YourMedPass
أكبر مرجع لامتحان الامتياز الأردني وامتحانات الإقامة
Adrenal gland anatomy and physiology
The adrenal glands are paired retroperitoneal endocrine organs located superior to each kidney that play crucial roles in metabolism, electrolyte balance, and stress response. Each gland consists of two functionally distinct regions: the outer cortex (steroid hormone production) and inner medulla (catecholamine production).
Last updated: July 24, 2025
Morphology & Location
- Shape: Left = crescent-shaped; Right = pyramidal
- Size: ~5 cm height, 1-2 cm width
- Weight: 4-6 grams each in adults
- Location: Retroperitoneal, superior to kidney upper poles
- Enclosure: Renal fascia and adipose capsule
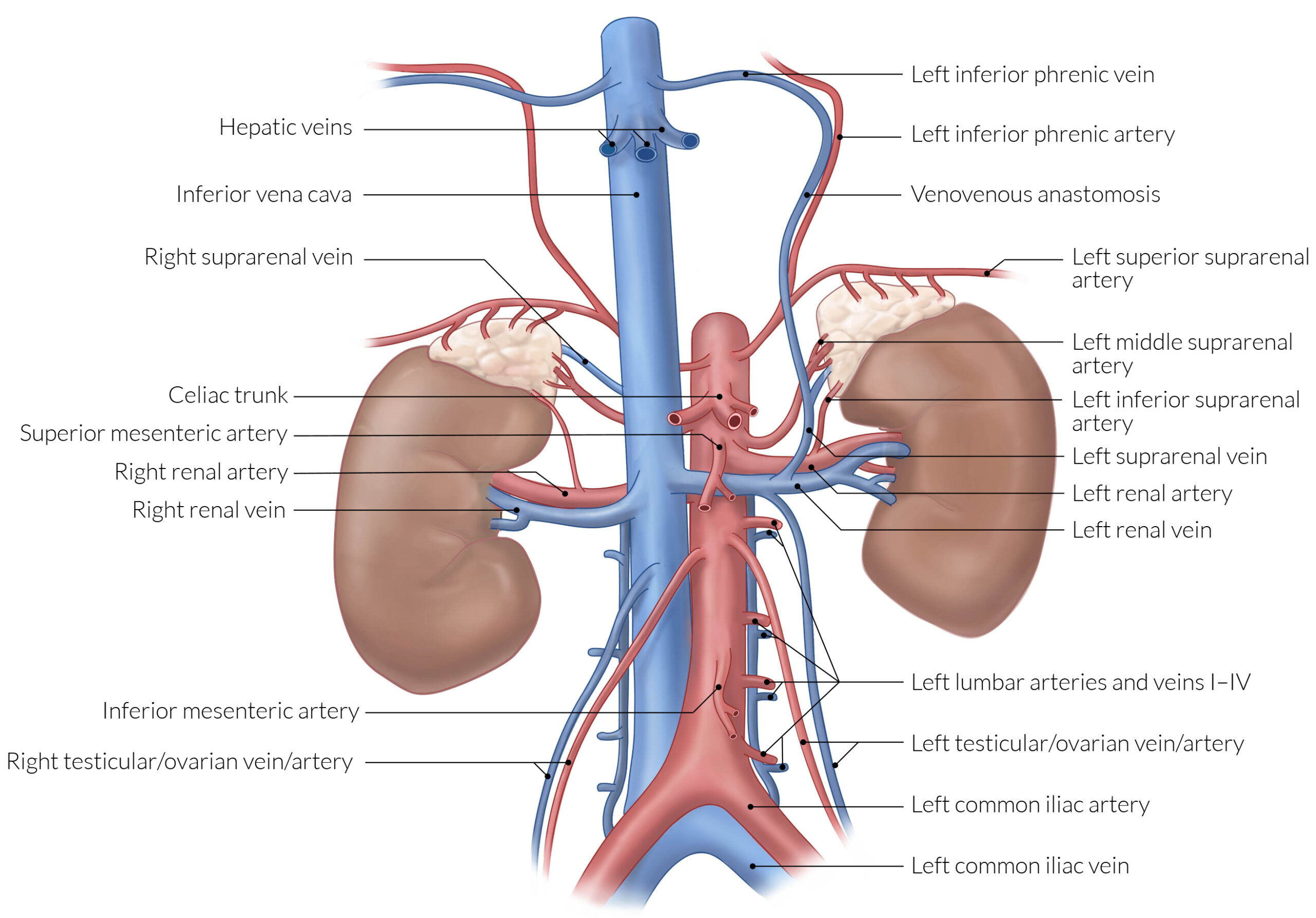
Vascular Supply
| Adrenal Gland Vascular Supply | |
| Arterial Supply | Venous Drainage |
|
|
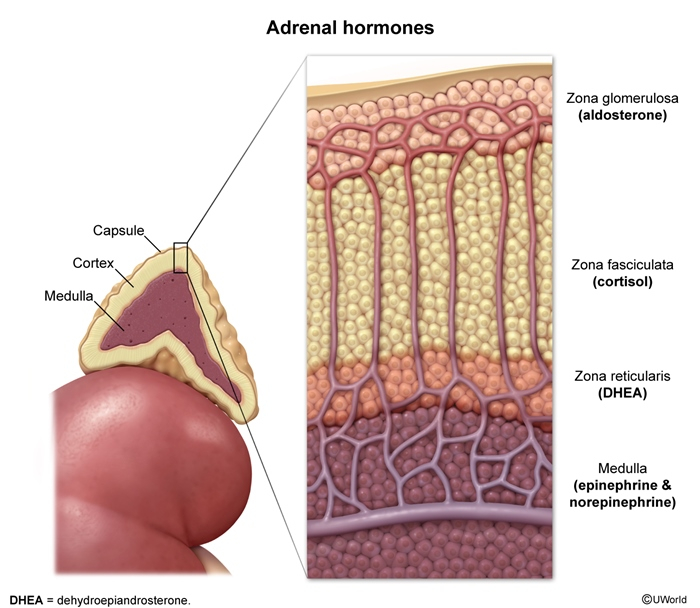
Adrenal Cortex Structure
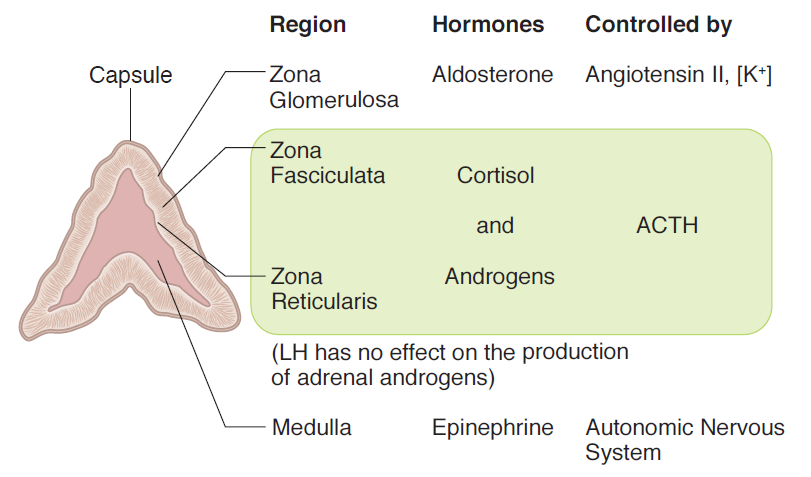
- G: Glomerulosa (outermost) → Aldosterone
- F: Fasciculata (middle) → Cortisol
- R: Reticularis (innermost) → Androgens
| Mnemonic for Adrenal Cortex Structure | |
|
GFR Mnemonic for Cortical Zones
|
جملة تذكرية |
| Adrenal Cortex Zones | |||
| Zone | % of Cortex | Cell Type | Primary Hormone |
| Zona Glomerulosa | 15% | Columnar cells in clusters | Aldosterone |
| Zona Fasciculata | 75% | Large, lipid-rich cells in cords | Cortisol |
| Zona Reticularis | 10% | Smaller, compact cells | DHEA/DHEAS |
Adrenal Medulla Structure
- Composition: Chromaffin cells (modified sympathetic neurons)
- Organization: Clusters and cords around blood vessels
- Innervation: Preganglionic sympathetic fibers (splanchnic nerves)
- Special Features:
- Chromaffin reaction: cells stain brown with chromium salts
- Contain neurosecretory granules
- No axons (hormones released directly into blood)

- Mineralocorticoids (Zona Glomerulosa)
- Aldosterone → The Salt Saver
