostic feature)
- Continued K+ and H+ excretion → Hypokalemia and alkalosis
- The Aldosterone Escape Phenomenon
Despite continuous aldosterone excess, patients with primary hyperaldosteronism do NOT develop edema: - Initial Na+ retention → ↑ Blood volume
- Volume expansion triggers compensatory mechanisms:
- ↑ Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) release
- ↑ Pressure natriuresis
- ↓ Proximal tubule Na+ reabsorption
- Result: New steady state without edema
Secondary Hyperaldosteronism: Physiologic Response
- ↓ Renal blood flow due to other diseases
- Key Concept: The RAAS is physiologically activated due to decreased renal perfusion
- Common Triggers:
- Heart failure → ↓ Cardiac output
- Cirrhosis → ↓ Effective blood volume
- Renal artery stenosis → ↓ Renal perfusion
- Sequence of Events:
-
- ↓ Renal perfusion sensed by JG cells
- ↑ Renin release → ↑ Angiotensin II → ↑ Aldosterone
- Persistent volume depletion despite Na+ retention
- NO aldosterone escape → Progressive edema ★
Key Pathophysiologic Differences
| Feature | Primary | Secondary |
|---|---|---|
| Initiating event | Autonomous aldosterone | ↓ Renal perfusion |
| Renin levels | Suppressed (↓) ★ | Elevated (↑) ★ |
| Volume status | Euvolemic / mild expansion | Volume depleted |
| Edema | Absent (escape present) | Present (no escape) |
| Pathophysiology | Inappropriate secretion | Physiologic response |

| Pathophysiology Pearls | |
|
ملاحظة |
Due to the effects of aldosterone, clinical presentation includes:
- Hypertension, often resistant to treatment.
- Hypokalemia: Serum potassium may be normal at baseline, but severe hypokalemia can be triggered by diuretic therapy.
- Mild hypernatremia may be present.
- Metabolic alkalosis.
Peripheral edema may be mild or absent due to aldosterone escape (increased intravascular volume increases pressure natriuresis and atrial natriuretic peptide release, thereby limiting net sodium retention)
| Clinical Pearls | |
|
ملاحظة |
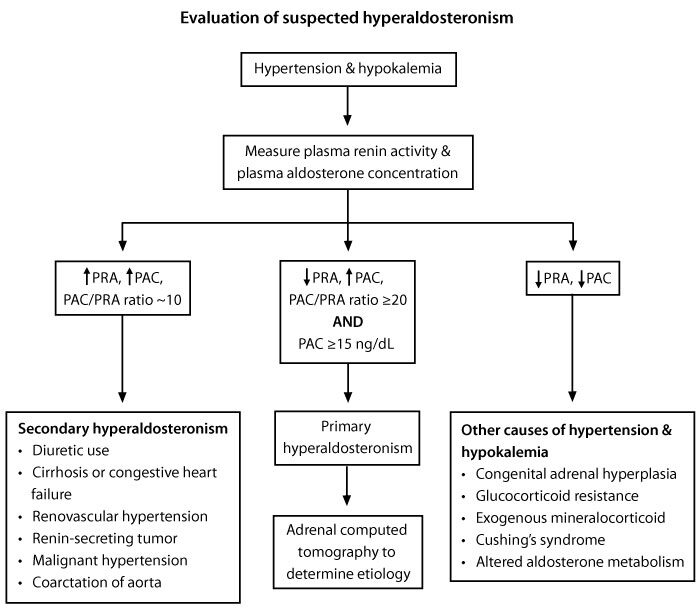
- Elevated plasma aldosterone concentration (PAC) and suppressed plasma renin activity (PRA); PAC/PRA ratio >20
- In contrast, elevated PAC and PRA with a PAC/PRA ratio ~10 suggests secondary hyperaldosteronism (eg, renovascular hypertension, cirrhosis, renin-secreting tumor)
- Confirmatory tests (eg, saline infusion test, oral sodium loading test [showing absence of aldosterone suppression due to renin-independent aldosterone secretion])
- Adrenal imaging (CT or MRI) to identify adenoma or hyperplasia
- Adenoma: Surgical resection (adrenalectomy)
- Bilateral adrenal hyperplasia: Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (eg, spironolactone, eplerenone)
| Mnemonic for Primary vs Secondary Hyperaldosteronism | |
|
RENIN Mnemonic for Differentiation
|
جملة تذكرية |
| Mnemonic for Aldosterone Effects | |
|
SIMON Mnemonic for Aldosterone Actions
|
جملة تذكرية |
| Mnemonic for Diagnostic Workup | |
|
PACS Mnemonic for Diagnosis
|
جملة تذكرية |
| Mnemonic for Clinical Presentation | |
|
HYPER Mnemonic for Hyperaldosteronism
|
جملة تذكرية |
| Mnemonic for Treatment Options | |
|
AMES Mnemonic for Management
|
جملة تذكرية |