- Primary Action: ↑ Na+ reabsorption, ↑ K+ excretion
- Target: Principal cells of collecting duct
- Mechanism: Genomic (slow) via mineralocorticoid receptors
- Clinical Correlation: Hyperaldosteronism → Hypertension + Hypokalemia
Aldosterone – Functional Effects Function Mechanism Clinical Effect Sodium Retention ↑ ENaC channels
↑ Na-K-ATPase↑ Blood volume
↑ Blood pressurePotassium Excretion ↑ K⁺ secretion in DCT/CD Risk of hypokalemia Hydrogen Excretion ↑ H⁺ secretion Metabolic alkalosis
- Aldosterone → The Salt Saver
- Glucocorticoids (Zona Fasciculata)
- Cortisol→ The Stress Master
- Peak Time: 8 AM (circadian rhythm)
- Binding: 90% protein-bound (cortisol-binding globulin)
- Half-life: 90 minutes
- Most Common Cause of Excess: Exogenous administration
Cortisol - Systemic Effects System Physiologic Effects Pathologic Effects (Excess) Metabolism • ↑ Gluconeogenesis
• ↑ Lipolysis
• ↑ Protein catabolism• Diabetes mellitus
• Central obesity
• Muscle wastingImmune • Anti-inflammatory
• Immunosuppression• ↑ Infection risk
• Poor wound healingCardiovascular • ↑ Cardiac output
• ↑ Vascular tone• Hypertension
• AtherosclerosisBone • ↓ Bone formation
• ↑ Bone resorption• Osteoporosis
• Fractures
- Cortisol→ The Stress Master
- Adrenal Androgens (Zona Reticularis)
- Primary Hormones:
- DHEA (Dehydroepiandrosterone)
- DHEAS (DHEA-Sulfate) - most abundant
- Androstenedione
- Clinical Significance:
- Women: Major source of androgens
- Men: Minimal contribution (testicular androgens dominate)
- Children: Responsible for pubarche
- Primary Hormones:
| Note | |
|
ملاحظة |
- Catecholamines (Adrenal Medulla)
- Epinephrine (Adrenaline) – 80% of medullary output
- Primary Effects: ↑ Heart rate, ↑ BP, ↑ Glucose, Bronchodilation
- Receptors: β₁, β₂ > α₁
- Unique Feature: Only made in adrenal medulla
- Clinical Correlation: Pheochromocytoma → Episodic hypertension
Catecholamine Output & Effects Catecholamine % of Output Primary Receptors Key Actions Epinephrine 80% β₁, β₂ > α₁ • Cardiac stimulation
• Bronchodilation
• Glycogenolysis
• LipolysisNorepinephrine 20% α₁, β₁ > β₂ • Vasoconstriction
• ↑ Blood pressure
• Modest cardiac effectsDopamine <5% D₁, D₂ • Renal vasodilation
• Neurotransmitter - Catecholamine Synthesis Pathway
- Tyrosine → L-DOPA → Dopamine → Norepinephrine → Epinephrine
- Tyrosine hydroxylase: Tyrosine → L-DOPA (rate-limiting)
- Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase: L-DOPA → Dopamine
- Dopamine β-hydroxylase: Dopamine → Norepinephrine
- PNMT: Norepinephrine → Epinephrine (requires cortisol)
- Metabolic Effects of Catecholamines
Catecholamine Effects by System System Epinephrine Effects Norepinephrine Effects Cardiovascular • ↑ Heart rate
• ↑ Contractility
• ↓ Peripheral resistance• ↑ Blood pressure
• ↑ Peripheral resistance
• Minimal heart rate changeMetabolic • ↑ Glucose (major)
• ↑ Lipolysis
• ↑ Metabolic rate• ↑ Glucose (minor)
• ↑ Lipolysis
• ↑ Metabolic rateRespiratory • Bronchodilation
• ↑ Respiratory rate• Minimal effects
- Epinephrine (Adrenaline) – 80% of medullary output
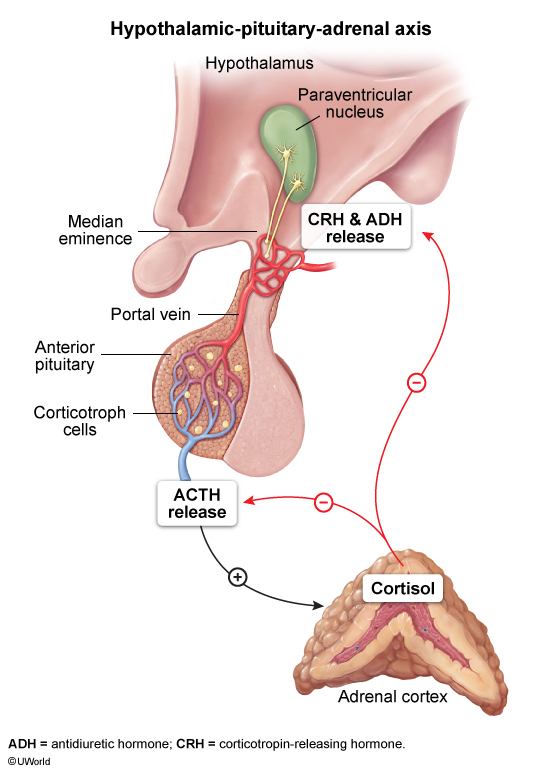
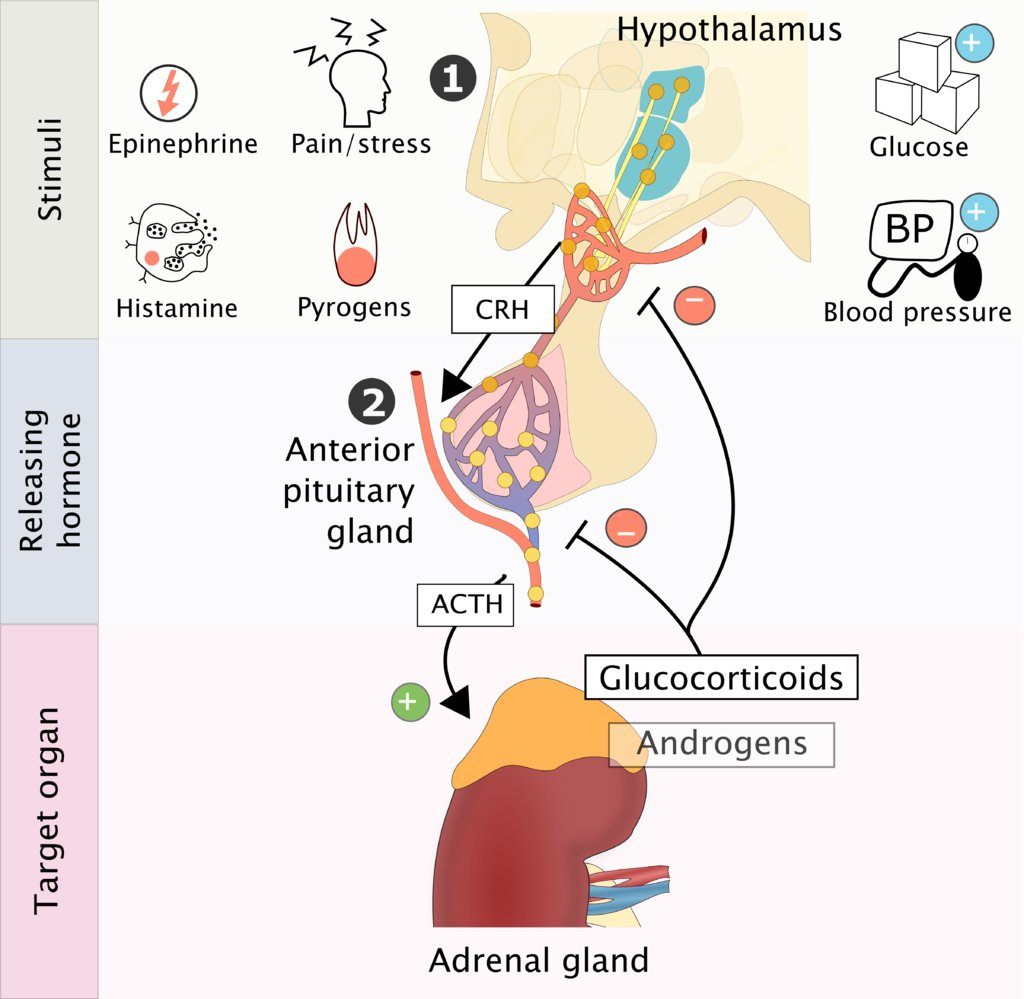
- Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) Axis
- Cortisol Regulation – "The Stress Response"
- Pathway: Stress → CRH → ACTH → Cortisol → Negative Feedback
- Circadian Pattern: Peak at 8 AM, trough at midnight
- Stress Response: Overrides negative feedback
- Clinical Pearl: Dexamethasone suppresses normal axis
- HPA Axis Components
- Hypothalamus:
- Releases CRH (Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone)
- Responds to stress, circadian rhythm
- Anterior Pituitary:
- Releases ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic Hormone)
- Responds to CRH
- Adrenal Cortex:
- Releases Cortisol
- Responds to ACTH
- Negative Feedback:
- Cortisol inhibits CRH and ACTH
- Maintains homeostasis
- Hypothalamus:
- Cortisol Regulation – "The Stress Response"
- Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS)
- Aldosterone Regulation – "The Volume Controller"
- Triggers: ↓ Blood volume, ↓ BP, ↓ Na⁺, ↑ K⁺
- Primary Stimulus: Angiotensin II
- Secondary Stimulus: Hyperkalemia
- Clinical Pearl: ACE inhibitors block aldosterone production
Step Stimulus Response Clinical Significance 1. Renin Release ↓ BP, ↓ Volume, ↑ Sympathetic Kidney releases renin JGA cells sense pressure 2. Angiotensin I Renin + Angiotensinogen Forms Angiotensin I Liver produces substrate 3. Angiotensin II ACE converts Ang I Forms Angiotensin II Lungs have highest ACE 4. Aldosterone Ang II stimulates zona glomerulosa Aldosterone secretion Independent of ACTH
- Aldosterone Regulation – "The Volume Controller"
- Sympathetic Nervous System Control
- Preganglionic Innervation:
- Splanchnic nerves (T5–T12)
- Acetylcholine → Nicotinic receptors
- Stimulus-Secretion Coupling:
- Calcium-dependent exocytosis
- Rapid response (seconds)
- Clinical Correlations:
- Spinal cord injury: Loss of sympathetic control
- Pheochromocytoma: Autonomous catecholamine release
- Preganglionic Innervation:
- Major Adrenal Disorders
- Most Common Adrenal Pathologies
- Benign: Adrenal adenoma (hyperaldosteronism)
- Malignant: Metastatic disease (lung, breast, kidney)
- Functional: Cushing syndrome (excess cortisol)
- Pediatric: Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Major Adrenal Disorders Condition Hormone Involved Key Features Diagnostic Test Cushing Syndrome ↑ Cortisol • Central obesity
• Striae
• Hypertension
• Diabetes• 24h urine cortisol
• Dexamethasone suppression
• Midnight salivary cortisolAddison Disease ↓ Cortisol + Aldosterone • Fatigue
• Hyperpigmentation
• Hypotension
• Hyperkalemia• AM cortisol
• ACTH stimulation test
• Renin/aldosteroneHyperaldosteronism ↑ Aldosterone • Hypertension
• Hypokalemia
• Metabolic alkalosis• Aldosterone/renin ratio
• Salt loading test
• Aldosterone suppressionPheochromocytoma ↑ Catecholamines • Episodic hypertension
• Headache
• Palpitations
• Sweating• 24h urine catecholamines
• Plasma metanephrines
• Clonidine suppression
- Adrenal Crisis
- Triggers: Stress, infection, surgery, abrupt steroid withdrawal
- Symptoms: Shock, hypotension, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain
- Laboratory: Hypoglycemia, hyponatremia, hyperkalemia
- Treatment: IV hydrocortisone 100mg q8h + IV fluids
- Most Common Adrenal Pathologies
- Clinical Pearls
- Bilateral adrenal enlargement: Think metastases, lymphoma, or hemorrhage
- Incidental adrenal mass: "Incidentaloma" – most are benign
- Waterhouse-Friderichsen: Adrenal hemorrhage in meningococcemia
- Adrenal insufficiency: May be first sign of autoimmune polyglandular syndrome
| Mnemonic for Adrenal Cortex Zones | |
| G: Glomerulosa → Aldosterone ("Go get salt") F: Fasciculata → Cortisol ("Fight stress") R: Reticularis → Androgens ("Reproduce") |
جملة تذكرية |
| Mnemonic for Aldosterone Functions | |
| S: Sodium retention I: Increases blood pressure M: Mineralocorticoid O: Opposes potassium N: Nephron (collecting duct) |
جملة تذكرية |
| Mnemonic for Cortisol Effects | |
| B: Blood glucose ↑ I: Immune suppression G: Gastric acid ↑ S: Stress response |
جملة تذكرية |
| Mnemonic for Cushing Syndrome | |
| C: Central obesity U: Urinary frequency (diabetes) S: Striae H: Hypertension I: Immunosuppression O: Osteoporosis N: Neuropsychiatric changes |
جملة تذكرية |
| Mnemonic for Pheochromocytoma | |
| H: Headache H: Heart palpitations H: Hypertension H: Hyperhidrosis (sweating) |
جملة تذكرية |
| Mnemonic for Addison Disease | |
| A: Adrenal insufficiency D: Darkening of skin D: Dehydration I: Infection prone S: Salt craving O: Orthostatic hypotension N: Nausea/vomiting |
جملة تذكرية |